Melanotan II: Exploring Its Dual Role in Cosmetic Tanning and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
Melanotan II is a synthetic peptide that was initially designed to increase melanin formation in order to protect the skin from harmful UV radiation. Its propensity to improve skin pigmentation has made it popular in cosmetic tanning, particularly among people who want to tan without getting too much sun exposure. Melanotan II modulates melanocortin receptors, which regulate sexual function and hunger. This opens the door for its usage in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and obesity. However, its unregulated selling poses substantial safety risks, and the long-term effects are still being investigated. While Melanotan II has potential in both cosmetic and medicinal uses, its future hinges on additional study and regulatory control to ensure its safety and efficacy.
Introduction to Melanotan II
A synthetic peptide called Melanotan II was created as a counterpart to the body’s naturally occurring hormone, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). Melanotan II was created to improve the body’s natural tanning process by activating melanocortin receptors, specifically MC1R, which are important for skin pigmentation. Melanotan II was first investigated for its capacity to increase melanin formation. This process protects against sun-induced skin damage by enabling enhanced melanin formation in response to UV exposure.
Melanotan II, created at the University of Arizona in the 1980s, was initially investigated for its ability to promote pigmentation and fend off skin cancer. But this peptide showed more benefits than just browning the skin. Researchers discovered that Melanotan II affected hunger regulation and sexual arousal, which may have applications in the treatment of obesity and erectile dysfunction. Its stimulation of other melanocortin receptors, like MC3R and MC4R, which are involved in energy balance and sexual function, is what causes these effects.
Melanotan II was first created for medicinal use, but it has since become well-known in the cosmetics market for its capacity to simulate tan skin without requiring a lot of sun exposure. However, safety concerns have been raised by its increasing use in unregulated settings, especially in light of potential side effects such nausea and appetite suppression, as well as the chance that unregulated products could have detrimental effects.
Despite its intriguing uses, Melanotan II is still being studied in order to completely comprehend its advantages, disadvantages, and long-term safety. The demand for controlled, safe use is growing in the domains of medicine and cosmetics as interest in these products continues to expand.
Mechanism of Action
Melanotan II works by imitating the effects of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), a component of the body’s melanocortin system. Numerous receptors (MC1R to MC5R) in the melanocortin system control a range of physiological functions, including hunger, sexual function, and pigmentation. Of these receptors, MC1R is principally in charge of controlling melanogenesis, the process that produces skin pigmentation. The pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes their color, melanin, is produced more readily when Melanotan II binds to MC1R on melanocytes. Melanotan II is especially helpful for people with fair skin who are prone to sunburn and skin malignancies like melanoma since this increase in melanin results in a darker skin tone and offers some protection against UV radiation damage.
Melanotan II, however, has effects that go beyond skin pigmentation. It binds to other melanocortin receptors, like MC3R and MC4R, which are involved in regulating energy balance and sexual function. Research has shown that Melanotan II acts on the central nervous system to increase sexual desire and arousal in men and women. This finding has prompted research into the possibility of using Melanotan II to treat sexual dysfunction, especially erectile dysfunction, where it could replace or supplement conventional treatments like sildenafil (Viagra). Melanotan II has also been found to suppress appetite, probably due to its action on MC4R, which makes it a viable candidate for treating obesity.
Potential Medical and Therapeutic Uses
Although Melanotan II is most recognized for its ability to enhance skin pigmentation, it has demonstrated promise in a number of therapeutic contexts. Its application in avoiding skin cancer is among the most important, especially for fair-skinned people who are more susceptible to melanoma. Melanotan II can boost the body’s natural defenses against UV radiation by promoting the formation of melanin, which lowers the chance of sunburn and the ensuing damage to skin. Its protective qualities have made it a desirable choice for people who want to look tanned but avoid too much sun exposure.
Melanotan II has demonstrated promise in the treatment of sexual dysfunction in addition to its potential in dermatology. Melanotan II activates MC4R, which has been shown in early clinical trials to cause spontaneous erections in males with erectile dysfunction. This influence on sexual arousal may offer a new therapeutic option for people who don’t respond well to conventional therapies or who would rather use something different than prescription drugs. Studies on how melanotan II affects sexual function in women have revealed that it may heighten sexual desire and enhance overall sexual satisfaction.
Melanotan II’s function in controlling obesity and suppressing hunger is another intriguing use for the compound. Melanotan II has the potential to cure obesity since it acts on MC4R to control energy balance and decrease food intake. Though research on this use is still in its early stages, the peptide’s capacity to affect hunger presents a novel treatment option for metabolic disorders.
Melanotan II is still being studied despite its possible advantages, and worries about side effects and long-term safety have restricted its broad medical use. Among the negative effects that have been documented are nausea, elevated blood pressure, and darkening of freckles and moles, which may cause skin problems to be misdiagnosed. Furthermore, there are hazards associated with the unregulated use and sale of Melanotan II for cosmetic reasons, as consumers may be harmed by contaminated or counterfeit items.
Melanotan II for Cosmetic Tanning
Melanotan II is widely recognized for its application in cosmetic tanning. Melanotan II stimulates the synthesis of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, by inducing melanogenesis through the activation of the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R). This method produces a darker skin tone without needing for prolonged sun exposure, which has drawn attention from people looking to get tanned while reducing the negative effects of UV radiation. Melanotan II has been more and more popular in recent years, especially in areas with fair-skinned populations where there is a larger danger of sunburn and skin cancer.
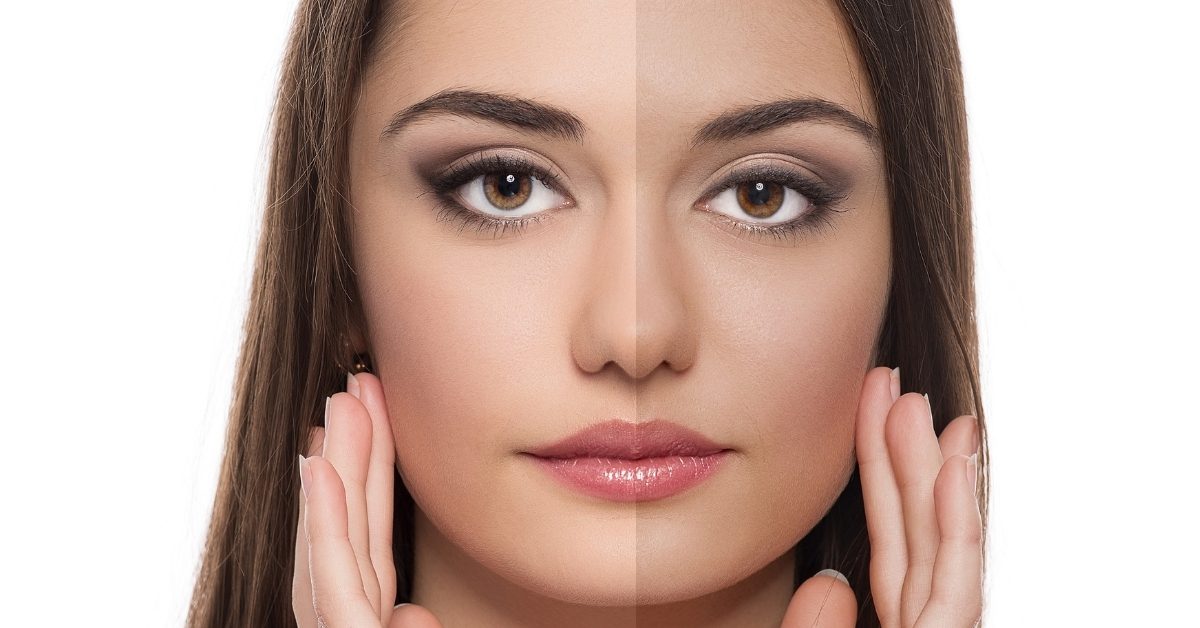

Fig.1 Melanotan II for Cosmetic Tanning
Melanotan II is appealing because it provides users with a tan with less sun exposure, which can help ward off UV-induced skin cancer and premature aging of the skin. Melanotan II is a popular drug, although there are issues with its uncontrolled usage and selling. Despite not having FDA or other regulatory agency approval for cosmetic usage, it is frequently sold online as a cosmetic product. This creates safety issues because products obtained through unregulated routes may differ in quality and purity and have unanticipated negative effects in users.
Safety, Side Effects, and Risks
Melanotan II’s safety profile is still a major worry, despite the drug’s potential for both medicinal and cosmetic applications. Increased blood pressure, appetite suppression, and nausea are among the negative effects that have been reported. More concerningly, users have mentioned that their freckles and moles have become darker, which may make it more difficult to diagnose skin diseases like melanoma. Melanotan II’s potential to induce hyperpigmentation in specific body regions, resulting in changes to the look of moles or uneven skin tone, raises questions over its safety when used without a physician’s supervision.
Users run the risk of injury from Melanotan II’s uncontrolled sale. The product is frequently obtained via unregulated online merchants, where quality control may be deficient, because it is not legally permitted for over-the-counter sale in many countries. Products that are tainted or counterfeit may have negative consequences in addition to Melanotan II’s usual side effects. Consequently, those thinking about using it for tanning should be aware of the risks associated with buying unregulated peptides.
It is essential to speak with a healthcare provider before using Melanotan II to verify safety. Medical specialists, especially those with a higher risk of skin cancer or other problems, can offer assistance on dosage, monitoring for side effects, and analyzing the risks involved.
Future Research and Applications
Although Melanotan II is mostly used for cosmetic tanning at the moment, further study indicates that it may have more uses in medical down the future. Research on its potential to prevent skin malignancies by boosting melanin formation and providing defense against damaging UV radiation is among the most promising. If you have fair skin and are more likely to develop melanoma, this may be especially helpful. Furthermore, because of Melanotan II’s impact on sexual function, there is increased interest in using it to treat sexual diseases such as erectile dysfunction in people who don’t react well to conventional treatments.
Moreover, the peptide may be useful in treating obesity and metabolic diseases due to its capacity to control appetite by binding to melanocortin receptors. Research on animal models has shown that Melanotan II can suppress hunger and reduce body weight; however, further studies are required to determine its safety and efficacy in people.
The potential benefits of Melanotan II in the treatment of obesity, sexual health, and dermatology are still fascinating areas of investigation. However, deciding on its potential uses in medicine in the future will depend heavily on obtaining regulatory approval and conducting additional clinical trials.
Conclusion
Melanotan II offers a rare combination of medicinal and cosmetic potential, mainly because of its capacity to improve skin pigmentation and impact physiological functions like hunger control and sexual function. Originally created to increase melanin production and provide protection from UV rays, it has subsequently become well-known for its advantages in cosmetic tanning. On the other hand, its unchecked use—especially on the internet—raises serious questions regarding purity, safety, and possible negative consequences like nausea, elevated blood pressure, and mole pigmentation changes.
Research into Melanotan II’s wider applications indicates promise in areas like treating erectile dysfunction, preventing skin cancer, and controlling obesity through appetite suppression. However, the drug’s beauty appeal is still growing. These medicinal applications demonstrate its potential to further research in the fields of metabolism, sexual health, and dermatology. Due to legal and regulatory issues, the peptide’s use is still restricted, and more clinical trials and long-term safety studies are required.
In order to guarantee safe and efficient usage, Melanotan II must be used in accordance with scientific research and approved by regulatory bodies as it is investigated further. Before deciding to use it, people should consult a doctor, especially considering the dangers of using unlicensed products. Melanotan II might have a role in medicine in the future, but only under strict regulation and when further research is done on its potential benefits.
References
- Peters B, Hadimeri H, Wahlberg R, Afghahi H. Melanotan II: a possible cause of renal infarction: review of the literature and case report. CEN Case Rep. 2020 May;9(2):159-161. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00447-z. Epub 2020 Jan 18. PMID: 31953620; PMCID: PMC7148395.
- Dreyer BA, Amer T, Fraser M. Melanotan-induced priapism: a hard-earned tan. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Feb 21;12(2):e227644. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227644. PMID: 30796078; PMCID: PMC6388891.
- Habbema L, Halk AB, Neumann M, Bergman W. Risks of unregulated use of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogues: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;56(10):975-980. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13585. Epub 2017 Mar 7. PMID: 28266027.
- Burian EA, Jemec GBE. Eruptive Melanocytic Nevi: A Review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 Oct;20(5):669-682. doi: 10.1007/s40257-019-00444-8. PMID: 31119650.
- Janvier S, De Spiegeleer B, Vanhee C, Deconinck E. Falsification of biotechnology drugs: current dangers and/or future disasters? J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Nov 30;161:175-191. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.08.037. Epub 2018 Aug 20. PMID: 30165334.