Recent Research and Emerging Applications of Fenofibrate
Abstract
With demonstrated advantages in lowering cardiovascular risk, fenofibrate is a lipid-lowering medication that is frequently used to treat hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Fenofibrate offers a complete approach to cholesterol management by promoting triglyceride breakdown, lowering VLDL, and raising HDL levels through the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α). Recent studies have demonstrated that fenofibrate has potential anti-inflammatory qualities, a prospective function in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and an influence on insulin sensitivity, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes, in addition to its lipid-modifying effects. Fenofibrate is positioned as a flexible therapeutic agent in the management of cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory health as further research examines its possible neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Introduction to Fenofibrate and Its Uses
A common lipid-modifying medication, fenofibrate is crucial for treating dyslipidemia, particularly in patients with high triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Fenofibrate is a useful choice in the therapeutic and preventive approaches meant to lower cardiovascular risk. It has been approved by health authorities for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. It is usually administered in conjunction with dietary changes and exercise to optimize its effectiveness, and it primarily helps people who have not reached optimal lipid levels with lifestyle changes alone.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a receptor essential to lipid metabolism, is activated by fenofibrate. As a result of this activation, fenofibrate increases the breakdown of lipids, especially triglycerides, which lowers very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) levels while increasing HDL levels. The risk of atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular disorders may be decreased in large part by this change in the lipid profile.
Patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, where cholesterol control is crucial for cardiovascular health, benefit most from fenofibrate’s therapeutic effects. Additionally, it is used for its modest anti-inflammatory properties, which help treat several chronic metabolic diseases. All things considered, fenofibrate is a key medication for controlling cholesterol, providing a substitute mechanism for statins and being crucial in the prevention of contemporary cardiovascular disease.
Mechanism of Action: How Fenofibrate Works
The stimulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a nuclear receptor that controls genes involved in lipid metabolism, is the main mechanism by which fenofibrate modifies lipid levels. When fenofibrate binds to PPAR-α, it sets off a series of molecular processes that improve lipid profiles by increasing lipid breakdown and decreasing lipid synthesis. This process raises high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol while lowering triglyceride and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) levels. One important factor in reducing cardiovascular risk is the combination of increased HDL and decreased VLDL.
Fenofibrate lowers plasma triglyceride levels by promoting the breakdown of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins through increased lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity. Furthermore, by decreasing the synthesis of apolipoprotein C-III, a protein that inhibits the action of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), fenofibrate enhances the removal of LDL from the bloodstream. Small, dense LDL particles, which are thought to be extremely atherogenic and aid in the development of plaque in arteries, are reduced as a result.
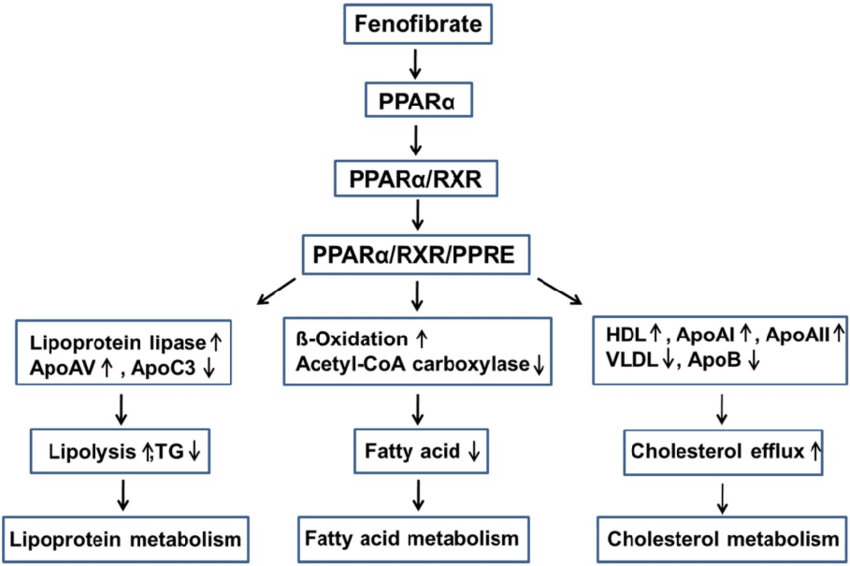
Fig.1 Lowering lipid mechanisms of fenofibrate
The anti-inflammatory qualities of fenofibrate, which aid in lowering vascular inflammation, a contributing factor to atherosclerosis, are one distinctive aspect of its process. Studies indicate that fenofibrate may also improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic management, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It differs from other lipid-lowering medications, such as statins, which mainly work by preventing the manufacture of cholesterol, in that it has a wider impact on metabolic health.
Fenofibrate provides a comprehensive approach to lipid regulation by specifically activating PPAR-α, which makes it a crucial component of treatment plans meant to control dyslipidemia and lower the risk of cardiovascular disorders in general.
Therapeutic Benefits and Key Advantages
Because of its many therapeutic advantages, fenofibrate is an essential part of treating lipid disorders, particularly in patients who have high triglyceride levels or are at risk of cardiovascular disease. Fenofibrate is essential in lowering very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and small, dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, which are linked to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk, by efficiently lowering triglycerides. Research shows that lowering VLDL and triglycerides can dramatically reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events, especially in individuals with diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Fenofibrate’s beneficial impact on high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels is one of its main benefits. Fenofibrate promotes cardiovascular health by increasing HDL cholesterol, which is known as “good cholesterol” because it helps move cholesterol from the arteries back to the liver for excretion. For patients in need of thorough cholesterol control, elevated HDL levels are extremely advantageous because they are associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease.
The therapeutic profile of fenofibrate is further enhanced by its possible anti-inflammatory properties. According to certain research, fenofibrate may aid in lowering inflammatory indicators, which would further protect the heart. Patients with long-term inflammatory diseases like metabolic syndrome may potentially benefit from this anti-inflammatory action.
Beyond lipid management, fenofibrate may also help patients with type 2 diabetes with their insulin sensitivity and glycemic control. Because it targets several risk factors linked to metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease, fenofibrate is particularly beneficial for diabetic people. Fenofibrate is a crucial option for treating complicated lipid and metabolic disorders because of its all-encompassing, multimodal action profile.
Recent Research and Advances in Fenofibrate Use
Research on fenofibrate is still ongoing because of its special ability to decrease cholesterol and possible advantages over conventional treatments for dyslipidemia. It has shown promise in treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), both of which are becoming more common as obesity rates rise, according to recent studies. According to research, fenofibrate may help prevent hepatic fat buildup and decrease the course of NAFLD and NASH patients’ diseases by lowering triglycerides and improving lipid profiles.
Recent research suggests that fenofibrate may enhance insulin sensitivity and glycemic management in addition to its effects on lipid metabolism, especially in people with type 2 diabetes. Because fenofibrate tackles several interrelated health problems, such as dyslipidemia and excessive blood sugar, it is a useful treatment for people with metabolic syndrome. Fenofibrate’s cardioprotective ability has been demonstrated by clinical trials, such as the FIELD (Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes) research, which found that diabetic individuals treated with the medication experienced fewer cardiovascular events.
There has also been interest in fenofibrate’s possible use in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Researchers are investigating how it affects vascular inflammation, a major contributing factor to atherosclerosis, as its anti-inflammatory properties may broaden its therapeutic uses beyond lipid management. Further research is required, although some studies have also looked at the drug’s neuroprotective qualities, which may be helpful for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease.
According to recent studies, fenofibrate is a flexible substance with potential uses outside of traditional cholesterol treatment. Fenofibrate may play a wider role in the treatment of inflammatory and metabolic disorders as further research investigates these novel pathways, underscoring its possible influence on overall metabolic and cardiovascular health.
References
- Keech, A., Simes, R. J., Barter, P., Best, J., Scott, R., Taskinen, M. R., … & FIELD study investigators. (2005). Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet, 366(9500), 1849-1861. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67667-2
- Nissen, S. E., & Wolski, K. (2007). Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. New England Journal of Medicine, 356(24), 2457-2471. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa072761
- Rader, D. J. (2006). Molecular regulation of HDL metabolism and function: Implications for novel therapies. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 116(12), 3090-3100. doi:10.1172/JCI30163
- Staels, B., & Fruchart, J. C. (2005). Therapeutic roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists. Diabetes Care, 28(8), 1886-1895. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.8.1886