The Pharmacological Wonders of Berberine: A Traditional Medicine Powerhouse
Abstract
Berberine is a yellow-colored bioactive compound extracted from various plant species, such as Berberis vulgaris and Coptis chinensis. Recognized for its wide-ranging pharmacological properties, berberine has garnered significant attention in both traditional and modern medicine. Its primary mechanism of action involves the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which enhances glucose uptake and lipid oxidation, making it particularly effective in managing metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clinical studies demonstrate that berberine significantly lowers blood glucose levels and improves insulin sensitivity while modulating lipid metabolism by decreasing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Beyond metabolic health, berberine exhibits strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, contributing to its efficacy in managing chronic inflammatory conditions. Additionally, its antimicrobial activity against a broad spectrum of pathogens highlights its potential in combating drug-resistant infections. Despite its promising benefits, careful consideration of dosage and potential side effects is essential. Future research is needed to further elucidate berberine’s mechanisms and expand its therapeutic applications, reinforcing its significance as a natural treatment option.
INTRODUCTION
Berberine is a yellow-colored bioactive compound extracted from various plant species, including Berberis vulgaris, Berberis aristata, Xanthorhiza simplicissima, Tinospora cordifolia, Argemone mexicana, Coptis chinensis, and Eschscholzia californica. It belongs to a class of compounds known as alkaloids, which are characterized by basic nitrogen compounds. The molecular formula of berberine is C20H18NO4, with a molecular weight of 336.337 g/mol. Plants containing alkaloids have been used for medicinal, recreational, and toxic purposes for centuries. Berberine is found in various parts of plants, including roots, rhizomes, stems, and bark, with concentrations ranging from 0.04% in young shoots to 1.41% in young arenchymatous roots.
It has a long history of use in traditional Chinese and Indian medicine, where it was used to treat various ailments. Now modern science has confirmed that it has impressive benefits for several different health problems.Alkaloids are normally alkaline and colourless but berberine is acidic in nature and identified by its bright yellow colour. Historically it has been used as a yellow dye in a number of countries. It has many actions in the body including anti-inflammatory, anti-tumour and broad spectrum antimicrobial against bacteria, fungus, viruses and parasites. It is powerful enough to target antibiotic resistance to have long term health benefits and it will reduces the chances of catching the flu or the viral cold due to bacterial infection. Berberine is one of the few compounds known to activate AMPK-Adenosine Monophosphate activated Protein Kinase, it is an enzyme inside the human body plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, AMPK activation boosts fat burning in the mitochondria. It aids in tissue repair, maintaining a healthy heart rhythm and to control lipid and blood sugar regulations, it is normoglycemic due to AMPK activation. It blocks proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9), which plays a key role in metabolism of lipoprotein. Berberine having inhibitory effects on the proliferation and reproduction of certain tumorigenic microorganisms and viruses such as hepatitis B virus and helicobacter pylori. According to some studies berberine works by inhibiting an enzyme called PCSK9.This leads to more LDL being removed from the blood stream. It increases energy expenditure, limits weight gain, improves cold tolerance and enhances brown adipose tissue activity. It was shown to reduce blood pressure by competitively inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cells α1 receptors, thereby blocking the release of the enzyme adenylyl cyclise. It promotes optimal joint health; according to 2017 berberine significantly improved joint health in rats. Berberine improves gastrointestinal and immune health by protecting mucous membrane throughout the body and it is able to fight against severe damage like that induced by heavy alcohol consumption. It also promote high bone mineral density, regular consumption of berberine improved the bone mineral density in male and female mice.
Several studies have also suggested that berberine may support optimal mental health as we age. Regular consumption of berberine can increase brain chemicals such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, which are essential for healthy brain function and maintaining a positive mood. For women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) undergoing in vitro fertilization, berberine has been shown to be more effective than metformin in achieving live births with fewer side effects. Additionally, pre-treatment with berberine significantly reduces cigarette smoke-induced acute lung inflammation due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Pharmacological Properties of Berberine
Berberine is a bioactive compound with a wide range of pharmacological properties that have garnered significant attention in recent years. One of its most important mechanisms of action is the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a critical regulator of cellular energy metabolism, and its activation leads to enhanced glucose uptake and lipid oxidation. This makes berberine particularly effective in the management of metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Research indicates that berberine can significantly lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity. In clinical trials, it has been shown to reduce fasting blood glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c, making it a viable alternative or adjunct to conventional diabetes treatments. Its ability to modulate lipid metabolism is equally impressive; berberine has been found to decrease levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” while simultaneously increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good cholesterol.” This dual action contributes to better cardiovascular health and helps mitigate the risk of atherosclerosis.
In addition to its metabolic benefits, berberine exhibits strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to various health issues, including heart disease and certain cancers. By reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting inflammatory pathways, berberine can help alleviate these conditions. Furthermore, its antioxidant effects help protect cells from oxidative stress, enhancing overall cellular health.
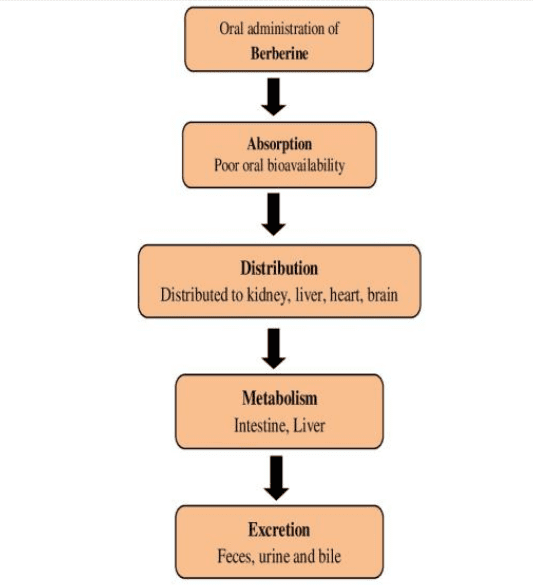
Figure1: Schematic representation of berberine pharmacokinetics
Berberine’s antimicrobial properties also merit attention. It has demonstrated effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Its potential use against drug-resistant strains makes it an appealing candidate for future therapeutic applications, particularly in an era of rising antibiotic resistance.In summary, the pharmacological properties of berberine encompass a wide array of beneficial effects, making it a valuable compound in both traditional and modern medicine.
Berberine in Treating Specific Conditions
Berberine has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for a variety of health conditions, thanks to its multifaceted pharmacological properties. One of the most notable areas of application is in the management of metabolic disorders, particularly type 2 diabetes and obesity. Studies have demonstrated that berberine effectively lowers blood glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and aids in weight loss. For instance, clinical trials show that berberine can reduce hemoglobin A1c levels, a crucial marker for long-term blood glucose control, making it a viable alternative to conventional antidiabetic medications.
In addition to metabolic disorders, berberine has shown potential in managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Research indicates that it can enhance insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS, leading to improved ovulation rates and a reduction in androgen levels. This makes berberine a valuable option for women seeking to regulate their menstrual cycles and enhance fertility.
Berberine’s anti-inflammatory properties also make it beneficial in treating chronic inflammatory conditions. By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, berberine can alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Furthermore, its antioxidant effects help protect cells from oxidative damage, contributing to overall health.
Lastly, berberine has demonstrated efficacy against various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its ability to combat multidrug-resistant strains positions it as a potential natural alternative to synthetic antibiotics. This property is particularly crucial in the face of rising antibiotic resistance, making berberine a candidate for further research in infectious disease management. In summary, berberine’s wide-ranging therapeutic applications underscore its importance in both traditional and modern medicine.
Conclusion
Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, which is present in number of medicinal plants that have been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for hundreds of years. Phytochemistry literature revealed that species are rich in alkaloids, of which biologically active berberine is the major and the potential one. Modern research has shown that berberine display several pharmacological effects through various mechanisms. It is a natural drug for the clinical uses in different disease and pathological conditions such as atherosclerosis, cancer, alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, PCOS, bacterial and viral infections etc. It has very low toxicity in usual doses and reveals clinical benefits without major side effects. It can be a potential source for future drug discovery and drug development.
Moreover, berberine’s applications extend beyond metabolic health. Its anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in managing chronic conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), where it improves insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance. Additionally, berberine’s effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens highlights its potential in combating infectious diseases, particularly in an era marked by rising antibiotic resistance.
The evidence supporting berberine’s benefits is steadily accumulating through clinical and preclinical studies. However, while it is generally considered safe, potential side effects, particularly gastrointestinal discomfort, necessitate caution. Proper dosage and medical supervision are essential to maximize its therapeutic effects and minimize risks.
Looking ahead, further research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms through which berberine operates and to explore its applications in new therapeutic areas. Its potential as a complementary treatment in conjunction with conventional therapies could enhance patient outcomes across various health domains.
In conclusion, berberine exemplifies the intersection of traditional wisdom and modern science, offering a promising avenue for improving health outcomes. Its extensive pharmacological properties and growing body of research make it a compound worthy of attention in both clinical practice and ongoing research endeavors.
REFERENCE
- Prajwala, B., Raghu, N., Gopenath, T. S., Kaginelli, S. B., Karthikeyan, M., Ashok, G., Ranjith, M. S., Srinivasan, V., & Basalingappa, K. M. (2020). Berberine and its pharmacology potential: A review. European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7(5), 115-123. JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research.
- Lee, Y. S., Kim, W. S., & Kim, K. S. (2006). Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes, 55(8), 2256-2264.
- Ye, F., Zhou, Q., Wang, M., Zhang, M., & Zhou, X. (2017). The protective effect of berberine hydrochloride on LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis through inhibiting TRAF6-Ca2+-calcineurin-NFATcl signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 16(5), 6228-6233.
- Srivastava, S., Srivastava, M., & Mishra, P. (2015). A review on biological and chemical diversity in Berberis (Berberidaceae). EXCLI Journal, 14, 247-267.
- Otani, M., Shitan, N., & Yazaki, K. (2005). Characterization of vacuolar transport of the endogenous alkaloid berberine in Coptis japonica. Plant Physiology, 138(4), 1939-1946.
- More, N. V., Kharat, K. R., & Bhajipale, N. S. (2017). Berberine from Argemone mexicana L. exhibits broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 64(1), 1-8.
- Liu, Y., Zhang, L., & Li, J. (2013). Update on berberine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2013, 308134, 1-8.
- Guo, Y., Li, F., Ma, X., & Cheng, X. (2017). CYP2D plays a major role in berberine metabolism in the liver of mice and humans. Xenobiotica, 41(11), 996-1005.
- Firouzi, S., Malekahmadi, M., & Jafari, A. (2018). Barberry in the treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome: Possible mechanisms of action. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, 11, 699-705.
- Guo, Y., Li, F., Ma, X., & Cheng, X. (2017). CYP2D plays a major role in berberine metabolism in the liver of mice and humans. Xenobiotica, 41(11), 996-1005.