Nintedanib: A Multifaceted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
Abstract
Nintedanib is a potent oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor, extensively used in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and various cancers. By targeting key proangiogenic and profibrotic pathways mediated by VEGFR, FGFR, and PDGFR, Nintedanib effectively disrupts disease progression at the molecular level. Clinical trials have demonstrated Nintedanib’s efficacy in significantly reducing the rate of decline in lung function for IPF patients and improving survival rates in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumors. Phase III studies, such as the INPULSIS and LUME-Lung trials, highlight its therapeutic potential and safety profile. In summary, Nintedanib represents a significant advancement in the treatment of IPF and cancer. We invite researchers and pharmaceutical companies to explore our offerings and collaborate with us for their research needs. For more information and to place orders, please contact us.
Introduction
Nintedanib, a potent oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has emerged as a pivotal drug in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and various types of cancer. Originally developed for its antiangiogenic properties, Nintedanib targets multiple pathways involved in the proliferation and migration of cells. Specifically, it inhibits the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR), and platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR). These pathways are critical in the processes of angiogenesis and fibrosis, making Nintedanib a versatile therapeutic agent.
The primary application of Nintedanib is in the management of IPF, a chronic and progressive fibrotic lung disease characterized by an excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components such as collagen. This pathological buildup leads to the stiffening of lung tissue, severely impairing respiratory function. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Nintedanib effectively slows the rate of decline in lung function, offering a significant therapeutic benefit to patients suffering from this debilitating condition. By targeting the key receptors involved in fibrotic processes, Nintedanib reduces fibroblast proliferation, migration, and differentiation, thereby mitigating the progression of fibrosis.
Beyond its use in IPF, Nintedanib has shown efficacy in the treatment of various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), ovarian cancer, and colorectal cancer. In the oncology setting, Nintedanib’s ability to inhibit angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors—helps to starve cancer cells of the nutrients and oxygen they require for growth and metastasis. Phase III clinical trials, such as the LUME-Lung 1 and 2 studies, have underscored the drug’s potential to improve progression-free survival and overall survival rates in patients with advanced NSCLC.
In conclusion, Nintedanib’s dual role in targeting both fibrotic and angiogenic pathways makes it a crucial drug in the arsenal against IPF and cancer. Its broad mechanism of action and proven clinical benefits highlight its significance in modern therapeutic strategies, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients afflicted with these challenging conditions.
Mechanism of Action
Nintedanib is a small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor that plays a crucial role in disrupting multiple signaling pathways integral to angiogenesis and fibrosis. It achieves this by targeting three key receptor families: the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR), and platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR). These pathways are fundamental to the proliferation and migration of cells in both cancer and fibrotic diseases, making Nintedanib’s broad inhibitory action particularly valuable.
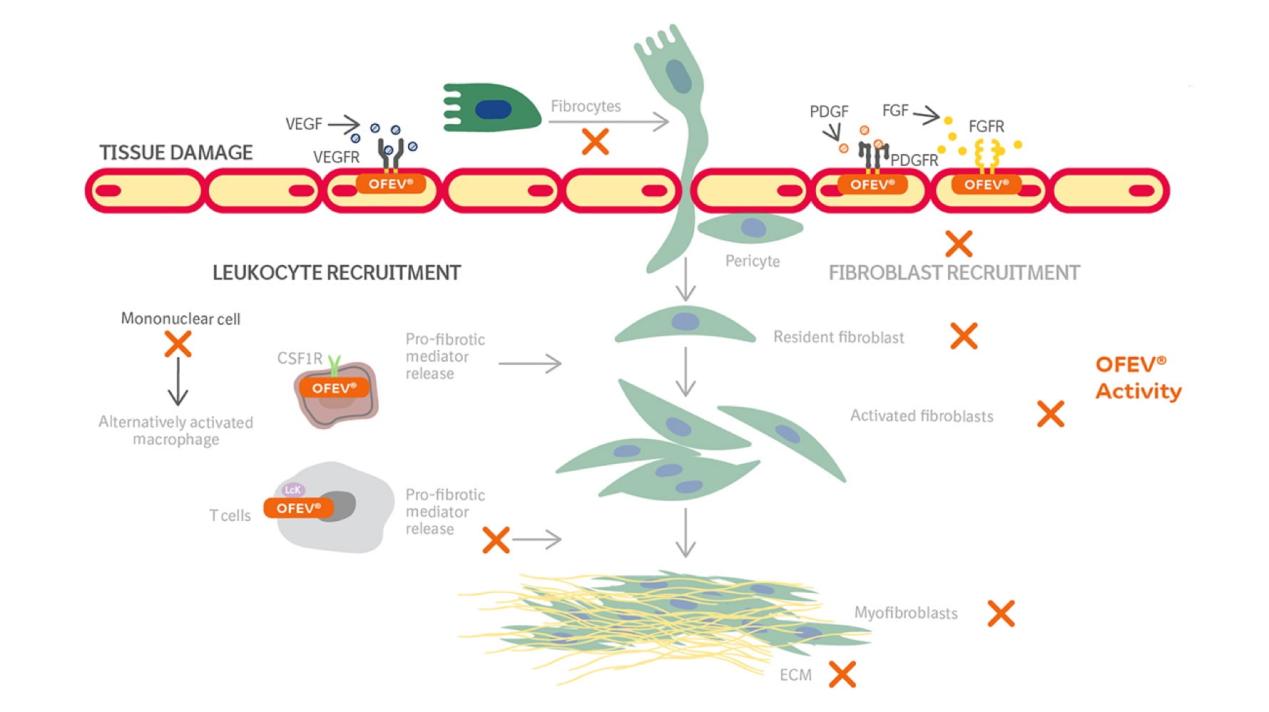
VEGFRs are primarily involved in angiogenesis, the process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing ones. This process is essential for tumor growth and metastasis, as tumors require a blood supply to obtain nutrients and oxygen. By inhibiting VEGFRs, Nintedanib effectively starves the tumor cells, preventing their growth and spread. Additionally, VEGFR inhibition also plays a role in reducing vascular permeability and inflammation, further hindering the tumor’s ability to sustain itself.
FGFRs are another critical target of Nintedanib. These receptors are implicated in cell growth, survival, migration, and differentiation. FGFR signaling is often upregulated in various cancers and fibrotic diseases, contributing to the pathological proliferation and migration of fibroblasts. By blocking FGFRs, Nintedanib hampers these processes, thereby limiting the progression of fibrosis and the growth of cancer cells.
PDGFRs are involved in the recruitment and proliferation of cells that form the structural framework of tissues, including pericytes and smooth muscle cells. In the context of cancer, PDGFRs support the formation of the tumor stroma, a critical component of the tumor microenvironment that facilitates tumor growth and metastasis. In fibrotic diseases, PDGFR signaling promotes the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, which produce excessive extracellular matrix components such as collagen. By inhibiting PDGFRs, Nintedanib disrupts these pathological processes, mitigating fibrosis and stroma formation.
Overall, Nintedanib’s ability to concurrently inhibit VEGFR, FGFR, and PDGFR pathways makes it a potent therapeutic agent against diseases characterized by aberrant angiogenesis and fibrosis. This multifaceted mechanism of action underpins its efficacy in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and various cancers, offering a significant therapeutic advantage in these challenging conditions.
Clinical Applications and Efficacy
Nintedanib has been extensively studied for its efficacy in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and various cancers, with numerous clinical trials highlighting its therapeutic benefits. Its dual role in inhibiting key pathways involved in fibrosis and angiogenesis underpins its broad clinical applications.
In the context of IPF, Nintedanib has shown significant efficacy in slowing disease progression. The pivotal INPULSIS-1 and INPULSIS-2 phase III trials evaluated the impact of Nintedanib on lung function decline in IPF patients. These studies demonstrated that Nintedanib significantly reduced the annual rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC), a critical measure of lung function, by approximately 50% compared to placebo. This reduction in FVC decline translates to a slower progression of IPF, offering patients improved quality of life and prolonged survival. Moreover, the trials reported a manageable safety profile, with the most common adverse events being gastrointestinal in nature, such as diarrhea, which were generally mild to moderate and manageable with dose adjustments.
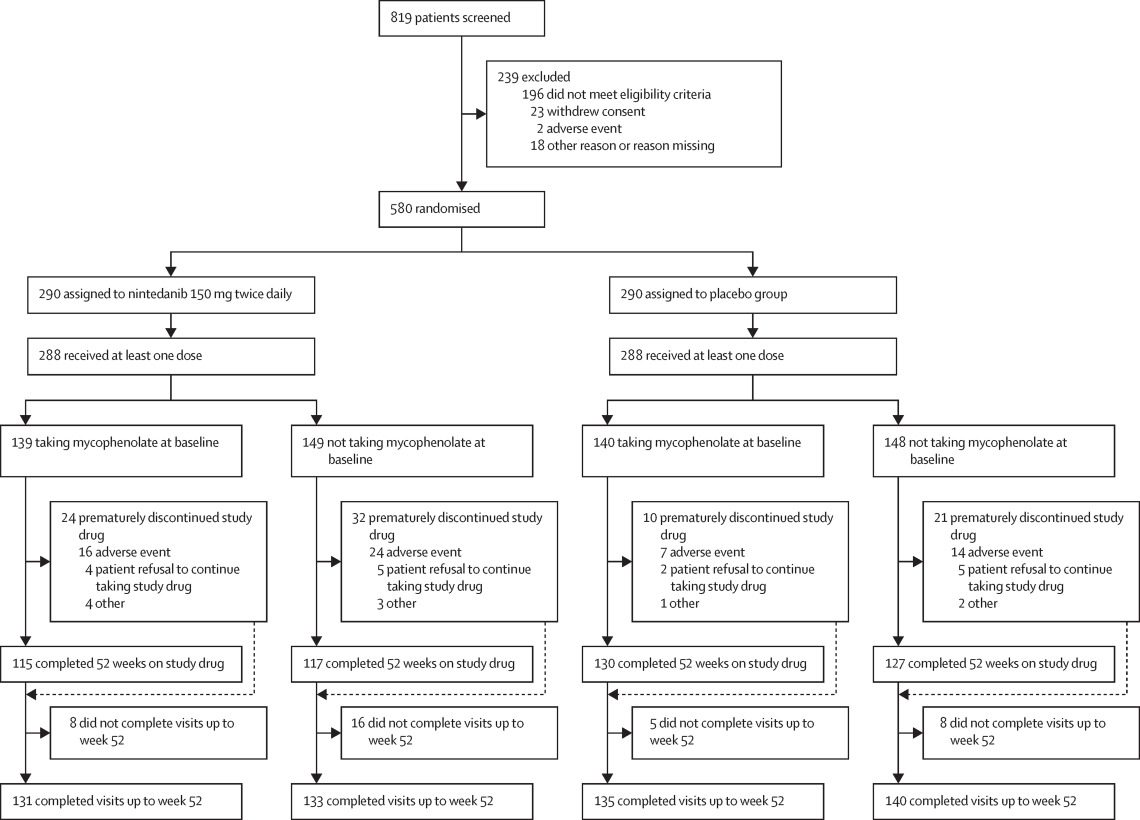
In oncology, Nintedanib has been investigated primarily for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), among other cancers. The LUME-Lung 1 phase III trial assessed the combination of Nintedanib with docetaxel in patients with advanced NSCLC who had progressed after first-line chemotherapy. The results indicated that Nintedanib, when combined with docetaxel, significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared to docetaxel alone. Patients with adenocarcinoma histology, in particular, showed a notable improvement in overall survival (OS) with Nintedanib treatment, underscoring its potential benefit in this subgroup. The LUME-Lung 2 study further supported these findings by demonstrating an improvement in PFS with the combination of Nintedanib and pemetrexed in advanced NSCLC patients.
Beyond NSCLC, Nintedanib has shown promise in other solid tumors, including ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer, where it has been studied in combination with standard chemotherapies. These studies collectively highlight Nintedanib’s ability to enhance the efficacy of existing cancer treatments, making it a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal.
In summary, Nintedanib’s clinical applications extend across fibrotic lung diseases and various cancers, with robust evidence supporting its efficacy in reducing disease progression and improving survival rates. Its ability to target multiple pathways involved in fibrosis and angiogenesis makes it a versatile and potent therapeutic agent in these challenging conditions.
Product and Related Compounds
Our company is proud to offer high-purity Nintedanib for advanced pharmaceutical research and clinical applications. Nintedanib, a potent tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is essential for studies targeting idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and various cancers. In addition to Nintedanib, we provide a comprehensive range of related chemicals, including impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks, supporting diverse research needs.
Our impurities and metabolites catalog enables precise analysis and characterization, crucial for understanding drug metabolism and safety. The isotope-labeled compounds facilitate detailed pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies, allowing for accurate tracing and quantification in biological systems. Building blocks offer researchers the tools to synthesize novel analogs and derivatives, advancing drug discovery and development.
We ensure that all our products meet the highest standards of purity and consistency, supporting reliable and reproducible results in scientific investigations. Our dedicated team is committed to providing exceptional customer service, technical support, and custom synthesis solutions tailored to your specific research requirements.
Conclusion
Nintedanib represents a significant advancement in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and various cancers, owing to its unique mechanism of action that targets key pathways involved in fibrosis and angiogenesis. The extensive clinical trials, such as INPULSIS and LUME-Lung, have demonstrated Nintedanib’s efficacy in slowing disease progression and improving survival rates. These findings underscore its importance as a therapeutic agent that offers hope and improved outcomes for patients with these challenging conditions.
In IPF, Nintedanib has shown a remarkable ability to reduce the rate of decline in lung function, translating to prolonged survival and enhanced quality of life for patients. By inhibiting the VEGFR, FGFR, and PDGFR pathways, Nintedanib effectively interrupts the pathological processes underlying fibrosis, making it a cornerstone in the management of this debilitating disease.
In oncology, Nintedanib’s role extends beyond lung cancer to include ovarian and colorectal cancers, among others. Its ability to enhance the efficacy of standard chemotherapy regimens by targeting angiogenesis and disrupting tumor growth and metastasis has been well-documented. The improvement in progression-free and overall survival rates in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) highlights its potential as a valuable addition to existing cancer therapies.
Our company is committed to supporting the research and clinical use of Nintedanib and related compounds. We offer a comprehensive range of high-purity products, including impurities, metabolites, isotope-labeled compounds, and building blocks, all essential for advanced pharmaceutical research. Our products are meticulously designed to meet the highest standards of purity and consistency, ensuring reliable and reproducible results.
We invite researchers and pharmaceutical companies to explore our extensive portfolio of Nintedanib and related compounds. Our dedicated team provides exceptional customer service, technical support, and custom synthesis solutions tailored to your specific needs. Partner with us to drive innovation and achieve groundbreaking discoveries in the fields of fibrosis and oncology.
For more information and to place orders, please contact us today. Together, we can advance the frontiers of medical science and improve patient outcomes through cutting-edge research and therapeutic development.