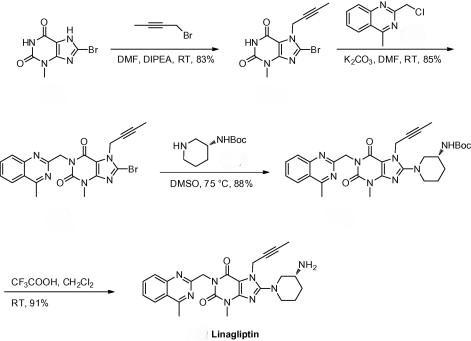
Linagliptin: A Comprehensive Overview for Pharmaceutical Research
Abstract
Linagliptin, a highly specific and potent DPP-4 inhibitor, is revolutionizing the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). By inhibiting the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme, Linagliptin prolongs the activity of incretin hormones, thereby enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release in a glucose-dependent manner. Clinical studies have demonstrated Linagliptin’s efficacy in significantly reducing glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, with a favorable safety and tolerability profile. Its unique pharmacokinetic properties, including predominantly non-renal elimination, make it suitable for patients with renal and hepatic impairments without dose adjustment. Our company is proud to offer Linagliptin along with its related impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks, supporting advanced pharmaceutical research and development. With our commitment to quality and innovation, we provide essential tools for scientists to explore the full potential of Linagliptin in therapeutic applications. Explore our extensive product catalog and leverage our custom synthesis services to accelerate your research endeavors.
Introduction to Linagliptin
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, leading to persistent hyperglycemia. The global prevalence of T2DM has reached epidemic proportions, driven by factors such as increasing obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles. Effective management of T2DM is crucial to prevent complications like cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy, which significantly impact the quality of life and healthcare costs.
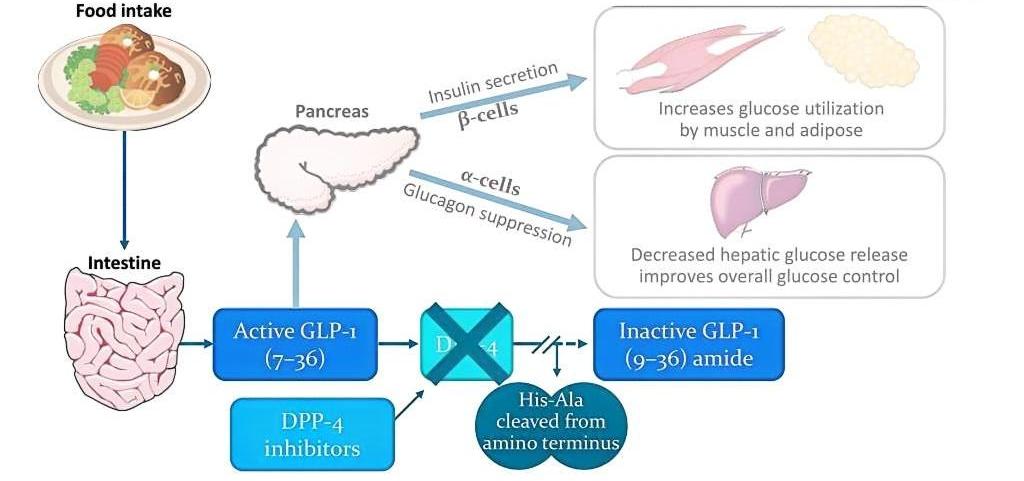
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have emerged as an essential class of oral hypoglycemic agents for T2DM management. These inhibitors work by blocking the DPP-4 enzyme, which is responsible for the degradation of incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). By preventing this degradation, DPP-4 inhibitors increase the levels and prolong the activity of incretin hormones, leading to enhanced insulin secretion and suppressed glucagon release in a glucose-dependent manner. This mechanism helps in achieving better glycemic control with a lower risk of hypoglycemia.
Linagliptin stands out among DPP-4 inhibitors due to its high specificity and potent inhibition of the DPP-4 enzyme. Unlike other agents in its class, Linagliptin exhibits a unique pharmacokinetic profile with predominantly non-renal elimination, making it suitable for patients with varying degrees of renal impairment without requiring dose adjustments. Additionally, Linagliptin does not necessitate dose modifications in patients with hepatic impairment, elderly patients, or those who are obese. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated Linagliptin’s efficacy in significantly reducing glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and improving overall glycemic control. Its safety profile is comparable to placebo, with minimal risk of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects.
Our company is dedicated to providing high-quality Linagliptin and related chemicals, including impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks. These products are crucial for advancing pharmaceutical research and developing new therapeutic applications for T2DM. By offering a comprehensive range of products and custom synthesis services, we support scientists and researchers in their quest to innovate and improve diabetes management strategies.
Pharmacological Profile
Mechanism of Action of Linagliptin
Linagliptin functions as a potent and selective inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. DPP-4 rapidly degrades incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which are crucial for regulating glucose homeostasis. By inhibiting DPP-4, Linagliptin prolongs the activity of these incretins, enhancing glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells and suppressing glucagon release from pancreatic alpha cells. This dual action helps to lower blood glucose levels effectively and safely, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Linagliptin exhibits a unique pharmacokinetic profile characterized by a high specificity for the DPP-4 enzyme and minimal renal excretion. Following oral administration, Linagliptin is rapidly absorbed, achieving peak plasma concentrations approximately 1.5 hours post-dose. The drug’s half-life is approximately 131 hours, supporting once-daily dosing. Notably, Linagliptin is primarily excreted via the enterohepatic system, with less than 1% eliminated unchanged in the urine. This feature makes Linagliptin particularly suitable for patients with varying degrees of renal impairment, as no dose adjustments are necessary. Additionally, the pharmacokinetics of Linagliptin are unaffected by hepatic impairment, age, or obesity, making it a versatile option for a broad range of patients.
Benefits of Linagliptin Over Other DPP-4 Inhibitors
Compared to other DPP-4 inhibitors, Linagliptin offers several distinct advantages. Its non-renal route of elimination sets it apart from other drugs in the same class, which are predominantly cleared by the kidneys. This unique elimination pathway reduces the burden on the renal system, making Linagliptin an ideal choice for patients with chronic kidney disease. Furthermore, Linagliptin’s high specificity for the DPP-4 enzyme, with minimal activity against other related enzymes, translates to a lower risk of off-target effects and associated adverse reactions. Clinical studies have demonstrated Linagliptin’s superior efficacy in reducing glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and maintaining glycemic control, all while offering a safety profile comparable to placebo. This combination of efficacy, safety, and broad patient applicability makes Linagliptin a valuable therapeutic option in the management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety
Summary of Clinical Studies and Trials
Linagliptin has been extensively studied in multiple clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety in the management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). These studies have consistently shown that Linagliptin effectively lowers glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, an essential marker of long-term glycemic control. In clinical trials, patients treated with Linagliptin demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels compared to placebo. Furthermore, Linagliptin was effective as both monotherapy and in combination with other oral antidiabetic agents such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and pioglitazone.
Efficacy in Reducing HbA1c Levels
In a 24-week study involving patients inadequately controlled on metformin, Linagliptin as an add-on therapy resulted in an HbA1c reduction of approximately 0.64% compared to placebo. Another study comparing Linagliptin to glimepiride showed non-inferiority, with similar HbA1c reductions but a significantly lower risk of hypoglycemia with Linagliptin. In a 52-week trial, patients receiving Linagliptin and metformin experienced sustained HbA1c reductions, indicating its long-term efficacy in glycemic control. Additionally, studies have shown that Linagliptin significantly improves fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and postprandial glucose (PPG) levels, contributing to overall improved glucose management.
Safety Profile and Tolerability
Linagliptin’s safety and tolerability have been well-documented in clinical trials. The incidence of adverse events with Linagliptin is similar to that of placebo, making it a safe option for long-term use. One of the most significant advantages of Linagliptin is its low risk of hypoglycemia, attributed to its glucose-dependent mechanism of action. This safety profile is particularly beneficial when Linagliptin is used in combination with other antidiabetic medications.
Furthermore, Linagliptin has a neutral effect on body weight, with no significant weight gain observed in clinical trials. This makes it a preferable choice for overweight or obese patients, a common concern in T2DM management. Studies have also shown that Linagliptin is safe for use in patients with renal and hepatic impairments, elderly patients, and those with cardiovascular risk factors, broadening its applicability across diverse patient populations.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Research
Importance of Linagliptin in Drug Development
Linagliptin’s unique pharmacological properties and favorable safety profile have made it a valuable asset in pharmaceutical research and drug development for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Its ability to inhibit the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme effectively, combined with its prolonged action due to non-renal elimination, provides researchers with a robust tool for developing new therapeutic strategies. Linagliptin’s versatility in being used as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents allows for a wide range of experimental designs and applications.
Our company is at the forefront of supplying high-quality Linagliptin and its related chemicals to support advanced pharmaceutical research. We provide Linagliptin along with its impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks, essential for various research applications. These products are meticulously manufactured and rigorously tested to ensure the highest standards of purity and consistency, enabling researchers to obtain reliable and reproducible results.
Impurities and Metabolites
Understanding and analyzing the impurities and metabolites of Linagliptin is crucial in the drug development process. Impurities can affect the safety and efficacy of the drug, while studying metabolites can provide insights into the drug’s pharmacokinetics and potential interactions. Our extensive catalog includes a wide range of Linagliptin-related impurities and metabolites, aiding researchers in comprehensive safety assessments and metabolic studies.
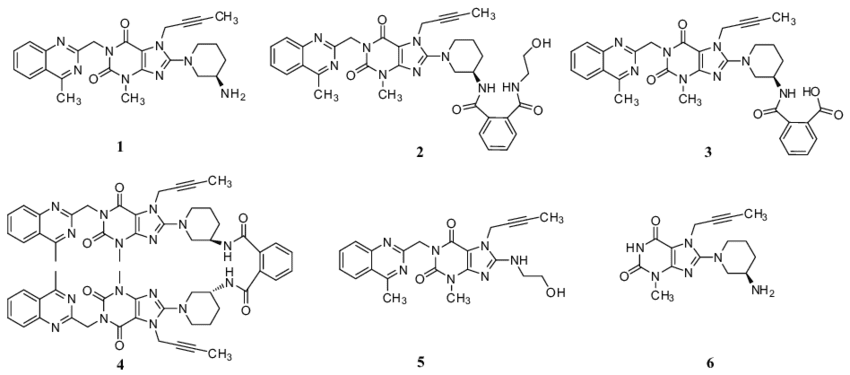
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Isotope-labeled compounds are invaluable tools in pharmaceutical research, particularly in pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. Linagliptin isotope-labeled compounds enable precise tracking of the drug and its metabolites in biological systems, facilitating detailed understanding of its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Our offerings include a variety of isotope-labeled Linagliptin compounds, tailored to meet the specific needs of your research.
Building Blocks for Custom Synthesis
In addition to providing Linagliptin and its related chemicals, we offer custom synthesis services to create specific derivatives and analogs. These building blocks are essential for researchers looking to explore new chemical spaces and develop novel therapeutic candidates. Our team of experts collaborates closely with clients to design and synthesize compounds that meet their unique research requirements, ensuring high-quality and timely delivery.
Our commitment to quality and innovation drives us to support the scientific community with the best possible resources. By offering a comprehensive range of Linagliptin-related products and custom synthesis services, we aim to facilitate groundbreaking research and the development of new therapies for T2DM and other related conditions. Partner with us to accelerate your research and achieve your scientific goals with confidence.
Conclusion
Linagliptin has established itself as a cornerstone in the management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) due to its highly specific inhibition of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. By prolonging the action of incretin hormones, Linagliptin enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and suppresses glucagon release, leading to effective glycemic control. Its unique pharmacokinetic profile, characterized by predominantly non-renal elimination, makes it suitable for patients with renal and hepatic impairments without the need for dose adjustments. Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated its efficacy in reducing glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and its favorable safety profile, including a low risk of hypoglycemia and a neutral effect on body weight.
Our company is dedicated to supporting advanced pharmaceutical research by providing high-quality Linagliptin and related chemicals. Our product offerings include Linagliptin, its impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks, all essential for comprehensive research and development. We ensure that our products meet the highest standards of purity and consistency, enabling researchers to achieve reliable and reproducible results. Our custom synthesis services are designed to meet the specific needs of our clients, providing tailored solutions for innovative drug development.
We invite researchers and pharmaceutical developers to explore our extensive catalog of Linagliptin-related products. Our team of experts is committed to providing exceptional support and services to facilitate your research endeavors. Whether you require standard products or custom synthesis, we are equipped to meet your needs with precision and efficiency. By partnering with us, you can leverage our expertise and high-quality products to advance your research and contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies for T2DM.
Reference
Scott, L. J. (2011). Linagliptin: in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs, 71, 611-624.