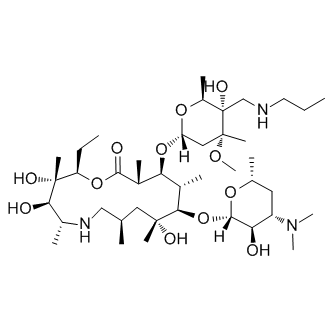
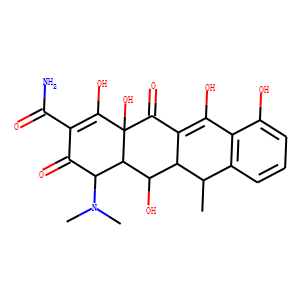
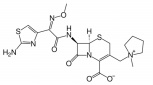
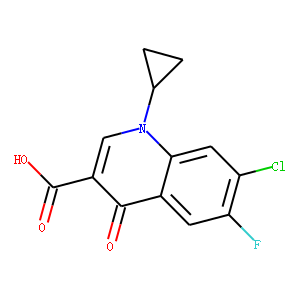
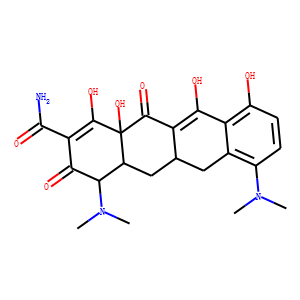
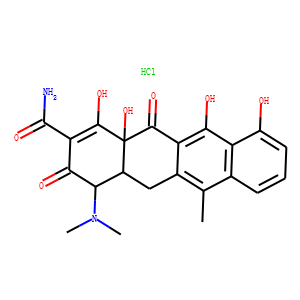
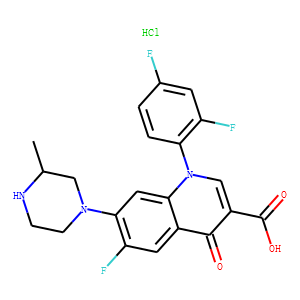
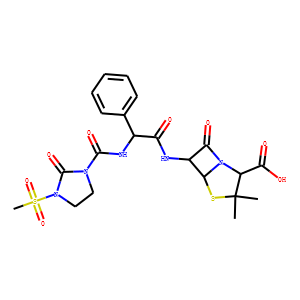
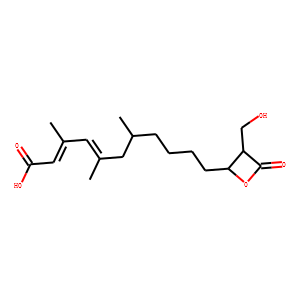
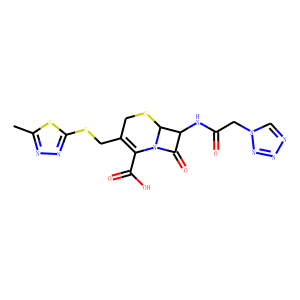
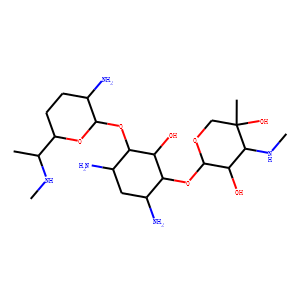
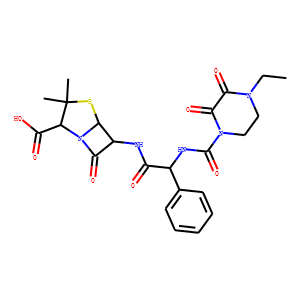
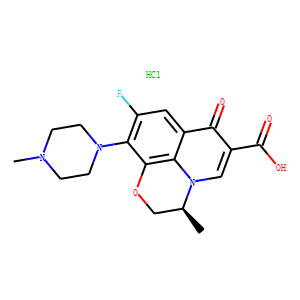
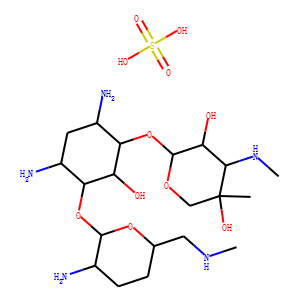
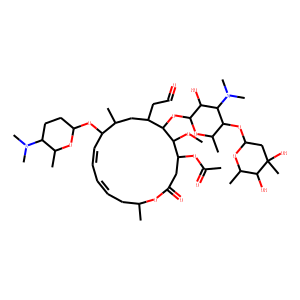
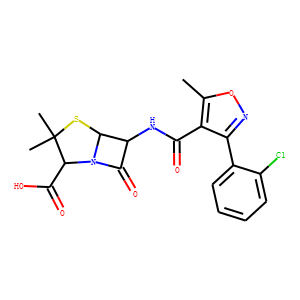
Antibiotic
Antibiotics are a class of drugs specifically designed to combat bacterial infections by either killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth. They target various essential bacterial functions, such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, nucleic acid replication, and key metabolic pathways, which are often absent or significantly different in humans, thus allowing for selective action against bacteria. The use of antibiotics has been pivotal in treating infectious diseases, surgeries, and immunocompromised conditions. However, the rise of antibiotic resistance, where bacteria evolve mechanisms to withstand these drugs, poses a significant global health threat. This has intensified efforts to develop new antibiotics with novel targets and mechanisms, alongside promoting prudent use to preserve their effectiveness.