Enhancing Depression Treatment: The Comprehensive Benefits of Agomelatine
Abstract
This paper explores the therapeutic efficacy and unique pharmacological profile of Agomelatine, an antidepressant distinguished by its dual action as a melatonergic agonist and a 5-HT2C antagonist. Unlike traditional antidepressants, Agomelatine addresses both mood regulation and circadian rhythm disturbances, which are common in patients with depression. The paper reviews the benefits of Agomelatine in improving mood and emotional stability, enhancing sleep patterns, and its favorable side effect profile compared to other antidepressants. Clinical evidence supporting its use, potential side effects, particularly concerning liver health, and patient experiences are discussed to highlight its overall effectiveness and safety. The conclusion underscores Agomelatine’s potential as a preferred treatment option for depression, advocating for its broader use and further research into its long-term benefits and applications in psychiatric practice.
Introduction to Agomelatine
Depression, a common yet severe mood disorder, affects millions worldwide and manifests through persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in daily activities, and a myriad of physical and psychological disruptions. This condition does more than just dampen mood—it fundamentally alters cognitive functions, daily productivity, and overall quality of life. Given its complex nature and varied manifestations, treating depression effectively remains a critical challenge in mental health.

Fig 1. What Is Depression & Who Experiences It?
In the realm of pharmacological treatments, Agomelatine offers a novel approach. This antidepressant is unique due to its dual action on melatonin and serotonin receptors, which makes it stand out from other treatments. Agomelatine is primarily an agonist at the MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors. These receptors play a vital role in maintaining the circadian rhythms that regulate sleep-wake cycles, which are often disrupted in individuals with depression. By normalizing these rhythms, Agomelatine helps alleviate one of the most burdensome symptoms of depression—disrupted sleep.
Additionally, Agomelatine acts as an antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2C receptors. This antagonistic action promotes the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine in the frontal cortex, which are crucial for mood regulation and emotional responsiveness. By simultaneously addressing both the regulatory mechanisms of mood and sleep, Agomelatine provides a comprehensive treatment solution that can lead to improvements in overall mental health and patient outcomes.
The clinical significance of Agomelatine extends beyond its pharmacodynamics. It offers a favorable side effect profile compared to traditional selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). For instance, it is less likely to cause sexual dysfunction, a common reason patients discontinue antidepressant therapy. Additionally, Agomelatine does not typically induce weight gain, another common deterrent to effective long-term treatment compliance.
In the fight against depression, Agomelatine represents a shift towards treatments that not only improve depressive symptoms but also enhance overall life quality by addressing associated aspects like sleep and circadian rhythm disturbances. This dual-action mechanism can potentially offer a more holistic improvement in mental health, especially for patients who have struggled with the side effects of conventional antidepressants.
What is Agomelatine?
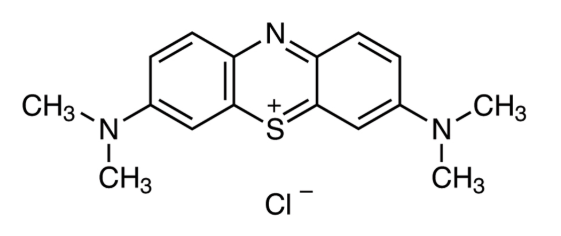
Agomelatine is an innovative antidepressant distinguished by its unique pharmacological action. Chemically, it is a synthetic analogue of melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland that regulates sleep and wakefulness. Agomelatine’s structure allows it to mimic some of the effects of melatonin, which is pivotal in its role as a treatment for depression.
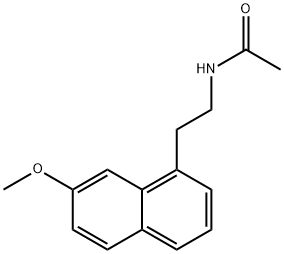
Fig 2.The structure of Agomelatine
Mechanism of Action
The primary mechanism of Agomelatine revolves around its interaction with melatonin receptors, MT1 and MT2, and serotonin receptors, specifically 5-HT2C. As an agonist at MT1 and MT2 receptors, Agomelatine enhances the positive effects of melatonin, which include regulation of circadian rhythms and promotion of a healthy sleep cycle. This is particularly beneficial for those with depression, as disrupted circadian rhythms are a common symptom of the disorder.
Furthermore, Agomelatine acts as an antagonist at 5-HT2C receptors located in the central nervous system. This antagonism is crucial because it leads to an increase in the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the frontal cortex. These neurotransmitters are vital for mood regulation and cognitive functions. By promoting their release, Agomelatine alleviates symptoms of depression such as sadness, lethargy, and a lack of motivation.
Fig 3. Mechanism of Action and Efficacy
Pharmacological Benefits
The dual action of Agomelatine offers a significant therapeutic advantage. By targeting both melatonin and serotonin pathways, it addresses two fundamental aspects of depression: mood regulation and sleep disturbances. This dual targeting makes Agomelatine particularly effective for patients whose depressive symptoms include significant disruptions in sleep patterns.
Moreover, unlike many traditional antidepressants, Agomelatine does not primarily focus on the serotonin system, which often leads to fewer gastrointestinal side effects and sexual dysfunction, common issues with SSRIs and SNRIs. This can lead to better treatment adherence among patients.
In conclusion, Agomelatine’s role as a melatonergic agonist and a 5HT2C antagonist offers a promising approach to depression treatment, particularly in cases where conventional antidepressants may not be effective or well-tolerated. Its ability to improve both mood and sleep could provide a more holistic improvement in the quality of life for patients suffering from depression.
Benefits of Agomelatine in Depression Treatment
Agomelatine is notable for its efficacy in treating depression, particularly through its unique action on melatonin and serotonin receptors. This antidepressant enhances mood and emotional stability while also regulating sleep and circadian rhythms, which are often disrupted in depression.
Mood Improvement and Emotional Stability
Agomelatine’s antagonistic action on the serotonin 5-HT2C receptors leads to an increase in the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the frontal cortex, which directly influences mood and emotional responses. This effect can alleviate common depressive symptoms such as persistent sadness and anhedonia (the inability to feel pleasure). The enhancement of dopamine and norepinephrine levels is crucial as these neurotransmitters play key roles in motivation and reward processes, areas often impaired in depressive states.
Regulation of Sleep Patterns and Circadian Rhythms
Unlike traditional antidepressants, Agomelatine’s agonistic action on melatonin receptors helps synchronize the sleep-wake cycle with the natural environment, promoting healthier sleep patterns. This regulation of circadian rhythms is vital for patients with depression, who frequently suffer from insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns. Improved sleep can have a cascading positive effect on mood, cognitive function, and overall health, making Agomelatine particularly valuable for its holistic approach to treating depressive symptoms.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Agomelatine
The efficacy of Agomelatine has been substantiated in various clinical trials and studies, which have demonstrated its advantages in both safety and effectiveness compared to other antidepressants.
Key Clinical Trials and Outcomes
Several large-scale, randomized controlled trials have shown that Agomelatine is effective in reducing depressive symptoms across different populations. Studies highlight its rapid onset of action, often showing significant improvement in depressive symptoms within the first two weeks of treatment. Additionally, long-term studies indicate that Agomelatine is effective in preventing relapse in patients with major depressive disorder.
Safety and Efficacy Profile
Agomelatine’s safety profile is notably favorable. It does not cause the sexual dysfunction or weight gain that are often associated with SSRIs and SNRIs, issues that can deter patients from continuing with those treatments. However, Agomelatine does require monitoring for liver function, as it can elevate liver enzymes, a potential side effect that necessitates periodic blood tests.
These combined characteristics of efficacy in mood improvement and sleep regulation, alongside a manageable safety profile, underscore Agomelatine’s potential as a preferred option for treating depression, particularly in patients who may be sensitive to the side effects of traditional antidepressants.Benefits of Agomelatine in Depression Treatment
Agomelatine is notable for its efficacy in treating depression, particularly through its unique action on melatonin and serotonin receptors. This antidepressant enhances mood and emotional stability while also regulating sleep and circadian rhythms, which are often disrupted in depression.
Mood Improvement and Emotional Stability
Agomelatine’s antagonistic action on the serotonin 5-HT2C receptors leads to an increase in the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the frontal cortex, which directly influences mood and emotional responses. This effect can alleviate common depressive symptoms such as persistent sadness and anhedonia (the inability to feel pleasure). The enhancement of dopamine and norepinephrine levels is crucial as these neurotransmitters play key roles in motivation and reward processes, areas often impaired in depressive states.
Regulation of Sleep Patterns and Circadian Rhythms
Unlike traditional antidepressants, Agomelatine’s agonistic action on melatonin receptors helps synchronize the sleep-wake cycle with the natural environment, promoting healthier sleep patterns. This regulation of circadian rhythms is vital for patients with depression, who frequently suffer from insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns. Improved sleep can have a cascading positive effect on mood, cognitive function, and overall health, making Agomelatine particularly valuable for its holistic approach to treating depressive symptoms.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Agomelatine
The efficacy of Agomelatine has been substantiated in various clinical trials and studies, which have demonstrated its advantages in both safety and effectiveness compared to other antidepressants.
Key Clinical Trials and Outcomes
Several large-scale, randomized controlled trials have shown that Agomelatine is effective in reducing depressive symptoms across different populations. Studies highlight its rapid onset of action, often showing significant improvement in depressive symptoms within the first two weeks of treatment. Additionally, long-term studies indicate that Agomelatine is effective in preventing relapse in patients with major depressive disorder.
Safety and Efficacy Profile
Agomelatine’s safety profile is notably favorable. It does not cause the sexual dysfunction or weight gain that are often associated with SSRIs and SNRIs, issues that can deter patients from continuing with those treatments. However, Agomelatine does require monitoring for liver function, as it can elevate liver enzymes, a potential side effect that necessitates periodic blood tests.
These combined characteristics of efficacy in mood improvement and sleep regulation, alongside a manageable safety profile, underscore Agomelatine’s potential as a preferred option for treating depression, particularly in patients who may be sensitive to the side effects of traditional antidepressants.
Improvement in mood and emotional stability
Regulation of sleep patterns and circadian rhythms.
Comparative advantages over other antidepressants (e.g., lower risk of sexual dysfunction and weight gain).
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Agomelatine, while innovative in its treatment of depression, also requires consideration of potential side effects and safety profiles. Most notably, the drug can impact liver health, which necessitates careful monitoring.
Liver Health Concerns
One of the primary safety concerns with Agomelatine is its potential to elevate liver enzymes, which can indicate liver damage. Patients prescribed Agomelatine should undergo regular liver function tests to monitor for any adverse effects. This monitoring is particularly crucial during the initial stages of treatment or with dosage increases. Patients with pre-existing liver conditions, or those who consume substantial amounts of alcohol, may be at increased risk and should discuss the suitability of Agomelatine with their healthcare provider.
Other Side Effects
Other reported side effects of Agomelatine include headaches, nausea, dizziness, and fatigue. These are generally mild and tend to decrease in severity as the body adjusts to the medication. Unlike many other antidepressants, Agomelatine does not typically cause sexual dysfunction or significant weight gain, making it a preferable option for individuals concerned about these specific side effects.
Patient Experiences with Agomelatine
The real-world effectiveness of Agomelatine can also be seen through the lens of patient experiences and testimonials, which provide insight into its impact on depression and overall quality of life.
Testimonials Highlighting Patient Responses
Numerous patient reports and clinical case studies have highlighted the positive impact of Agomelatine on both mood and sleep quality. Patients often report improvements in sleep patterns almost immediately, with mood enhancements following soon after. These changes can significantly improve daily functioning and overall life satisfaction.
Discussion on Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Life Improvements
Studies and surveys on patient satisfaction have shown that Agomelatine’s unique mechanism, which targets both depressive symptoms and sleep disturbances, leads to high levels of patient satisfaction. The improvements in sleep and circadian rhythm often translate into better management of daily stress and higher energy levels, which are pivotal for patients battling depression.
Overall, Agomelatine’s approach to treating depression, by not only addressing mood but also enhancing sleep and circadian rhythms, offers a comprehensive therapeutic benefit that can be crucial for long-term recovery and wellness.
Conclusion
Agomelatine represents a significant advancement in the treatment of depression, distinguishing itself through its unique dual mechanism of action as a melatonergic agonist and a 5-HT2C antagonist. This pharmacological profile not only addresses the core symptoms of depression, such as low mood and lack of interest but also targets disrupted sleep and circadian rhythms, issues commonly associated with the disorder. By improving sleep patterns and regulating melatonin and serotonin pathways, Agomelatine offers a holistic approach to treating depression, enhancing overall patient well-being and daily functioning.
Clinical trials and patient testimonials consistently highlight Agomelatine’s efficacy in alleviating depressive symptoms and its superior side effect profile compared to traditional antidepressants. Particularly, its minimal impact on sexual function and weight makes it a preferable choice for long-term treatment. However, due to potential hepatotoxicity, the requirement for regular monitoring of liver function underscores the need for careful patient management and tailored therapeutic approaches.
The integration of Agomelatine into clinical practice promises not only to improve mood and sleep among patients with depression but also to enhance their quality of life by offering a treatment that is both effective and well-tolerated. As mental health professionals continue to seek better treatment outcomes for depression, Agomelatine’s role becomes increasingly vital. Future research should focus on further delineating its long-term benefits and exploring additional therapeutic potentials in broader psychiatric applications. Ultimately, Agomelatine exemplifies the ongoing evolution in antidepressant therapy, aiming for comprehensive care and improved patient satisfaction in mental health treatment.
References
Montgomery, S. A. (2009). Agomelatine: A novel mechanism of antidepressant action involving the melatonergic and the serotonergic system. European Psychiatry, 24(6), 396-402.
Zajecka, J., Schatzberg, A., & Stahl, S. (2010). Agomelatine, the first melatonergic antidepressant: Discovery, characterization, and development. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 6, 245-254.
https://www.nature.com/articles/nrd3140
Kennedy, S. H., & Rizvi, S. (2010). Agomelatine in the treatment of major depressive disorder: Potential for clinical effectiveness. CNS Drugs, 24(6), 479-499.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/11534420-000000000-00000
Kasper, S., & Hamon, M. (2009). Beyond the monoaminergic hypothesis: Agomelatine, a new antidepressant with an innovative mechanism of action. World Psychiatry, 8(2), 108-115.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15622970902717024
Loo, H., Hale, A., & D’haenen, H. (2002). Determination of the dose of agomelatine, a melatonergic agonist and selective 5-HT2C antagonist, in the treatment of major depressive disorder: a placebo-controlled dose range study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology, 17(5), 239-247.
Montgomery, S. A., & Kasper, S. (2007). Severe depression and antidepressants: focus on a pooled analysis of placebo-controlled studies on agomelatine. International Clinical Psychopharmacology, 22(5), 283-291.
Stahl, S. M., Fava, M., Trivedi, M. H., Caputo, A., Shah, A., & Post, A. (2007). Agomelatine in the treatment of major depressive disorder: an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 68(5), 761-774.
https://www.psychiatrist.com/jcp/agomelatine-treatment-major-depressive-disorder-week/
Lemoine, P., & Guilleminault, C. (2011). Improvement in subjective sleep in major depressive disorder with a novel antidepressant, agomelatine: Randomized, double-blind comparison with venlafaxine. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 72(11), 1433-1442.
de Bodinat, C., Guardiola-Lemaitre, B., Mocaër, E., Renard, P., Munoz, C., & Millan, M. J. (2010). Agomelatine, the first melatonergic antidepressant: Discovery, characterization and development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 9(8), 628-642.
https://www.nature.com/articles/nrd3140
Kennedy, S. H., Rizvi, S. J., Fulton, K., & Rasmussen, J. (2008). A double-blind comparison of sexual functioning, antidepressant efficacy, and tolerability between agomelatine and venlafaxine XR. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 28(3), 329-333.