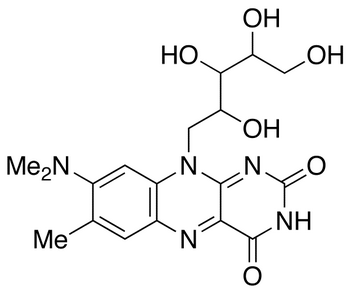
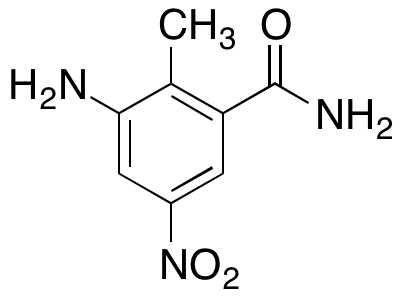
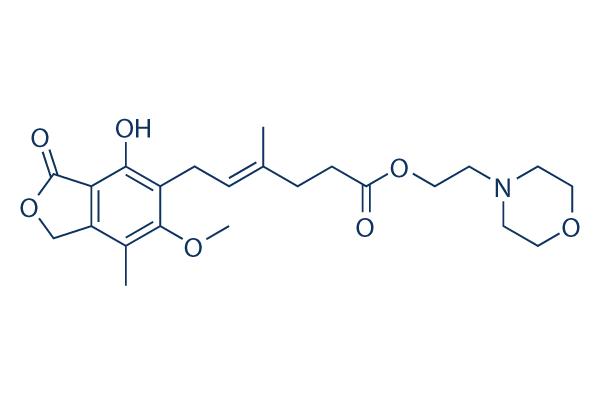
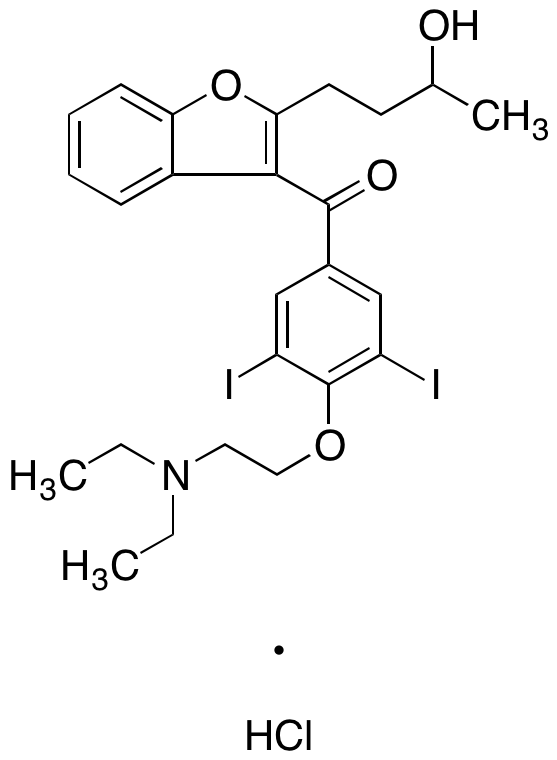
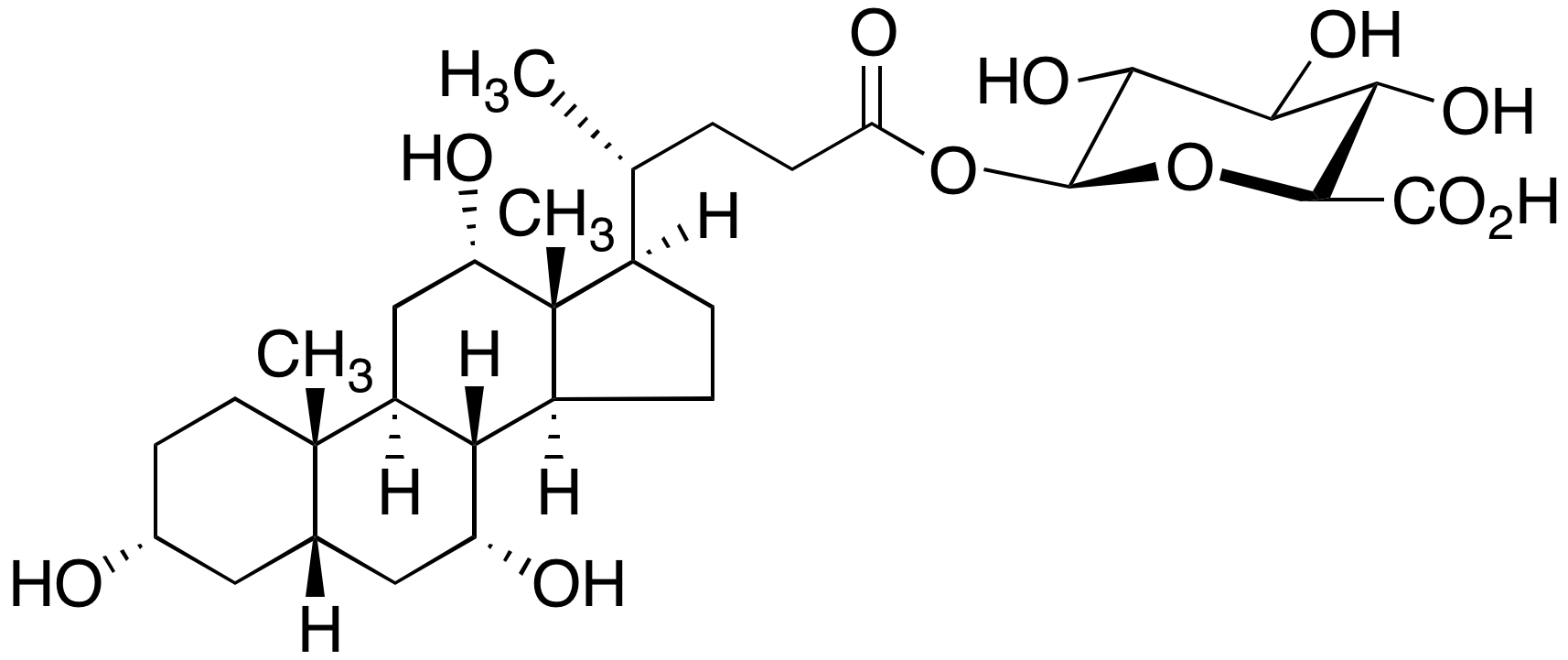
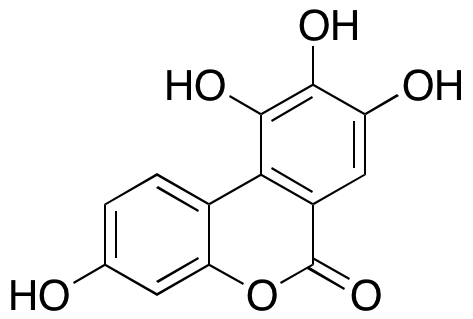
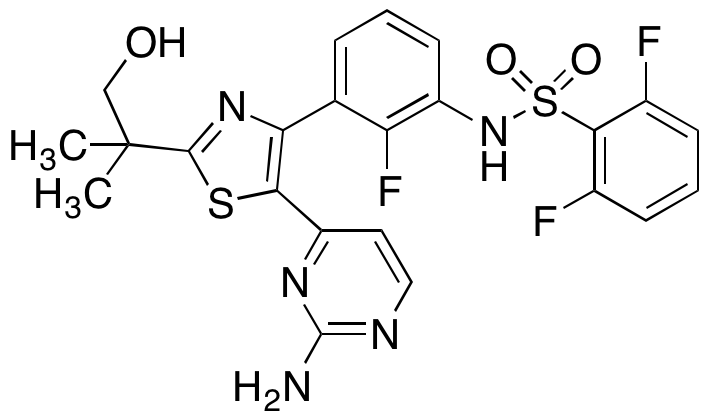
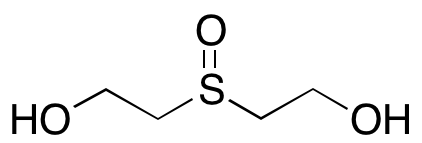
Metabolites
Metabolites are substances that are produced or consumed through metabolic processes; biomolecules are not included. Precursors and degradation products of biomolecules are true metabolites. Metabolites are intermediate or final products of metabolism and are usually referred to as small molecules. Primary metabolites are involved in the general stages of growth, development, and reproduction. Ethylene, which is manufactured in large quantities in industry, is one of the primary metabolites. Secondary metabolites, on the other hand, are not involved in those processes, but they are important in physiological functions. They include antibiotics and pigments, like resins and pinene. Actinomycins are secondary metabolites that are converted from the primary metabolite tryptophan, but not all antibiotics use the primary metabolite as a precursor. In the metabolic pathway, glucose and fructose in sugars are metabolites.