Laduviglusib: A GSK3β Inhibitor with Potential Across Multiple Diseases
Abstract
Laduviglusib, a potent GSK3β inhibitor, has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for a variety of diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and metabolic diseases. By targeting GSK3β, an enzyme critical for numerous biological processes such as cell survival, metabolism, and apoptosis, Laduviglusib modulates key pathways involved in the progression of these conditions. Clinical trials have shown its potential in treating Alzheimer’s disease by reducing tau hyperphosphorylation and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by enhancing chemotherapy sensitivity. The drug’s versatility extends to managing metabolic disorders like diabetes, highlighting its broad applicability. Despite early positive results, further research is necessary to assess its long-term safety and efficacy. With continued clinical development, Laduviglusib could become a transformative treatment option, offering significant therapeutic benefits across multiple disease areas.
Introduction: What is Laduviglusib?
Laduviglusib is a promising small molecule compound that serves as a potent inhibitor of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Beta (GSK3β). This enzyme plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes, including metabolism, cell growth, survival, and differentiation. Laduviglusib targets GSK3β’s activity, which has drawn significant attention in medical research, particularly for its potential in treating diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
GSK3β is involved in numerous pathological processes, particularly in diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative conditions. It regulates several signaling pathways, including Wnt, insulin, and inflammatory pathways, all of which are critical for normal cellular function. By inhibiting GSK3β, Laduviglusib may block disease progression, especially in cancers where GSK3β promotes cell survival and resistance to therapy. It also shows promise in diseases such as Alzheimer’s, where GSK3β is implicated in tau hyperphosphorylation, a hallmark of the disease.
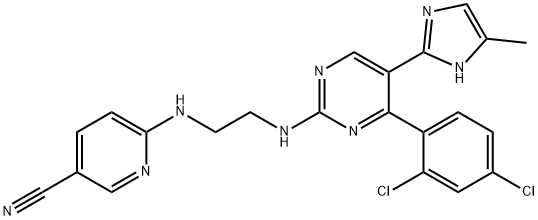
Fig.1 Structure of Laduviglusib
Laduviglusib is currently under investigation in clinical trials, showing its potential to be a therapeutic agent not just in oncology but also in neurology and metabolic disorders. As research advances, the compound’s mechanisms of action and safety profile will be further clarified, but initial studies indicate that it could become an important treatment option for various complex diseases.
Understanding Laduviglusib: The Basics
Laduviglusib functions by inhibiting Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Beta (GSK3β), an enzyme that plays a pivotal role in a variety of cellular processes. GSK3β regulates important pathways, including cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and metabolism, making it a crucial target in treating several diseases. In particular, GSK3β is implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, and in the progression of cancers like leukemia.
To understand how Laduviglusib works, it’s important to first understand GSK3β’s role. Under normal circumstances, GSK3β is involved in the phosphorylation of target proteins, which controls their activity. Inhibition of this enzyme has been shown to disrupt these signaling processes, affecting cell survival, inflammation, and even the regulation of certain tumor suppressors. Specifically, Laduviglusib interferes with GSK3β’s kinase activity, preventing it from carrying out these functions, and thereby inhibits the harmful signaling pathways that contribute to disease progression.
In the context of cancer, GSK3β helps cancer cells survive by promoting cell cycle progression and inhibiting apoptosis. By blocking GSK3β, Laduviglusib may render cancer cells more sensitive to chemotherapy and other treatments. Similarly, in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, GSK3β’s role in the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which is a hallmark of disease pathology, makes it an attractive therapeutic target.
Laduviglusib’s ability to modulate these pathways opens the door for potential treatments for not only cancer and Alzheimer’s but also other diseases where GSK3β activity is dysregulated, such as diabetes and metabolic disorders.
The Medical Applications of Laduviglusib
Laduviglusib, as a potent GSK3β inhibitor, has garnered attention for its therapeutic potential across a range of diseases. Its ability to modulate cellular pathways critical for cell growth, survival, and differentiation has made it a promising candidate for treating complex medical conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders.
Fig.2 The Medical Applications of Laduviglusib
Neurodegenerative Diseases:
One of the most exciting applications of Laduviglusib is in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. GSK3β plays a significant role in the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, a key feature of Alzheimer’s pathology. By inhibiting GSK3β, Laduviglusib may help prevent the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, which are associated with cognitive decline. Preliminary studies suggest that Laduviglusib could protect neurons and improve brain function, offering a potential treatment avenue for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease.
Cancer Treatment:
Laduviglusib’s effects in cancer therapy are equally promising. GSK3β is involved in regulating the growth of various cancers by modulating pathways like Wnt/β-catenin and apoptosis. By inhibiting GSK3β, Laduviglusib disrupts these pathways, potentially reducing tumor growth and promoting cancer cell death. Its application in leukemia, specifically in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), has shown encouraging results. It may also work synergistically with other chemotherapy agents, making it a valuable addition to cancer treatment regimens.
Metabolic Disorders:
Another emerging application is in the treatment of diabetes and other metabolic disorders. GSK3β is implicated in the regulation of insulin signaling and glucose metabolism. Inhibiting this enzyme with Laduviglusib could improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control, offering a potential strategy for managing type 2 diabetes.
As research continues, the broad spectrum of Laduviglusib’s potential medical applications underscores its importance in modern therapeutics.
Laduviglusib in Clinical Trials
Laduviglusib is currently under investigation in various clinical trials to evaluate its safety, efficacy, and potential therapeutic benefits across a range of diseases. Given its role as a GSK3β inhibitor, it holds promise in conditions like neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders. The clinical trials for Laduviglusib are designed to explore these possibilities and to provide a clearer understanding of how this drug works in human subjects.
Current Status of Clinical Trials:
As of now, clinical trials involving Laduviglusib are primarily focused on evaluating its effects in Alzheimer’s disease and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Initial results have shown that Laduviglusib may help reduce the progression of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients by inhibiting tau hyperphosphorylation. Similarly, trials investigating its use in cancer, particularly leukemia, are assessing its ability to improve patient outcomes by enhancing chemotherapy sensitivity.
Challenges and Risks in Laduviglusib’s Development:
While Laduviglusib’s early-stage trials have produced positive results, there are still challenges to be addressed before it becomes a widely accepted therapeutic option. Some concerns include potential side effects related to GSK3β inhibition, such as its effects on immune function and metabolism. Further trials are necessary to determine the optimal dosage, long-term safety, and any possible adverse effects in different patient populations. Despite these challenges, the potential of Laduviglusib as a multifaceted therapeutic agent makes it a drug to watch in the coming years.
Laduviglusib: Market Potential and Future Outlook
The market potential of Laduviglusib is substantial, driven by its broad applicability across several disease areas, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and metabolic diseases. As a GSK3β inhibitor, Laduviglusib could provide a much-needed therapeutic alternative for diseases with limited treatment options.
Pharmaceutical Potential:
The global market for Alzheimer’s drugs is expected to grow significantly, and Laduviglusib’s ability to modulate tau phosphorylation presents it as a strong contender in this space. Additionally, its application in cancer therapy—particularly in leukemia—could open doors for combination treatments, making it an attractive option for oncology. Its potential to manage metabolic disorders like diabetes also adds to its versatility, expanding its market to both chronic diseases and acute medical conditions.
What Does the Future Hold for Laduviglusib?
Looking ahead, Laduviglusib could significantly impact the pharmaceutical industry. If it successfully completes clinical trials and is approved, it may not only be a breakthrough treatment in areas like Alzheimer’s and cancer, but also in metabolic conditions such as diabetes. The ongoing research and clinical testing will likely influence its integration into mainstream medical treatments in the coming years. With more positive trial outcomes, pharmaceutical companies may look to partner with developers of Laduviglusib to bring it to market, potentially creating new alliances in the field of precision medicine.
As research continues, Laduviglusib’s future looks promising, with the potential to revolutionize treatment for complex diseases and carve out a significant position in the pharmaceutical market.
The Promising Future of Laduviglusib
Laduviglusib represents a significant advancement in the field of drug development, offering a novel approach to the treatment of various complex diseases. As a GSK3β inhibitor, it targets a critical enzyme involved in a wide range of biological processes, from cell survival to metabolism. The compound’s ability to modulate these pathways positions it as a promising candidate for treating neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders.
The early clinical trials have shown great potential, particularly in the areas of Alzheimer’s disease and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). By inhibiting GSK3β, Laduviglusib has demonstrated its ability to reduce tau hyperphosphorylation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s pathology, and to enhance chemotherapy sensitivity in cancer. These results underscore its therapeutic potential in improving patient outcomes for diseases that currently lack effective treatments.
Moreover, the market potential for Laduviglusib is substantial. Its broad applicability across multiple disease areas makes it an attractive candidate for pharmaceutical companies looking to address unmet medical needs. If the ongoing clinical trials continue to yield positive results, Laduviglusib could be a game-changer in modern medicine, especially for those suffering from chronic or complex diseases.
Despite the promising outlook, further research is required to establish its long-term safety and efficacy. However, with continued investment and clinical testing, Laduviglusib has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of a variety of debilitating conditions, offering hope for millions of patients worldwide.
As the landscape of modern medicine continues to evolve, Laduviglusib’s future in therapeutic interventions remains one to watch closely, with the possibility of it becoming a cornerstone treatment in the coming years.
References
- Liu M, Zhao J, Xue C, Yang J, Ying L. (2024). Uncovering the ferroptosis related mechanism of laduviglusib in the cell-type-specific targets of the striatum in Huntington’s disease. BMC Genomics, 25(1), 633. Link
- Cohen P, Frame S. (2001). The renaissance of GSK3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2(10), 769-76. Link
- Arenas V, Castaño JL, Domínguez JJ, Yáñez L, Pipaón C. (2025). Distinct NF-kB Regulation Favors a Synergic Action of Pevonedistat and Laduviglusib in B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells Ex Vivo. Cancers (Basel), 17(3), 533. Link
- Hamdon S, Fernandez-Gonzalez P, Omar MY, González-Sepúlveda M, Ortiz J, Gil C. (2024). CHIR99021 causes inactivation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and depletion of dopamine in rat brain striatum. Neuropharmacology, 242, 109759. Link
- Qian Y, Zhang H, Li J, Huang L, Qin Y, Zhang J, Wang W. (2024). Wnt signaling aberrant activation drives ameloblastoma invasion and recurrence: bioinformatics and in vitro insights. BMC Oral Health, 24(1), 1421. Link