How Selpercatinib Is Revolutionizing Treatment for RET-Positive Cancers
Abstract
Selpercatinib is a RET kinase inhibitor that has emerged as a promising treatment for cancers driven by RET alterations, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and medullary thyroid cancer. Its targeted mechanism of action allows it to specifically inhibit RET-positive tumors, providing effective cancer control with a generally manageable safety profile. Clinical trials have demonstrated substantial response rates and improved outcomes in RET-altered cancers, supporting Selpercatinib’s potential in precision oncology. Ongoing research explores its use in combination therapies to address resistance and extend benefits to additional RET-positive tumor types. As a pioneering example of molecularly targeted cancer therapy, Selpercatinib contributes to advancing personalized treatment options for patients with limited alternatives.
Introduction to Selpercatinib
Selpercatinib is a groundbreaking targeted therapy specifically designed to treat cancers driven by mutations or fusions in the RET (rearranged during transfection) gene. RET alterations are known to play a significant role in the development and progression of several types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), medullary thyroid cancer, and other less common tumors. By selectively inhibiting RET kinase, Selpercatinib disrupts the signaling pathways essential for tumor growth, offering a promising approach to cancer treatment that directly targets the genetic drivers of the disease.
The development of Selpercatinib is a significant advancement in the field of precision oncology, a field focused on developing treatments tailored to the genetic profile of a patient’s cancer. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2020, Selpercatinib became the first FDA-approved drug specifically targeting RET alterations. Its approval was based on promising clinical trial results showing strong efficacy and a favorable safety profile in patients with RET-positive cancers who had exhausted other treatment options.
RET alterations, which include gene fusions and point mutations, are relatively rare but have profound implications for cancer progression in the patients affected. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which attacks rapidly dividing cells without distinction, Selpercatinib’s targeted action offers a more precise approach, potentially reducing side effects and improving outcomes in those with RET-driven cancers. This selectivity highlights the potential of targeted therapies in transforming cancer care, particularly for patients with aggressive or treatment-resistant tumors.
Selpercatinib represents an essential tool in precision medicine, demonstrating the value of understanding and targeting genetic mutations to create highly effective therapies for specific patient populations.
Mechanism of Action of Selpercatinib
Selpercatinib functions as a selective RET (rearranged during transfection) kinase inhibitor, directly targeting RET alterations to halt cancer cell proliferation. RET alterations, including gene fusions and point mutations, play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of several cancer types by promoting uncontrolled cell growth. Selpercatinib’s targeted action against RET kinase offers a more precise approach than traditional therapies, selectively disrupting pathways necessary for cancer cell survival while minimizing off-target effects.
RET fusions, which involve the joining of the RET gene with other genes, produce abnormal RET proteins that drive tumor growth, particularly in cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and papillary thyroid carcinoma. In other cases, RET mutations, especially common in medullary thyroid cancer, lead to similar oncogenic signaling. Selpercatinib binds to the active site of the RET protein, preventing it from interacting with downstream molecules necessary for cell growth and division.
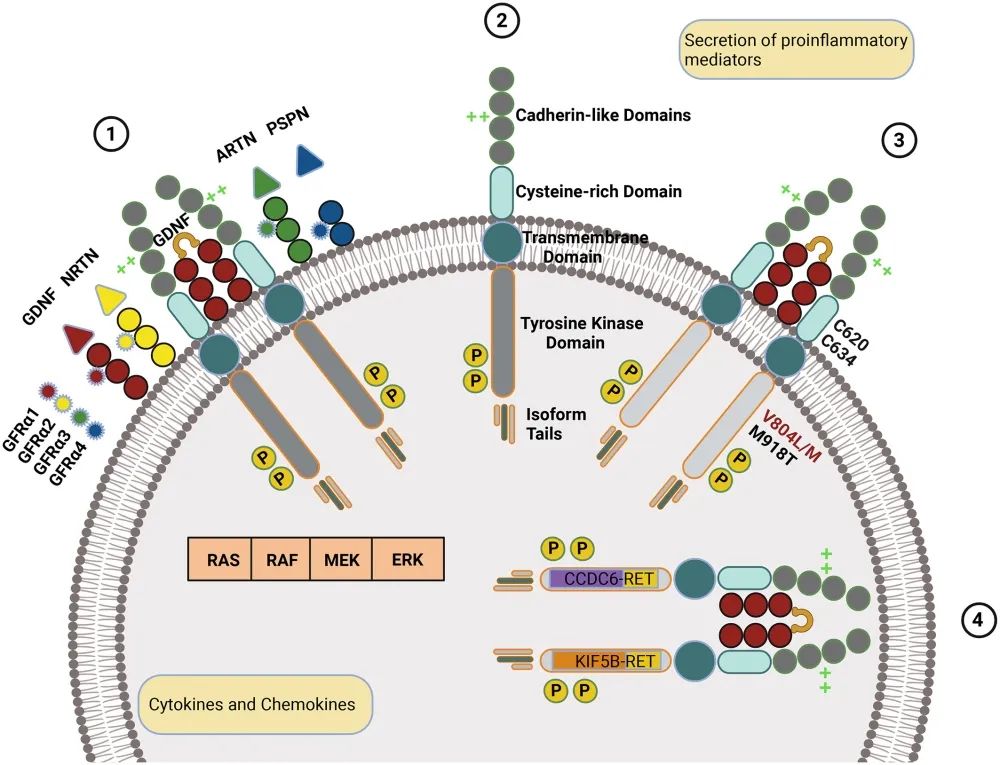
Fig.1 RET mechanisms in normal and oncogenic states
One of Selpercatinib’s defining advantages is its high specificity for RET over other kinases. This selectivity reduces the likelihood of side effects commonly associated with broad-spectrum kinase inhibitors. By effectively blocking RET signaling, Selpercatinib prevents the tumor from progressing and can even shrink existing tumors in patients with RET-driven cancers. This precise targeting showcases the drug’s role in advancing precision medicine, underscoring the importance of identifying genetic drivers in oncology and developing therapies tailored to those molecular alterations.
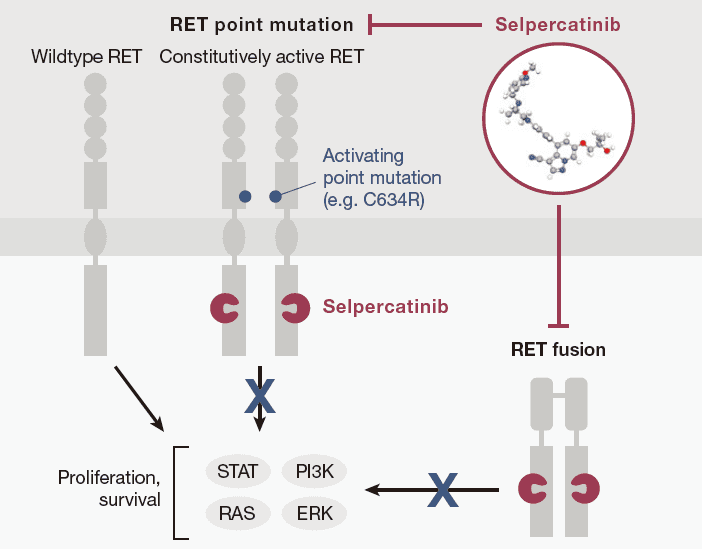
Fig.2 Selpercatinib How it works
Selpercatinib’s unique mechanism enables it to specifically inhibit RET-driven tumors, positioning it as a vital tool for treating RET-positive cancers and a significant step forward in targeted cancer therapy.
Therapeutic Applications of Selpercatinib
Selpercatinib has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in treating RET-driven cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), medullary thyroid cancer, and other tumors harboring RET alterations. In non-small cell lung cancer, RET fusions occur in a small subset of cases but can drive aggressive tumor behavior. Selpercatinib’s selective inhibition of RET has led to significant tumor shrinkage in NSCLC patients with RET-positive status, offering a potent option for individuals who may not respond to traditional treatments.
In medullary thyroid cancer, RET mutations are a primary driver, and patients often face limited options, especially in advanced stages. Selpercatinib’s ability to specifically target RET has proven beneficial for these patients, providing substantial disease control and prolonged progression-free survival. Additionally, research is exploring Selpercatinib’s potential in other rare tumors with RET fusions, broadening its applications in precision oncology.
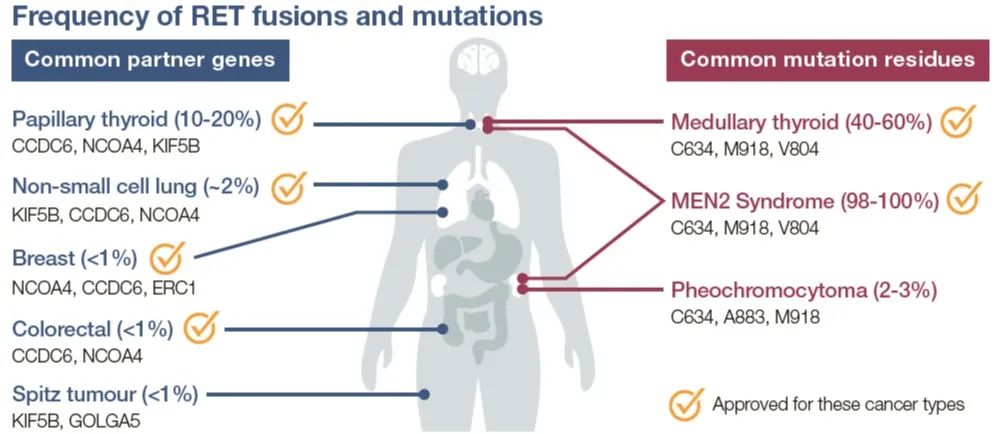
Fig.3 RET fusions and mutations that can be treated with selpercatinib
This drug represents a shift toward highly targeted therapies in oncology, offering personalized treatment that aligns with each patient’s genetic profile. For many, Selpercatinib’s effectiveness against RET-driven cancers translates to improved quality of life and a reduction in the burden of aggressive disease.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy of Selpercatinib
Selpercatinib’s efficacy has been validated through several pivotal clinical trials, which demonstrated its strong therapeutic potential in patients with RET fusion-positive or mutated cancers. The LIBRETTO-001 trial, a global, multicenter study, showcased high response rates and prolonged progression-free survival in patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC and RET-mutant thyroid cancers. This study formed the foundation for Selpercatinib’s regulatory approvals, highlighting its impressive clinical impact.
In NSCLC patients, Selpercatinib achieved an objective response rate of 64%, with many patients experiencing significant tumor shrinkage and disease stabilization. For thyroid cancer, including medullary thyroid cancer with RET mutations, Selpercatinib achieved response rates around 70%, showcasing its high efficacy against RET-driven cancers. This efficacy, combined with a manageable side effect profile, has positioned Selpercatinib as a critical therapeutic option for RET-altered cancers, offering renewed hope for patients.
Safety Profile and Side Effects of Selpercatinib
While Selpercatinib has proven effective in treating RET-driven cancers, it is also associated with a manageable safety profile. Common side effects include dry mouth, diarrhea, hypertension, and fatigue, which are typically mild to moderate in severity and manageable with supportive care. More serious but less common side effects can include elevated liver enzymes and QT interval prolongation, which may require dose adjustments or closer monitoring in certain patients.
Compared to traditional chemotherapy, Selpercatinib’s targeted mechanism offers an advantage by minimizing off-target effects, contributing to a better quality of life for patients. The drug’s selectivity for RET over other kinases reduces unwanted interactions, making it generally well-tolerated. However, physicians monitor patients carefully, particularly those with pre-existing conditions that may increase the risk of side effects. Overall, Selpercatinib’s safety profile supports its continued use and development in RET-altered cancer therapies, reflecting a balance of efficacy and tolerability.
Future Perspectives and Ongoing Research
The promise of Selpercatinib in targeting RET alterations has opened new avenues for cancer research and combination therapies. Ongoing studies are exploring Selpercatinib’s efficacy when used with other targeted agents or immunotherapies, aiming to overcome potential resistance mechanisms and broaden its applicability. Researchers are investigating RET as a target in additional tumor types and evaluating whether Selpercatinib can provide therapeutic benefits across a wider range of RET-positive cancers.
Moreover, future research may reveal insights into optimizing Selpercatinib dosing and administration to enhance patient outcomes and reduce adverse effects. The exploration of combination therapies with Selpercatinib holds potential to enhance its anticancer effects, particularly for patients whose cancers show resistance to single-agent therapy. As understanding of RET-targeted therapy evolves, Selpercatinib remains a cornerstone in personalized cancer treatment, illustrating the power of precision medicine in improving patient prognosis.
Conclusion
Selpercatinib represents a significant advance in targeted cancer therapy, especially for patients with RET-driven cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and medullary thyroid cancer. By specifically inhibiting RET kinase, Selpercatinib disrupts crucial pathways that promote tumor growth and progression. This targeted action not only improves the drug’s efficacy against RET-positive cancers but also reduces the likelihood of adverse effects typically associated with less selective treatments. As a result, patients benefit from a therapy that offers both effectiveness and a generally manageable safety profile, improving their overall quality of life.
The development and clinical application of Selpercatinib underscore the value of precision medicine in oncology, where treatments are increasingly tailored to the unique genetic makeup of each patient’s tumor. Clinical trials have demonstrated high response rates and durable outcomes in RET-altered cancers, underscoring Selpercatinib’s potential to transform cancer care for patients with few therapeutic options.
Looking ahead, ongoing research is exploring the expanded use of Selpercatinib, including its effectiveness in combination with other targeted therapies or immunotherapies. These studies aim to address potential resistance mechanisms and extend Selpercatinib’s benefits to a broader range of cancer types with RET alterations. Additionally, further exploration of optimal dosing and administration strategies may enhance patient outcomes and minimize any residual adverse effects.
In sum, Selpercatinib stands as a powerful example of the impact of molecularly targeted therapies in advancing cancer treatment. Its selective mechanism and efficacy in RET-driven cancers have established it as a critical option for patients, providing renewed hope and opening new doors in the evolving landscape of precision oncology.
References
- Wirth, L. J., Sherman, E., Robinson, B., Solomon, B., Kang, H., Lorch, J., … & Cabanillas, M. E. (2020). Efficacy of selpercatinib in RET-altered thyroid cancers. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(9), 825-835.
- Takahashi, M., Ritz, J., & Cooper, G. M. (1985). Activation of a novel human transforming gene, ret, by DNA rearrangement. Cell, 42(2), 581-588.
- Kato, S., Subbiah, V., Marchlik, E., Elkin, S. K., Carter, J. L., & Kurzrock, R. (2017). RET aberrations in diverse cancers: next-generation sequencing of 4,871 patients. Clinical Cancer Research, 23(8), 1988-1997.
- Oliveira, L. C., & Mulligan, L. M. (2023). Selpercatinib: First approved selective RET inhibitor. Cell, 186(8), 1517-1517.