PF-04447943: A Potential Game-Changer in Cognitive and Neurological Research
Abstract
PF-04447943 is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9), a key enzyme involved in regulating cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels in the brain. By inhibiting PDE9, PF-04447943 enhances cGMP signaling, which is crucial for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. This mechanism positions the compound as a promising therapeutic for cognitive and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and other forms of cognitive decline. Early preclinical and clinical studies have shown potential improvements in memory and learning in animal models, but further research is needed to evaluate its long-term safety and efficacy in human populations. Despite challenges in translating preclinical findings to human applications, PF-04447943 represents a novel approach to treating neurological diseases by targeting the molecular pathways underlying cognitive dysfunction. Its specificity and targeted action make it a promising candidate for future clinical use in addressing cognitive impairment and neurological disorders.
Introduction
PF-04447943 is a groundbreaking pharmacological compound that has garnered significant attention in the field of neuroscience and drug development. Developed by Pfizer, this compound is classified as a selective phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibitor. By targeting the PDE9 enzyme, PF-04447943 enhances the levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a signaling molecule that plays a critical role in brain function. The regulation of cGMP has implications for memory, learning, and overall cognitive performance, making PF-04447943 a promising candidate for treating neurological disorders.
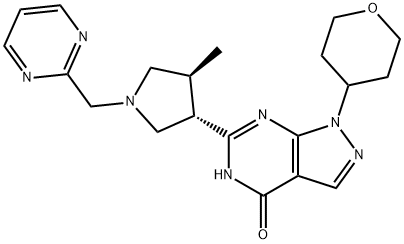
Fig.1 Structure of PF-04447943
Neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and other cognitive impairments are characterized by disrupted signaling pathways in the brain. PDE9 inhibitors like PF-04447943 aim to restore these pathways, potentially mitigating cognitive decline. Preclinical studies have demonstrated its potential to improve synaptic plasticity, which is essential for learning and memory. These findings have spurred early-phase clinical trials to evaluate its safety and efficacy in humans.
What makes PF-04447943 particularly exciting is its potential to fill a gap in current therapeutic approaches. Unlike traditional treatments that focus on symptom management, PDE9 inhibitors target underlying molecular mechanisms. Although the journey from lab studies to clinical application is fraught with challenges, PF-04447943 has emerged as a beacon of hope in tackling some of the most debilitating cognitive and neurological disorders.
This blog delves deeper into the mechanism, applications, and ongoing research surrounding PF-04447943. By understanding its potential, we can appreciate how science is advancing toward more effective solutions for complex brain disorders.
What is PF-04447943?
PF-04447943 is a selective inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9), developed by Pfizer as a potential treatment for cognitive and neurological disorders. PDE9 plays a critical role in the regulation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a signaling molecule involved in numerous physiological processes, particularly within the central nervous system. By inhibiting PDE9, PF-04447943 increases the levels of cGMP in the brain, which can improve synaptic plasticity and memory functions.
The compound’s selective action on PDE9 differentiates it from other drugs targeting broader phosphodiesterase families. This specificity minimizes off-target effects and enhances its potential as a therapeutic option for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia. These disorders are associated with disruptions in signaling pathways that rely on cGMP, underscoring the importance of this molecule in maintaining cognitive health.
Preclinical studies of PF-04447943 have shown promising results, including improved learning and memory performance in animal models. Additionally, early clinical trials have explored its safety and pharmacokinetics in humans, providing insights into its potential therapeutic applications. Despite the encouraging findings, further research is required to fully understand its efficacy and long-term safety profile in diverse patient populations.
PF-04447943 represents a novel approach in drug development by targeting molecular pathways that underpin neurological disorders. Its precision and mechanism of action offer hope for developing treatments that go beyond symptom management, addressing the root causes of cognitive decline.
How Does PF-04447943 Work?
PF-04447943 functions by selectively inhibiting the activity of phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9), an enzyme responsible for breaking down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in cells. cGMP is a key second messenger in cellular signaling, playing an essential role in processes such as synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and vascular function. By blocking PDE9, PF-04447943 prevents the degradation of cGMP, resulting in elevated cGMP levels in the brain.
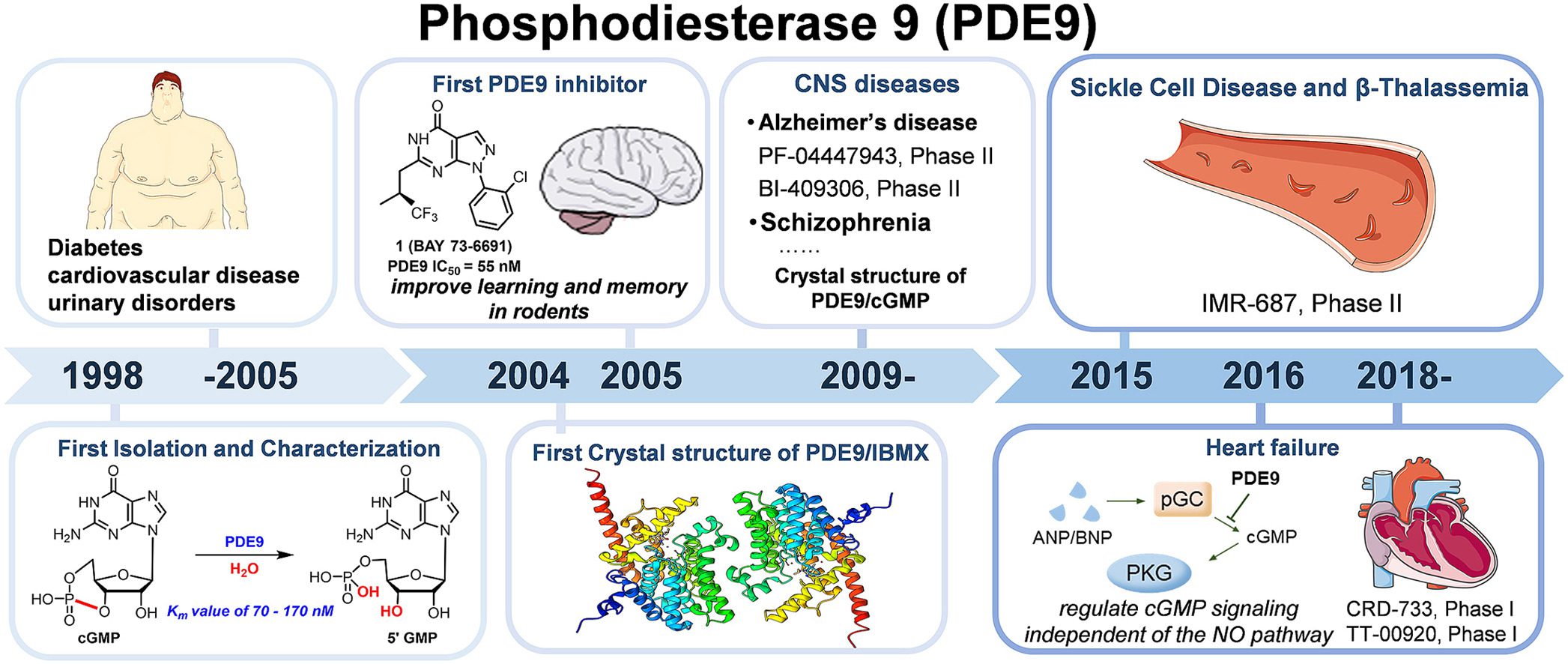
Fig.2 Development of phosphodiesterase 9
The enhanced cGMP signaling boosts the efficiency of synaptic connections, improving communication between neurons. This mechanism is particularly relevant in the hippocampus, a brain region critical for learning and memory. In neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia, disruptions in cGMP pathways are believed to contribute to cognitive impairments. By restoring these pathways, PF-04447943 offers a potential therapeutic avenue to mitigate cognitive decline.
Moreover, the compound’s high selectivity for PDE9 minimizes off-target effects compared to less specific phosphodiesterase inhibitors, potentially leading to fewer side effects. This targeted approach highlights its promise as a safe and effective intervention for treating cognitive deficits in various neurological disorders.
Potential Applications of PF-04447943
PF-04447943 shows promise across several therapeutic areas, particularly in treating neurological and cognitive disorders. Its ability to enhance cGMP levels makes it a candidate for addressing deficits in brain function associated with conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and other forms of dementia.
In Alzheimer’s disease, the compound could help counteract the loss of synaptic connections that leads to memory decline. By improving synaptic plasticity, PF-04447943 aims to restore cognitive function. Similarly, in schizophrenia, where cognitive impairment is a core symptom, the drug has the potential to enhance information processing and memory.
Beyond treating established disorders, PF-04447943 could also be explored for cognitive enhancement in healthy aging populations. Cognitive decline is a natural part of aging, and the drug’s mechanism of action suggests it could mitigate age-related changes in memory and learning.
Preclinical studies have demonstrated improved performance in learning and memory tasks among animal models treated with PF-04447943. Early clinical trials have further supported its potential by showing favorable pharmacokinetics and safety profiles. While additional studies are required, the compound holds promise as a breakthrough in cognitive and neurological therapeutics.
Safety and Side Effects
The safety profile of PF-04447943 has been investigated in both preclinical and early-phase clinical trials. As a selective PDE9 inhibitor, the compound is designed to minimize off-target effects and focus its action on enhancing cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling in the brain. However, like all pharmacological interventions, PF-04447943 is not without potential side effects.
In preclinical studies, PF-04447943 demonstrated a good safety profile, with minimal adverse effects at therapeutic doses. However, some potential side effects were observed, including gastrointestinal discomfort and mild behavioral changes at higher doses. Early clinical trials involving human participants confirmed tolerability in small cohorts, although larger studies are needed to fully assess its safety across diverse populations.
One of the key concerns is the potential for off-target effects on other phosphodiesterase enzymes, which could lead to unintended physiological consequences. While PF-04447943’s selectivity minimizes these risks, long-term studies are necessary to evaluate chronic use, particularly in conditions requiring prolonged treatment such as Alzheimer’s disease or schizophrenia. Understanding its impact on cardiovascular function, as cGMP also plays a role in the vascular system, remains an important area for research.
Despite these uncertainties, PF-04447943 represents a significant step forward in targeted cognitive therapeutics, with its safety profile aligning well with its potential applications.
Challenges and Future Directions
While PF-04447943 offers promising prospects in cognitive and neurological research, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize its therapeutic potential. One of the primary hurdles is translating the success observed in preclinical animal studies to human clinical trials. Cognitive and neurological disorders in humans involve complex pathophysiological mechanisms that may not be fully replicated in animal models.
Another significant challenge lies in understanding the long-term safety and efficacy of PF-04447943. Neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia often require prolonged treatment, raising concerns about the cumulative effects of PDE9 inhibition. Comprehensive studies exploring the drug’s impact over extended periods are critical for regulatory approval and clinical adoption.
Moreover, identifying the specific patient populations that would benefit most from PF-04447943 is a key focus for future research. Biomarker-based approaches could help determine which individuals are likely to respond positively to PDE9 inhibition, optimizing the drug’s therapeutic potential.
The future of PF-04447943 research hinges on large-scale clinical trials to confirm its efficacy and safety in treating conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and age-related cognitive decline. Additionally, exploring its potential for use in combination therapies could open new doors for enhancing its clinical utility.
Conclusion
PF-04447943 represents a promising new frontier in the treatment of cognitive and neurological disorders. As a selective PDE9 inhibitor, it offers a novel approach to enhancing brain function by increasing levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a molecule critical for synaptic plasticity and cognitive processes like learning and memory. Its mechanism of action positions it as a potential therapeutic for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and other forms of cognitive decline, where traditional treatments often fail to address underlying molecular disruptions.
Early preclinical and clinical studies have shown encouraging results, particularly in improving memory and learning performance in animal models. Though promising, the compound’s full therapeutic potential still requires thorough investigation in larger clinical trials to confirm its safety and efficacy over the long term. Challenges remain, particularly in translating animal study success to human applications and understanding the long-term impact of PDE9 inhibition.
Despite these challenges, PF-04447943’s targeted mechanism offers a unique opportunity to address the root causes of cognitive dysfunction, providing a more effective approach to treating debilitating neurological diseases. As research continues, PF-04447943 holds great promise in shaping the future of cognitive therapeutics and improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from neurological disorders.
References
Xu, P., Opmeer, E. M., van Tol, M. J., Goerlich, K. S., & Aleman, A. (2018). Structure of the alexithymic brain: A parametric coordinate-based meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 87, 50-55.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149763417305298
Wang, J. F., He, W. J., Zhang, X. X., Zhao, B. Q., Liu, Y. H., & Zhou, X. J. (2015). Dicarabrol, a new dimeric sesquiterpene from Carpesium abrotanoides L. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 25(19), 4082-4084.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0960894X15008690
Zhang C, Xue ZH, Luo WH, Jiang MY, Wu Y. The therapeutic potential of phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) inhibitors: a patent review (2018-present). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024 Sep;34(9):759-772. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2024.2376632. Epub 2024 Jul 9. PMID: 38979973.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13543776.2024.2376632
Ribaudo G, Memo M, Gianoncelli A. A Perspective on Natural and Nature-Inspired Small Molecules Targeting Phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9): Chances and Challenges against Neurodegeneration. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jan 13;14(1):58. doi: 10.3390/ph14010058. PMID: 33451065; PMCID: PMC7828511.
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/14/1/58
Heckman PR, Wouters C, Prickaerts J. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors as a target for cognition enhancement in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: a translational overview. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(3):317-31. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140826114601. PMID: 25159073.
https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/cpd/2015/00000021/00000003/art00005