Dulaglutide: A Comprehensive Tool in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes (T2D), poses significant challenges to global health, affecting over 415 million adults worldwide. This condition, which disrupts normal glucose metabolism resulting in chronic hyperglycemia, significantly contributes to the morbidity and mortality associated with cardiovascular and renal complications. Managing T2D effectively to maintain glycemic control within recommended levels is crucial to mitigating these risks. Dulaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist administered subcutaneously once weekly, has become a cornerstone in the global strategy against T2D. This comprehensive review examines dulaglutide’s therapeutic efficacy, tolerability, and its role in the broader context of diabetes management, drawing from pivotal studies such as the REWIND CVOT.
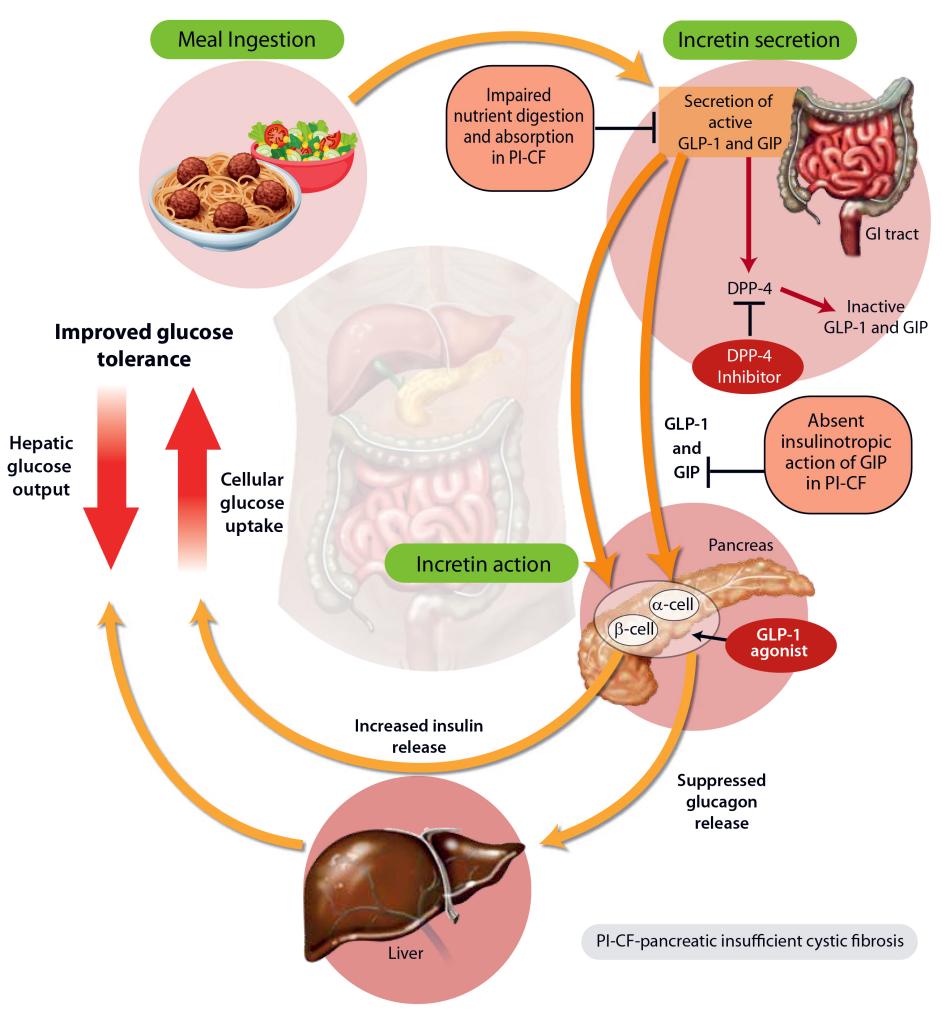
Dulaglutide’s Mechanism of Action
Dulaglutide functions by mimicking the incretin hormones that are typically reduced in T2D. It enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppresses elevated glucagon secretion, and slows gastric emptying. These actions collectively improve glycemic control and have secondary benefits on weight management, a common concern in T2D management.
Therapeutic Efficacy of Dulaglutide
Clinical Trials Overview
The efficacy of dulaglutide has been extensively validated in a series of robust clinical trials known as the AWARD studies. These trials have assessed dulaglutide’s performance across a spectrum of populations with varying degrees of glycemic control, treatment backgrounds, and comorbid conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD).
In trials like AWARD-7, dulaglutide was specifically evaluated in patients with T2D and moderate to severe CKD, showing significant improvements in glycemic control without compromising safety. Across other AWARD trials, dulaglutide demonstrated consistent efficacy in reducing HbA1c levels from a diverse range of baseline values, typically between 7% and 11%.
Comparisons and Combinations
When combined with common oral antihyperglycemic drugs (OADs) like metformin, dulaglutide showed superior efficacy compared to other treatments such as sitagliptin, improving both glycemic control and aiding in weight loss. Its performance alongside other therapies, like sulfonylureas or insulin, also demonstrated significant benefits in managing blood glucose levels more effectively than many comparative treatments.
Dulaglutide’s efficacy extends to comparisons with other GLP-1 receptor agonists. It has proven non-inferior to liraglutide and more effective than exenatide, with a somewhat less efficacy compared to semaglutide according to some studies.
Real-World Effectiveness
Real-world studies, such as those conducted across the U.S., have reinforced findings from clinical trials, showing dulaglutide’s superior efficacy in routine clinical practice. Studies like DISPEL have highlighted its advantages over basal insulin, noting not only better glycemic control but also higher patient adherence and lower discontinuation rates.
Retrospective studies in various global regions have also supported dulaglutide’s high adherence and persistence rates, further establishing its favorable profile in real-world settings.
REWIND Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial
The REWIND trial is a landmark study that explored the cardiovascular outcomes associated with dulaglutide in patients with T2D at high risk for cardiovascular events. The study demonstrated a significant 12% reduction in major cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction and stroke, highlighting dulaglutide’s potential in providing cardiovascular benefits alongside glycemic control.
Tolerability and Safety Profile
Dulaglutide has generally shown a favorable tolerability profile in both clinical trials and real-world settings. The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal, such as nausea and diarrhea, which are typically mild to moderate and tend to decrease over time.
Low Hypoglycemia Risk
An important advantage of dulaglutide is its low risk of hypoglycemia, particularly when not combined with sulfonylureas or insulin. This feature is crucial in diabetes management, where avoiding low blood glucose levels is as important as managing high levels.
Cardiovascular and Pancreatic Safety
While some GLP-1 receptor agonists have been scrutinized for potential cardiovascular and pancreatic risks, dulaglutide has maintained a profile that shows no increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or significant pancreatic issues in the vast majority of patient populations.
Integrating Dulaglutide into Diabetes Management
Clinical Guidelines
Current diabetes management guidelines emphasize a patient-centered approach to therapy, recommending GLP-1 receptor agonists like dulaglutide early in the treatment sequence, especially for patients with specific comorbidities like cardiovascular disease or CKD. Dulaglutide’s efficacy in managing both glycemic and cardiovascular health makes it an ideal choice in such scenarios.
Patient-Centered Considerations
The convenience of dulaglutide’s once-weekly dosing and its delivery via a user-friendly injectable device enhance patient compliance and satisfaction, factors that are crucial in long-term disease management.
Future Directions and Innovations
The ongoing evolution of dulaglutide includes exploring its full potential in combination therapies and specific patient subsets. With advancements in diabetes care leaning towards more integrated and personalized treatments, dulaglutide’s role is expected to expand, potentially improving outcomes for a broader range of patients with T2D.
Conclusion
Dulaglutide represents a significant breakthrough in the treatment of T2D, providing robust glycemic control, proven cardiovascular benefits, and a well-tolerated safety profile. Its role in modern diabetes care exemplifies the shift towards more effective, patient-friendly, and comprehensive therapeutic options, making it a cornerstone of T2D management strategies. As we move forward, dulaglutide will likely continue to be a key component of integrated care approaches that address the complex needs of individuals living with diabetes.
Reference
- Scott, L. J. (2020). Dulaglutide: a review in type 2 diabetes. Drugs, 80(2), 197-208.
- Gerstein, H. C., Colhoun, H. M., Dagenais, G. R., Diaz, R., Lakshmanan, M., Pais, P., … & Zucchiatti, N. (2019). Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet, 394(10193), 121-130.
- Ludvik, B., Frías, J. P., Tinahones, F. J., Wainstein, J., Jiang, H., Robertson, K. E., … & Milicevic, Z. (2018). Dulaglutide as add-on therapy to SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes (AWARD-10): a 24-week, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The lancet Diabetes & endocrinology, 6(5), 370-381.
- Garber, A. J., Handelsman, Y., Grunberger, G., Einhorn, D., Abrahamson, M. J., Barzilay, J. I., … & Umpierrez, G. E. (2020). Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm–2020 executive summary. Endocrine Practice, 26(1), 107-139.