Icariin's Expanding Role in Health: From Tradition to Modern Science
Abstract
Icariin, a flavonoid glycoside derived from Epimedium species, is traditionally known for its role in enhancing sexual health, particularly in treating erectile dysfunction. Modern research has confirmed its effectiveness as a natural phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor, offering a plant-based alternative to synthetic medications. Beyond sexual health, Icariin shows promise in promoting bone health by stimulating osteoblast activity, making it a candidate for osteoporosis treatment. Its neuroprotective and antioxidant properties suggest potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Additionally, Icariin provides cardiovascular benefits by improving blood circulation and reducing inflammation. While generally well-tolerated, it is important to monitor dosage and potential interactions with other medications. As research continues to advance, Icariin is gaining recognition for its diverse therapeutic applications.
Introduction to Icariin
A bioactive flavonoid glycoside called icaridin is mostly present in the plant species known as Epimedium, or “Horny Goat Weed.” For many years, this herb has been utilized to enhance sexual energy and health in traditional Chinese medicine. Icariin, the primary constituent of the plant, is believed to be accountable for the well-researched impacts it has on sexual function, specifically with regard to erectile dysfunction and heightened libido.
Icariin’s popularity extends beyond its conventional uses, as more research begins to explore its potential medicinal purposes. Icariin promotes the production of nitric oxide, which results in vasodilation and enhanced blood flow. It does this by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). The effects of sildenafil, a medication used frequently to treat erectile dysfunction, are comparable to these. Icariin is therefore a viable natural option for anyone seeking herbal remedies for sexual health issues.
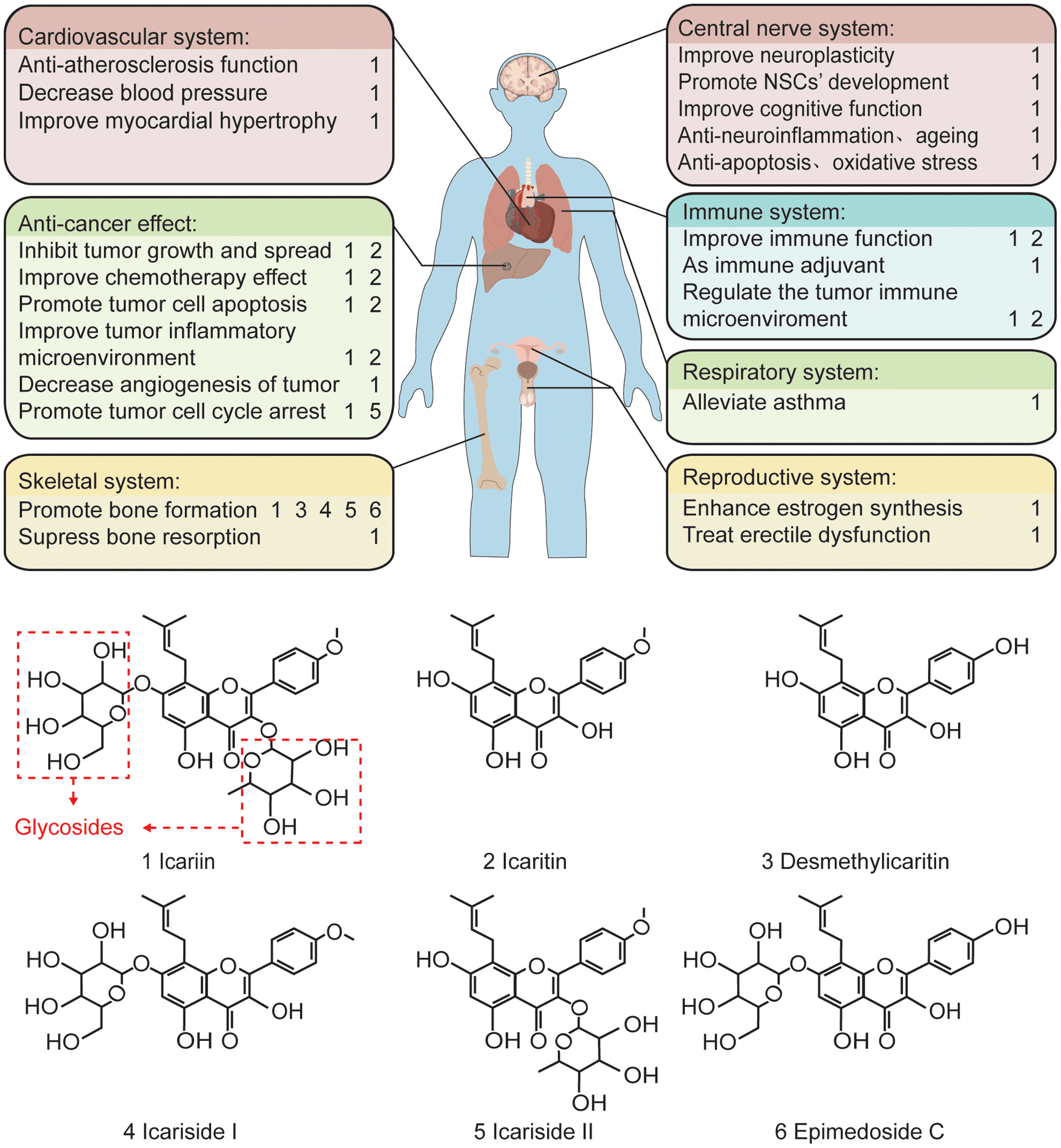
Figure 1. The pharmacological effects of the main components of epimedium and the related chemical formula.
But the advantages of Icariin go beyond its impact on libido. It may also improve bone health by increasing osteoblast activity, suggesting that it could be used as an osteoporosis treatment. Icariin’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties have also opened the door for greater research into its potential to treat a range of illnesses, such as inflammatory disorders, cardiovascular problems, and neurological diseases. Because of this, Icariin’s many health advantages are becoming more well known, and interest in both clinical research and natural medicine is rising. Given its many attributes, this chemical holds great promise for future study, especially when it comes to creating more natural, plant-based pharmaceutical substitutes.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Icariin is a flavonoid glycoside whose distinct molecular makeup enhances its biological properties. The substance is composed of a polyphenolic structure known as a flavonoid backbone, to which a sugar molecule is bonded. This process is known as glycosylation. Because of its increased sugar moiety, Icariin is more effectively absorbed by the body due to its increased bioavailability.
Icariin’s flavonoid core, which is made up of one heterocyclic ring and two aromatic rings, is the main structural component. The antioxidant qualities of this structure stem from its ability to give hydrogen atoms to free radicals, neutralizing them and averting oxidative damage. The glycosidic bond that binds the sugar group to the flavonoid structure of icaridin is crucial for maintaining its metabolic stability and facilitating its efficient interaction with biological systems.
One of isaridin’s best studied chemical properties is its ability to inhibit phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme that regulates blood flow by breaking down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). By inhibiting PDE5, Icariin increases the production of cGMP, which improves blood circulation and vasodilation, particularly in erectile tissue. Icariin is a natural substitute for synthetic PDE5 inhibitors used to treat erectile dysfunction in this situation due to its similar action.
Icariin is also osteogenic, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory due to its flavonoid structure, which makes it a useful compound in modern pharmacological research. Its ability to interact with multiple biological pathways highlights its potential for therapeutic applications outside of sexual health, including the management of bone and neurodegenerative diseases.
Mechanisms of Action
The main method that Icariin works is by modifying many metabolic pathways, the most notable of which is that it inhibits phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). The essential component that promotes vasodilation, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), is broken down by the enzyme PDE5. By inhibiting PDE5, icaridin helps to raise cGMP levels and promote blood flow, particularly in the penis’ corpus cavernosum tissue. Icariin’s mechanism is comparable to that of conventional drugs, making it an enticing natural replacement for erectile dysfunction treatments.
Icariin demonstrates antioxidant qualities in addition to inhibiting PDE5. This is mainly because of its flavonoid structure, which scavenges free radicals and lessens oxidative stress. This antioxidant impact aids in cell damage prevention, which is an important mechanism in anti-aging and neuroprotective settings. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that Icariin modifies signaling pathways associated with the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO), which promotes vasodilation and other positive effects on the cardiovascular system. Icariin has also been linked to increasing osteoblast activity, which is necessary for the creation of bones, and decreasing osteoclast activity, which is responsible for the degradation of bone structure. Icariin is positioned as a possible therapeutic drug for the treatment of osteoporosis because of its dual mechanism.
Health Benefits of Icariin
Icariin is a compound that has been found to have a wide range of potential health benefits due to its diverse mechanisms of action. While its action as a PDE5 inhibitor has been extensively studied in the context of erectile dysfunction, its most well-known benefit is its ability to improve sexual health by enhancing erectile function. As a natural alternative to synthetic drugs, this action of Icariin has been shown to be beneficial for impotence.
Icariin has major advantages for bone health in addition to sexual wellness. Inhibiting osteoclasts reduces bone resorption while concurrently promoting osteoblast development and activity, which aids in the production and strengthening of bones. These findings imply that Icariin may be essential for both treating and preventing osteoporosis.
Another area of investigation is the neuroprotective qualities of icariin. Icariin may shield neurons from harm by lowering oxidative stress and modifying neuroinflammatory pathways. This might provide therapeutic advantages for neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
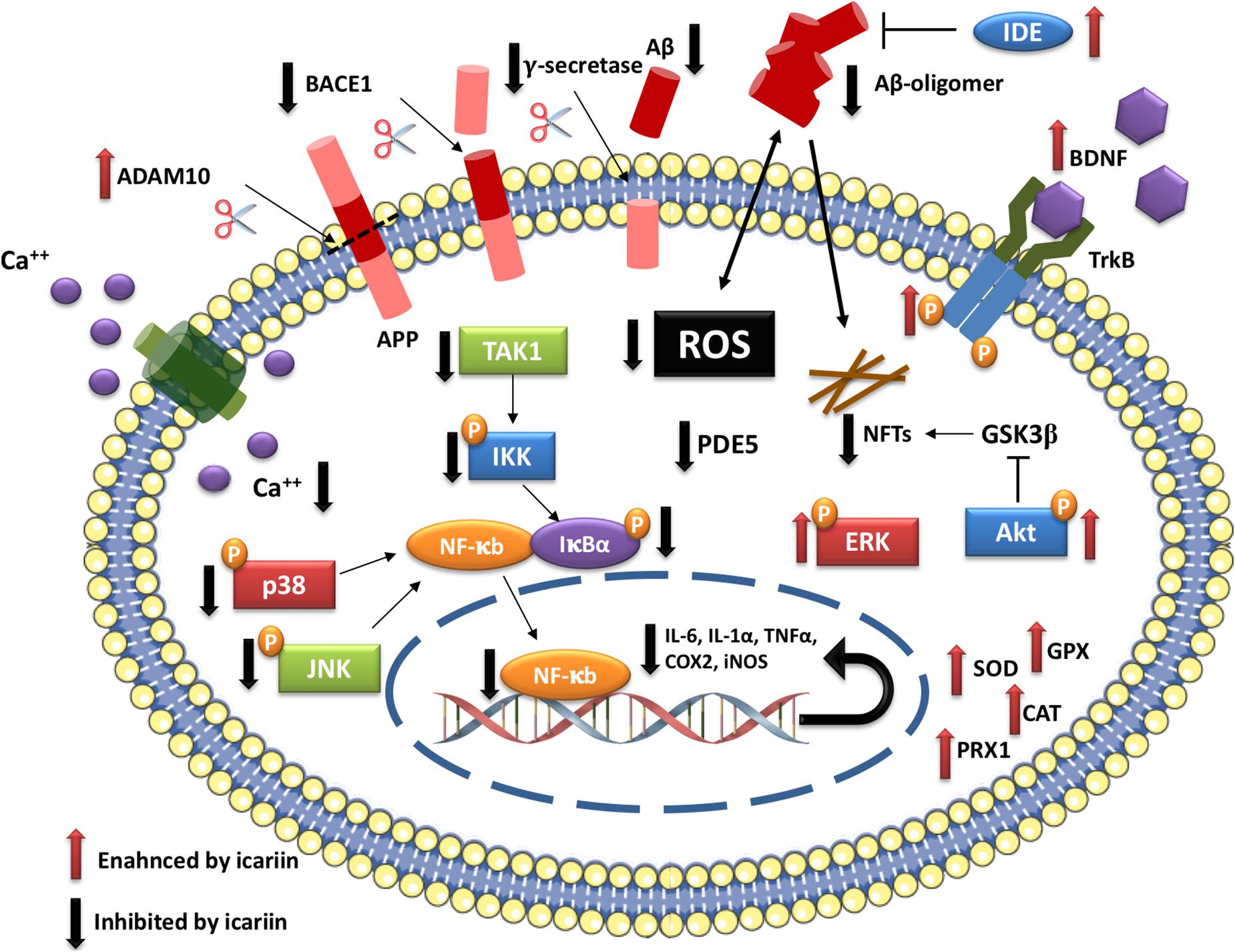
Figure 2. Icariin molecular targets in AD.
Icariin is also a possibility for cardiovascular health because of its advantages, which include vasodilation and better blood flow, which may help lower the risk of heart disease. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties increase its medicinal potential and promote general health and wellbeing.
Icariin in Modern Research
Icariin’s varied therapeutic potential has drawn a lot of interest in contemporary scientific research in recent years. Its use in the treatment of erectile dysfunction is among the most thoroughly researched fields. Icariin functions as a natural phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor, much like medications like sildenafil, as numerous studies have shown. Because of this characteristic, Icariin has emerged as a potentially effective substitute for those looking for natural treatments for sexual dysfunction, especially in men.
Icariin is a topic of interest in osteoporosis research since it has demonstrated amazing effects on bone health, which extend beyond sexual health. Icariin inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone resorption while promoting osteoblast development and activity, which are critical for bone growth, according to preclinical research. Consequently, Icariin may be developed as an anti-osteoporotic medication.
Icariin’s capacity to lessen oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the context of neuroprotection has prompted scientists to look into the possibility of using it to treat neurodegenerative illnesses. Icariin may shield neurons from harm and enhance cognitive function, providing patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease with hope, according to preclinical studies.
The cardiovascular advantages of Icariin have been investigated further. Due to its vasodilatory properties, which are mediated via PDE5 inhibition and nitric oxide modulation, it may be helpful in lowering the risk of cardiovascular illnesses and enhancing blood circulation. Its potential as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent is also being investigated by researchers, potentially expanding the range of disorders for which it can be used, including chronic inflammatory diseases and arthritis.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
Icariin has a number of possible health advantages, but it’s important to take its safety profile into account. Icariin is generally well tolerated when administered at moderate doses, according to studies. Like many bioactive substances, it can, however, have adverse consequences, especially if taken in excess or for an extended length of time.
Mild gastrointestinal problems including nausea or upset stomach are common adverse effects. Rarely, headaches or dizziness may result with large dosages of Icariin. It’s also important to remember that Icariin’s interactions with other PDE5 inhibitors and erectile dysfunction drugs have not been thoroughly investigated, which may provide dangers for patients who combine treatments.
Before using Icariin, like with any supplement or natural substance, people should speak with a healthcare provider, especially if they have any underlying medical concerns or are on prescription medication. Comprehending the suitable dosage and possible interactions is crucial for securely incorporating Icariin into a medical routine.
Conclusion
Icariin has shown promise as a potent bioactive substance with a variety of medical uses. Through its action as a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor, it has been traditionally utilized in herbal medicine, especially to improve sexual health. Recent study has validated its usefulness in treating erectile dysfunction. This organic substitute for manufactured pharmaceuticals has drawn interest from those looking for plant-based treatments to enhance erotic function.
Icariin’s adaptability goes beyond sexual health to other aspects of health, such as bone health, where it has demonstrated potential in enhancing osteoblast activity and halting bone deterioration. This suggests that it could be used as a medicinal agent to treat osteoporosis, especially in older people and postmenopausal women. Furthermore, as Icariin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities aid to lower neuroinflammation and shield neurons from oxidative stress, its neuroprotective effects have drawn attention in the domains of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Icariin has significant cardiovascular benefits as well because of its vasodilatory actions, which enhance circulation and lower the risk of heart disease. It is a potential treatment option for chronic inflammatory diseases due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities.
Despite the fact that Icariin has several health advantages, it’s crucial to take its safety profile into account. Icariin is usually well taken at normal dosages, but at greater levels, it may have mild adverse effects such headaches or stomach discomfort. Furthermore, it’s important to keep an eye out for any possible drug interactions, especially for people using other PDE5 inhibitors.
In conclusion, Icariin is a promising substance with a wide range of therapeutic applications. As research into this molecule deepens, it may become more and more significant in modern medicine for treating a range of ailments.
References
- Zhang J, Fan F, Liu A, Zhang C, Li Q, Zhang C, He F, Shang M. Icariin: A Potential Molecule for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 5;13:811808. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.811808. PMID: 35479319; PMCID: PMC9037156.
- Seyedi Z, Amiri MS, Mohammadzadeh V, Hashemzadeh A, Haddad-Mashadrizeh A, Mashreghi M, Qayoomian M, Hashemzadeh MR, Simal-Gandara J, Taghavizadeh Yazdi ME. Icariin: A Promising Natural Product in Biomedicine and Tissue Engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 12;14(1):44. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010044. PMID: 36662090; PMCID: PMC9862744.
- Wang S, Ma J, Zeng Y, Zhou G, Wang Y, Zhou W, Sun X, Wu M. Icariin, an Up-and-Coming Bioactive Compound Against Neurological Diseases: Network Pharmacology-Based Study and Literature Review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Aug 20;15:3619-3641. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S310686. PMID: 34447243; PMCID: PMC8384151.
- Khezri MR, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M. Icariin: A Potential Neuroprotective Agent in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2022 Oct;47(10):2954-2962. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03667-0. Epub 2022 Jul 8. PMID: 35802286.
- Liu Y, Yang H, Xiong J, Zhao J, Guo M, Chen J, Zhao X, Chen C, He Z, Zhou Y, Xu L. Icariin as an emerging candidate drug for anticancer treatment: Current status and perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jan;157:113991. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113991. Epub 2022 Nov 9. PMID: 36370524.
- Wang Y, Shang C, Zhang Y, Xin L, Jiao L, Xiang M, Shen Z, Chen C, Ding F, Lu Y, Cui X. Regulatory mechanism of icariin in cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114156. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114156. Epub 2022 Dec 28. PMID: 36584431.
- Liu X, Wang Z, Qian H, Tao W, Zhang Y, Hu C, Mao W, Guo Q. Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:945129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945129. PMID: 35979373; PMCID: PMC9376257.