Ringing in Revolution: How Cyclic Peptides Are Shaping the Future of Drug Development
Abstract
In the quest for novel and more effective drugs, cyclic peptides have emerged as a beacon of hope within the pharmaceutical landscape. These ring-shaped molecules, crafted through a seamless covalent bond at the ends of peptide chains, are gaining fame not just for their unique structure but for their robust ability to confront and conquer complex diseases.
The Fascination with Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides are not newcomers in the natural world. They are a diverse group of structures naturally synthesized by various organisms, including plants, bacteria, and animals. These molecules play a pivotal role in defense mechanisms, offering protection against predators and diseases. Historically, their medicinal properties have not gone unnoticed, making appearances in the healing traditions of numerous cultures around the globe.
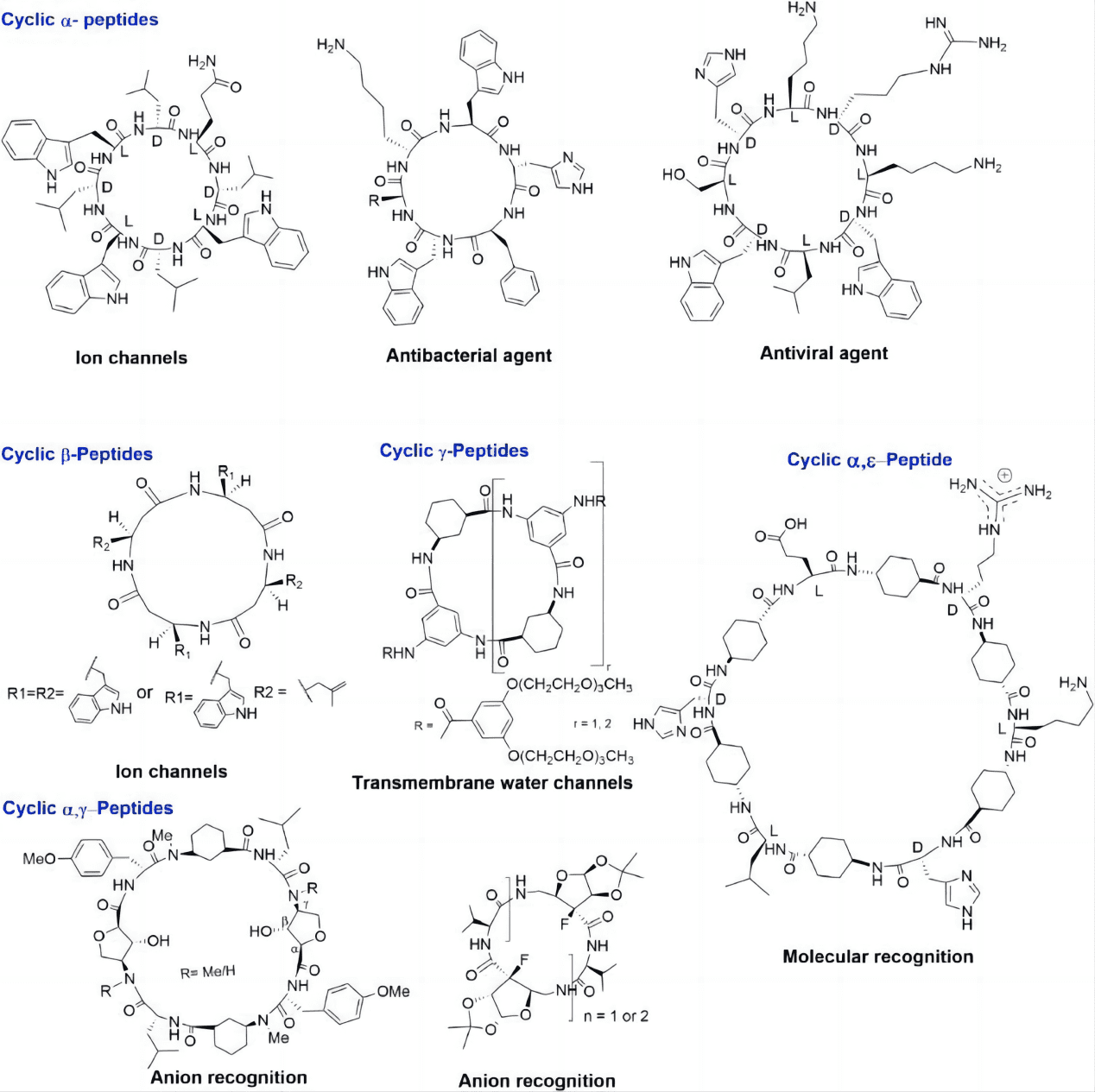
What Sets Cyclic Peptides Apart?
The magic of cyclic peptides lies in their circular configuration. This ring structure lends an extraordinary stability and makes them tougher against enzymatic breakdown, a common fate for their linear relatives. It’s not just about longevity; the shape of cyclic peptides allows for more selective and potent interactions with biological targets. This specificity makes them particularly effective in therapeutic settings, where precision is paramount.
Beyond Structure: The Advantages Over Linear Peptides
When compared to linear peptides, the advantages of cyclic peptides are clear. Their inherent stability in the body means they can function longer without degradation, maximizing their therapeutic impact. Moreover, their ability to snugly fit and interact with disease-related proteins allows for targeted treatment approaches, reducing unwanted side effects typically caused by less specific interactions.
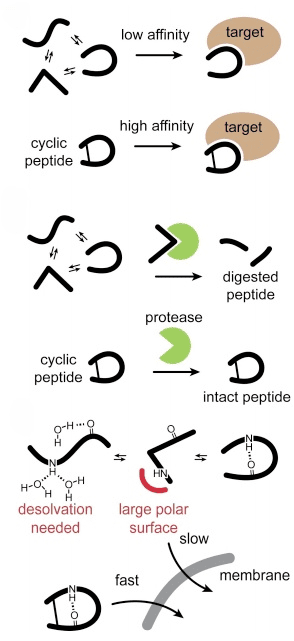
The Scientific Evolution: Broadening Our Understanding
The leap in our comprehension of cyclic peptides has been substantial, thanks to the relentless pace of scientific research. We now understand not only their structural benefits but also their versatile role in mimicking or blocking essential biological molecules. This ability positions them as formidable candidates for tackling diseases that have eluded other therapeutic strategies, including small molecule drugs and biologics.
The ongoing fascination with cyclic peptides is fueled by significant advancements in the fields of peptide synthesis and drug delivery. These technological leaps have transformed cyclic peptides from a scientific curiosity into powerful tools in the arsenal of modern medicine, bridging the gap between natural compounds and pharmaceutical innovation.
Revolutionizing Peptide Synthesis
The journey from basic chemical methods to sophisticated, controlled peptide synthesis has been revolutionary. Techniques like solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) have streamlined the way cyclic peptides are assembled, making the process more efficient and scalable. The capability to incorporate non-natural amino acids has further expanded the drug developer’s toolkit, enabling the introduction of properties that enhance drug stability, efficacy, and safety.
Accelerating Drug Discovery Through High-Throughput Screening
The development of high-throughput screening (HTS) technologies has accelerated the identification and optimization of cyclic peptides. Techniques such as phage display and mRNA display allow for the rapid screening of millions of peptide variants, efficiently identifying those with optimal characteristics for drug development. This not only speeds up the discovery process but also reduces the costs associated with the development of new therapeutic agents.
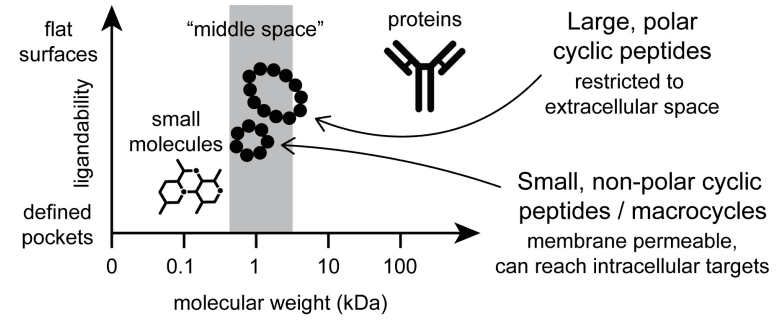
Broad Applications: From Extracellular to Intracellular Targets
One of the most compelling attributes of cyclic peptides is their ability to engage with both extracellular and intracellular protein targets. This dual capability is crucial for the development of drugs aimed at a wide range of diseases, from external infections to internal cellular dysfunctions like cancer and genetic disorders. Recent innovations have even enabled cyclic peptides to cross cellular membranes, reaching previously inaccessible intracellular targets and expanding their therapeutic potential.
Navigating Clinical Development Challenges
Despite their promise, cyclic peptides face several challenges in clinical development. Issues such as poor oral bioavailability and rapid clearance from the body can limit their practical use. To address these hurdles, researchers are turning to advanced delivery mechanisms like nanoparticle encapsulation, which protects the peptides from premature degradation and enhances their delivery to the targeted sites within the body.
Developing orally available cyclic peptides remains a formidable challenge, spurring ongoing research aimed at enhancing their stability and absorption in the digestive system.
Future Prospects: The Road Ahead
The future of cyclic peptides in drug development is vibrant and full of potential, driven by continuous innovations in synthesis, screening, and design technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to further revolutionize the field, enhancing the speed and accuracy of cyclic peptide design and optimization.
As our understanding of disease mechanisms deepens, cyclic peptides are poised to play an increasingly significant role in the development of next-generation therapeutics. Their unique properties, combined with advancements in science and technology, hold the promise of transforming treatment approaches across various diseases, heralding a new era of precision medicine.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in Drug Development
Cyclic peptides represent a dynamic and promising class of bioactive compounds, poised to redefine the boundaries of pharmaceutical science. With their unique ring-shaped structures, these molecules offer a robust platform for addressing complex therapeutic challenges. Their stability, specificity, and broad applicability make them ideal candidates for the development of targeted, effective, and personalized treatments.
The advances in synthetic techniques, coupled with breakthroughs in high-throughput screening, have propelled cyclic peptides to the forefront of biomedical research. As the field continues to evolve, cyclic peptides are expected to transform the landscape of drug development, offering new hope for the treatment of diseases that have long challenged the medical community.
In embracing the full potential of cyclic peptides, the scientific community is not just advancing drug development; it is taking a significant step toward a future where medicine is safer, more effective, and remarkably tailored to the needs of individual patients. This is not just a scientific achievement; it is a milestone in our ongoing quest to enhance human health and wellbeing.
Reference
- Ji, X., Nielsen, A. L., & Heinis, C. (2024). Cyclic peptides for drug development. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 63(3), e202308251.
- Martinovich, V. P., & Baradzina, K. U. (2022). Peptide Hormones in Medicine: A 100-Year History. Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 48(2), 221-232.
- Philippe, G. J., Craik, D. J., & Henriques, S. T. (2021). Converting peptides into drugs targeting intracellular protein–protein interactions. Drug Discovery Today, 26(6), 1521-1531.
- Buyanova, M., & Pei, D. (2022). Targeting intracellular protein–protein interactions with macrocyclic peptides. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 43(3), 234-248.