Medetomidine: A Versatile Sedative and Analgesic in Veterinary Medicine
Abstract
With its sedative, analgesic, and muscle-relaxing properties, medetomidine is a powerful α2-adrenergic agonist that is frequently utilized in veterinary medicine. It functions by inhibiting the activity of the sympathetic nervous system by binding to α2 receptors in the central nervous system. Medetomidine is frequently used in small animal practice for operations like pain management, minor surgeries, and diagnostic imaging. Its effects can be reversed by giving atipamezole. Its uses in neuroprotection, sedation of wildlife, and combining it with other medications to maximize benefits and reduce negative effects have all been studied. Future studies are likely to broaden the usage of medetomidine because of its consistent sedative effects and good safety profile, which make it a mainstay of veterinary therapy.
Introduction to Medetomidine
In veterinary medicine, medetomidine is a highly effective sedative and analgesic that is frequently used, especially for small animals like dogs and cats. It is a member of the class of α2-adrenergic agonists, which lower sympathetic nervous system activity by acting on α2 receptors in the central nervous system. Its ability to provide deep drowsiness, relax muscles, and relieve pain makes it a necessary medication for operations involving immobilization or pain control.
Medetomidine has a number of benefits, one of which is its dose-dependent action, which enables vets to adjust sedation levels according to the animal’s demands and the difficulty of the surgery. It also acts quickly, which is especially helpful in circumstances where sedation is needed right away. Atipamezole, an α2-adrenergic antagonist, can counteract its effects, enabling animals to recover from drowsiness more quickly than with other sedatives.
Medetomidine’s consistent sedative effects make it a popular choice for operations like dental cleanings, minor surgical procedures, and diagnostic imaging. It is widely used in veterinary offices because to the fact that it minimizes the risk of problems by reducing the quantity of general anesthetic necessary in addition to providing efficient sedation.It is still very important to animal healthcare since it makes sedative and pain control therapies safer and more effective.
Mechanism of Action
Medetomidine functions as an α2-adrenergic agonist, mainly targeting receptors in the central nervous system (CNS), to produce its calming and analgesic effects. Primarily located in the brain and spinal cord, the α2 receptors are essential for controlling the release of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine. Medetomidine lowers norepinephrine release by activating these receptors, which lowers sympathetic nervous system activity. This reduction in sympathetic tone has sedative, muscle-relaxing, and analgesic effects, making it an excellent choice for a variety of veterinary operations.
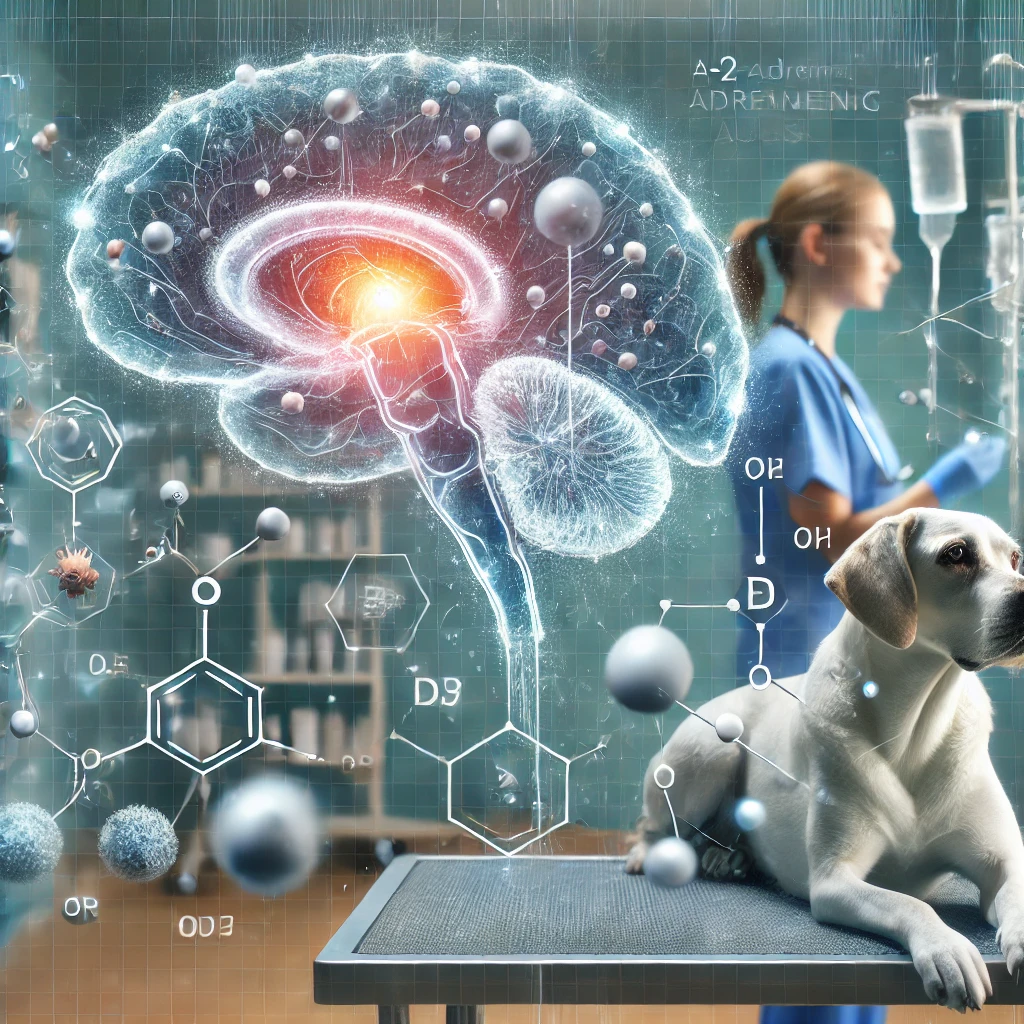

Fig.1 mechanism of action of Medetomidine as an α2-adrenergic agonist
The locus coeruleus, a part of the brainstem involved in the control of alertness and attention, is the main site of action for medetomidine’s sedative effects. This area has a decrease in norepinephrine transmission, which causes drowsiness and calmness. Furthermore, medetomidine inhibits nociceptive transmission, which lessens pain perception, and has analgesic effects by influencing both the spinal and supraspinal pathways. Medetomidine’s combined analgesic and sedative effects make it especially helpful for treatments that call for both pain relief and immobility.
When administered appropriately, medetomidine produces a dependable sedative with little circulatory depression in contrast to many other sedatives. Its dose-dependent effects, however, may cause a noticeable drop in blood pressure and heart rate, therefore careful monitoring is necessary when using it. The administration of atipamezole, which competes for the same receptors and successfully reverses the effects of medetomidine, allows for the reversal of these physiological alterations and expedites recovery following the treatment.
Clinical Uses of Medetomidine
Because of medetomidine’s many sedative, analgesic, and muscle-relaxing properties, it is frequently utilized in veterinary medicine. It is frequently used in a variety of clinical contexts, from simple procedures to more involved therapies. The medication is especially helpful for treatments like dental cleanings, small surgeries, and diagnostic imaging that need for immobilizing animals. Medetomidine reduces the dangers associated with anesthetic medications in these circumstances by providing enough sedation without the necessity for deeper, general anesthesia.
Medetomidine not only causes drowsiness but also has potent analgesic effects, which make it useful for managing pain in animals undergoing surgery or other traumatic treatments. Veterinarians can precisely adjust the degree of sedation and pain relief based on the surgery and the health of the animal thanks to its predictable dose-dependent effects. This adaptability is especially helpful in small animal practice, where several sedative techniques may be needed for each patient.
To maximize its benefits or lower the dosages of individual medications, medetomidine is frequently coupled with opioids or other anesthetics to limit the possibility of adverse effects. When addressing high-risk animals—such as those with underlying cardiovascular conditions—this combined strategy is especially helpful since it reduces the amount of stress that drugs might cause the heart. Overall, medetomidine is an essential tool in contemporary veterinary practice due to its consistent ability to offer sedation and pain relief in a variety of veterinary applications.
Reversibility and Safety Profile
Atipamezole, an α2-adrenergic antagonist, is used to achieve medetomidine’s reversibility, which is one of its major advantages. Atipamezole efficiently reverses the sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine by competing with it for the same receptors in the central nervous system. This reversibility is especially helpful for treatments when a quick sedative recovery is required. For instance, the animal and the veterinarian benefit when normal function is quickly restored following a diagnostic procedure.
Although medetomidine has a well-regarded safety profile, it does have some cardiovascular side effects, such as bradycardia (slowing of the heart rate) and hypotension (lowered blood pressure), like many sedatives. In healthy animals, these effects are usually well-tolerated and dose-dependent. They do, however, need to be closely watched, especially in animals that already have cardiac issues. The general safety of medetomidine administration in veterinary settings is greatly improved by the capacity to regulate these effects through dose modifications and the availability of atipamezole as a reversal medication.
Advancements and Research on Medetomidine
Recent discoveries have broadened our knowledge of the effects and possible uses of medetomidine, especially in veterinary medicine. Optimizing the drug’s use in conjunction with other medications, such as opioids and anesthetics, to maximize its sedative and analgesic effects while reducing side effects, is a major field of research. Medetomidine can be used in conjunction with ketamine, propofol, or opioids to lower the dosages needed for each medication. This can help animals having surgery or other invasive operations recover more quickly and with fewer adverse effects on their cardiovascular systems.
Medetomidine’s application in exotic animal sedative and wildlife is a promising field of study. It is a useful tool for veterinarians and researchers who work with difficult-to-handle animals because of its capacity to produce strong, reversible drowsiness with little disturbance to the animal. The combination of medetomidine and atipamezole reduces the danger of predation or injury following release in wildlife settings by enabling secure immobilization and a prompt return to normal activity.
Additionally, medetomidine’s neuroprotective qualities have been investigated. Its α2-adrenergic agonist activity may aid in protecting neural tissues after a stroke or traumatic brain injury, according to some research. This presents the medication with potentially new therapeutic applications, especially in emergency and critical care situations when maintaining brain function is essential.
Future studies are looking into the long-term effects of medetomidine use, particularly in situations when therapy is repeated or prolonged. These studies explore medetomidine’s expanded uses in veterinary and human medicine, with the goal of ensuring that it remains a safe and effective alternative for a variety of veterinary applications.
Conclusion: Importance of Medetomidine in Veterinary Care
Due of its strong α2-adrenergic agonist action, medetomidine has become an essential sedative and analgesic in veterinary therapy. Because it may effectively relieve pain, relax muscles, and produce reversible drowsiness, it is a vital tool for many clinical and diagnostic processes. The medication’s dose-dependent effects, along with the quick reversal potential of atipamezole, guarantee that animals can be handled safely both before and after medical procedures. Because of its reversibility, medetomidine can be used with greater control over the sedative process, which makes it especially helpful for treatments requiring exact timing or quick recovery.
Medetomidine has found a wider application in the sedation of exotic and wildlife animals, providing safe and effective sedation in difficult situations, beyond its customary use in small animal medicine. Recent study suggests that it has neuroprotective qualities, which could lead to wider therapeutic applications and even the use of it in emergency and critical care situations.
The safety profile of medetomidine, together with its adaptability to a range of veterinary uses, keeps it popular. Medetomidine continues to be a vital component of contemporary veterinary care, with research efforts centered on maximizing its application and mitigating adverse effects via combination treatments. Its ability to enhance the safety and effectiveness of animal sedative and pain management guarantees its continued important use in veterinary care for years to come.
References
- Creighton, C. M., & Lamont, L. A. (2024). Sedatives and Tranquilizers. Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia: The Sixth Edition of Lumb and Jones, 333-354.
- Sinclair, M. D. (2003). A review of the physiological effects of α2-agonists related to the clinical use of medetomidine in small animal practice. The Canadian Veterinary Journal, 44(11), 885-897.
- Granholm, M., McKusick, B. C., Westerholm, F. C., & Aspegrén, J. C. (2006). Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine or medetomidine in dogs and their reversal with atipamezole. Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 33(4), 214-223.
- Scheinin, M., & MacDonald, E. (1989). An introduction to the pharmacology of α2-adrenoceptors in the central nervous system. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 85(Suppl), 11-19.