Abstract
In patients suffering from immunological thrombocytopenia (ITP) and chronic liver disease, avatrombopag, a thrombopoietin receptor agonist, has emerged as an essential treatment option for thrombocytopenia management. By encouraging platelet synthesis, avatrombopag successfully raises platelet counts, hence lowering the need for transfusions and the risk of bleeding during invasive procedures. The medication’s oral administration and acceptable safety profile make it a convenient and well-tolerated option for long-term treatment, with few dietary restrictions and a low frequency of severe side effects. Avatrombopag’s potential therapeutic uses are being investigated further, including the treatment of thrombocytopenia brought on by combination treatments and chemotherapy. These uses might increase the drug’s clinical usefulness and enhance patient outcomes.
Introduction to Avatrombopag
Avatrombopag is a significant advancement in the treatment of thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by abnormally low blood platelet counts. This medication is particularly helpful for patients with chronic liver illness who have low platelet counts, particularly if they have upcoming invasive medical or dental procedures. In these circumstances, limiting platelet levels is crucial to lowering the risk of potentially lethal bleeding issues.
In order to work, avatrombopag mimics the actions of thrombopoietin, a hormone that the body naturally produces and which encourages the production of platelets in the bone marrow. It functions as a thrombopoietin receptor agonist by binding to and activating the receptor, which raises platelet production. This mechanism makes avatrombopag a valuable therapeutic alternative for those in circumstances where having platelet transfusions is impractical or when normal medications may not be sufficient.
Additionally, avatrombopag is a treatment for chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), a condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets. Avatrombopag is being offered as a possible treatment option for patients with ITP who have not responded adequately to traditional therapy. Because the drug can increase platelet counts in a predictable and controlled way, patients’ quality of life is improved and less urgent medical treatment is required.
One of the primary advantages of avatrombopag over other thrombopoietin receptor agonists that may require injections is its oral form. This is a result of its greater convenience. This feature improves patient adherence and expands the therapeutic options for patients who require or prefer oral medication. As research into its full potential is done, avatrombopag remains a cornerstone in the treatment of thrombocytopenia, providing a safer and more effective way of platelet count normalization.
Mechanism of Action of Avatrombopag
By precisely targeting the body’s platelet manufacturing route, avatrombopag, a thrombopoietin receptor agonist, plays a critical role in the management of thrombocytopenia. Avatrombopag works by binding to and activating the thrombopoietin receptor (TPO-R), which is mostly present on the surface of bone marrow-derived megakaryocytes and the precursor cells that give rise to them. Large bone marrow cells called megakaryocytes are in charge of producing platelets, which are necessary blood components for clotting.
Thrombopoietin is a naturally occurring hormone that controls platelet synthesis by encouraging megakaryocyte maturation and proliferation. By attaching to the thrombopoietin receptor and starting a signaling cascade that increases platelet synthesis and release into the bloodstream, avatrombopag imitates the effects of thrombopoietin. When a patient has thrombocytopenia from immunological thrombocytopenia (ITP) or chronic liver illness, its agonistic activity on the thrombopoietin receptor helps to raise platelet counts.
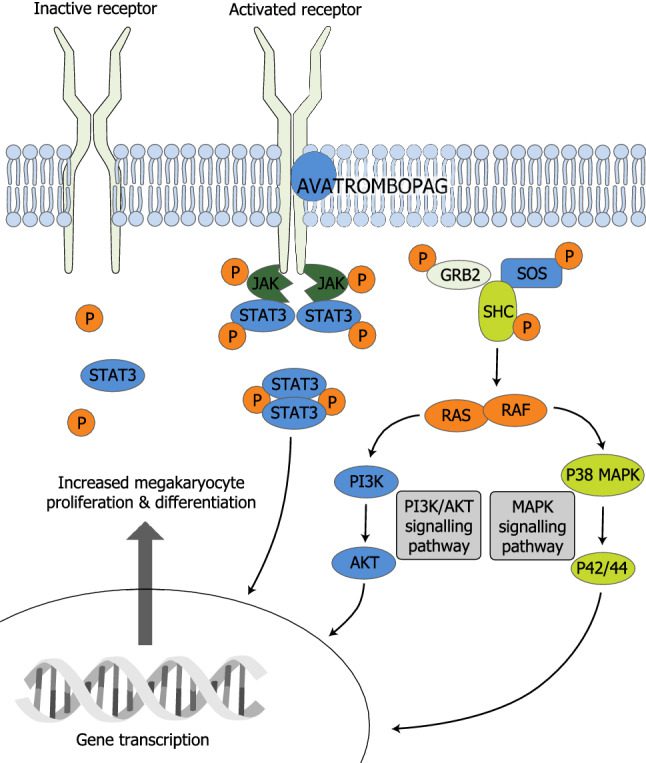
Fig 1 Mechanism of action of avatrombopag
Avatrombopag is a more practical option for patients because it does not require special dietary restrictions like some other thrombopoietin receptor agonists do, nor does it interact with common food components like calcium. Additionally, because it is taken orally, dosage may be consistently and carefully regulated, which is especially advantageous for patients whose conditions require long-term care.
Furthermore, Avatrombopag’s highly tailored mode of action minimizes the possibility of side effects and lessens the possibility of off-target consequences, which are frequently connected to broader-acting drugs. Its good safety profile, which is bolstered by its specificity, makes it a viable and well-tolerated therapeutic choice for thrombocytopenia patients. Avatrombopag is therefore beneficial in raising platelet counts as well as keeping them at therapeutic levels, which lowers the need for platelet transfusions and enhances patient outcomes.
Clinical Applications
In patients with chronic liver illness and chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), avatrombopag has become an essential medication for the management of thrombocytopenia. Thrombocytopenia, a condition marked by an abnormally low platelet count, presents serious difficulties, particularly for individuals with chronic liver illness who are more likely to experience bleeding. Insufficient platelet counts increase the risk of severe bleeding consequences in these patients, who frequently need invasive medical or dental operations.
It is permitted to administer avatrombopag in these patients to increase platelet counts prior to these surgeries, which will lessen the requirement for platelet transfusions. The hazards associated with low platelet counts, such as excessive bleeding after surgery or spontaneous bleeding, are reduced when platelets are properly raised. Avatrombopag has been shown in clinical trials to be helpful in raising platelet counts in a predictable manner, which enables improved planning and safer results while performing medical procedures.
Avatrombopag is a potentially effective therapy option for people with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have not reacted well to previous medications. In autoimmune disorders like ITP, the body’s immune system accidentally targets and eliminates platelets. Keeping these patients’ platelet counts within a healthy range is essential to preventing bleeding episodes. Because avatrombopag stimulates platelet formation, it offers ITP patients—especially those who are not responding to previous treatments—a much-needed therapeutic choice. Avatrombopag improves patients’ overall quality of life by raising platelet counts, which also lessens the need for emergency platelet transfusions and aids in patient stabilization.
Advantages of Avatrombopag
Among thrombopoietin receptor agonists, avatrombopag stands out for a number of important reasons, which make it a preferred option for patients and healthcare providers. Firstly, avatrombopag is highly advantageous because it can be taken orally, which offers greater convenience and ease of use compared to some other thrombopoietin receptor agonists that require injections. This is especially important for patients who require long-term treatment, as it eliminates the discomfort and logistical challenges associated with frequent injections.
In clinical trials, Avatrombopag has demonstrated a predictable and consistent increase in platelet counts without causing significant off-target effects. This specificity lowers the risk of adverse reactions and makes the medication well-tolerated by the majority of patients. Another benefit of Avatrombopag is its favorable safety profile. The drug has been shown to have a low incidence of serious adverse effects, which is an important consideration in the treatment of chronic conditions.
Avatrombopag also has an advantage over certain other thrombopoietin receptor agonists in that it does not require dietary restrictions. Some drugs in this family interact with food, especially calcium-containing ones, therefore following strict dietary recommendations is necessary to prevent diminished efficacy. The absence of these interactions in avatrombopag streamlines treatment plans and makes it simpler for patients to follow their doctor’s recommendations.
Furthermore, regardless of prior treatments or the severity of the disease, avatrombopag has demonstrated success in a variety of patient populations, including those with chronic liver disease and ITP. It is a flexible alternative for managing thrombocytopenia due to its broad applicability, which provides consistent results in a variety of therapeutic settings.
In summary, avatrombopag is a very successful and well-tolerated thrombocytopenia medication that provides substantial therapeutic advantages to individuals with ITP and chronic liver disease. It is a practical and patient-friendly choice due to its oral administration, acceptable safety profile, and lack of dietary restrictions. Avatrombopag is expected to continue being a mainstay in the treatment of thrombocytopenia, enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life as research into its full potential is conducted.
Safety and Side Effects
The good safety profile of avatrombopag is well known, and it plays a big role in the long-term treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with immunological thrombocytopenia (ITP) and chronic liver disease. Numerous clinical trials conducted on the medication have shown that it is generally well tolerated and has a low incidence of serious adverse effects. Like any drug, avatrombopag may have adverse effects, therefore it’s important for patients and healthcare professionals to be aware of these.
In clinical trials, these adverse effects were more common in the early stages of treatment and tended to decrease as the patient’s body adapted to the medication. Common side effects of Avatrombopag include headache, fatigue, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infections. These side effects are usually mild to moderate in severity and often resolve without the need to stop the drug.
Although they are uncommon, more severe side effects have been documented and need to be carefully watched. Thromboembolic events, such as pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are among them. Avatrombopag and other thrombopoietin receptor agonists enhance platelet counts, which can increase the risk of blood clots, especially in patients who also have other thromboembolism risk factors. Thus, before starting Avatrombopag medication, healthcare professionals must evaluate each patient’s unique risk factors for clotting and keep an eye out for any signs or symptoms of thrombosis while the patient is receiving treatment.
Furthermore, some Avatrombopag users have reported abnormal liver function; however, they are usually reversible when the medication is stopped. Since many Avatrombopag users already have underlying liver illness, it is advised to regularly monitor liver function tests in order to guarantee early detection and management of any potential liver problems.
Avatrombopag in Research
Avatrombopag is the focus of continuing research that aims to improve patient outcomes and explore new therapeutic uses in addition to its established clinical use. Avatrombopag’s possible application in the management of thrombocytopenia linked to other illnesses, such as thrombocytopenia brought on by chemotherapy, is one area of attention. Avatrombopag may be able to help treat low platelet counts in chemotherapy patients, which could minimize the need for dose reductions or treatment delays for cancer. These findings are based on preliminary research.
Utilizing avatrombopag in combination with other medicines to maximize treatment outcomes is another exciting area of research. For example, in patients with thrombocytopenia and chronic hepatitis C, combining Avatrombopag with antiviral therapy may improve the efficacy of antiviral therapy while reducing the hazards related to low platelet counts. This may result in treatment plans for patients with complicated medical issues that are more thorough and efficient.
Additionally, studies are being conducted to determine Avatrombopag’s long-term safety in a variety of patient populations, including those with various underlying thrombocytopenia causes. The purpose of these studies is to find any patient subgroups that might benefit most from Avatrombopag therapy and to offer more comprehensive data on the drug’s safety profile.
In conclusion, even though avatrombopag has been shown to be an effective treatment for thrombocytopenia, further research is still needed to fully grasp its possibilities. Avatrombopag is probably going to be a mainstay in the treatment of thrombocytopenia for a long time to come because of its favourable safety profile and growing therapeutic possibilities.
Conclusion
Particularly for patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and chronic liver illness, avatrombopag has established itself as a vital treatment alternative in the therapy of thrombocytopenia. Its thrombopoietin receptor agonist mode of action enables it to stimulate platelet formation efficaciously, offering a dependable approach to augment platelet counts and mitigate the danger of bleeding problems in susceptible patient populations. The medication is an easy and well-tolerated option for long-term treatment because of its oral delivery, good safety profile, and lack of dietary restrictions.
Avatrombopag has proven to be a highly effective treatment in lessening the necessity for platelet transfusions in patients with chronic liver disease, hence minimizing the hazards involved with invasive treatments. Avatrombopag is a viable alternative for ITP patients, especially those who have not reacted well to previous medications, as it can stabilize platelet levels and enhance quality of life. The significance of Avatrombopag as a flexible and efficient therapy for thrombocytopenia management in a range of patient demographics is highlighted by these therapeutic applications.
Another important aspect of Avatrombopag’s extensive use is its safety profile. Although most side effects are modest and temporary, vigilant patient monitoring is necessary because to the possibility of significant adverse events, such as thromboembolic events. However, the majority of patients find that the advantages of Avatrombopag in treating thrombocytopenia much outweigh the dangers, and the overall risk of substantial side effects is still minimal.
Our grasp of Avatrombopag’s potential is still being expanded by ongoing research, which is looking into its use in combination therapies and other indications such thrombocytopenia brought on by chemotherapy. These studies have the potential to increase Avatrombopag’s usefulness even more, expanding its therapeutic uses and maybe improving patient outcomes for a variety of ailments.
To sum up, avatrombopag is a safe, practical, and successful therapy choice for patients with chronic liver illness and ITP, marking a significant development in the management of thrombocytopenia. Avatrombopag is well-positioned to continue being a mainstay in the management of thrombocytopenia, improving patient care and clinical outcomes as research on the drug’s potential uses grows.