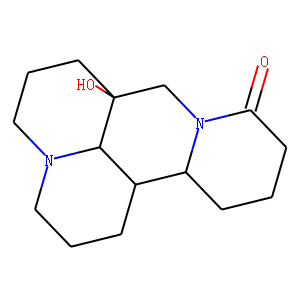
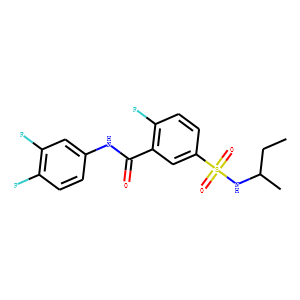
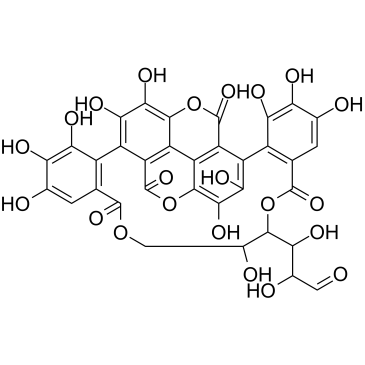
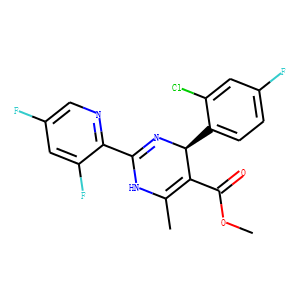
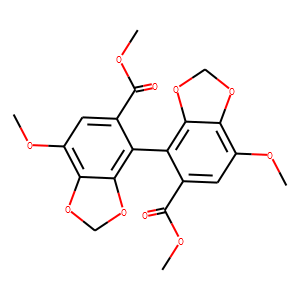
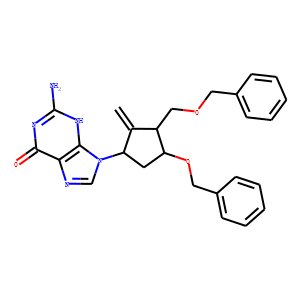
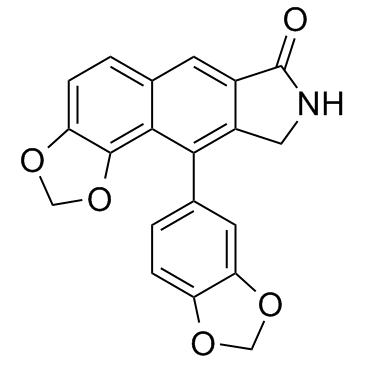
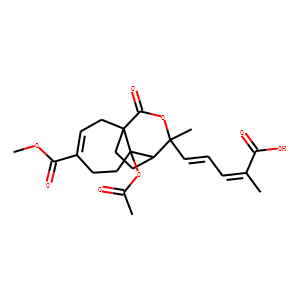
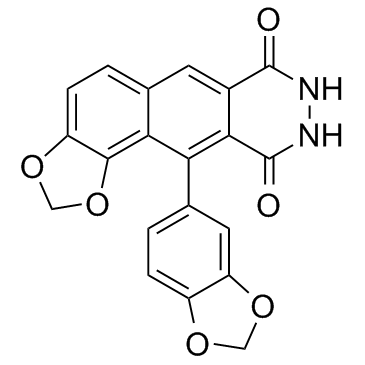
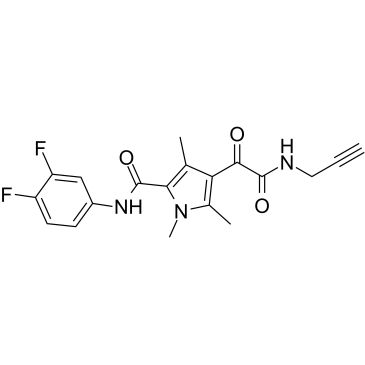
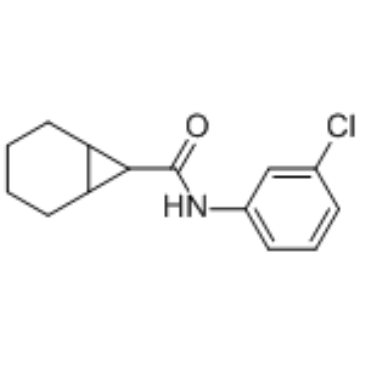
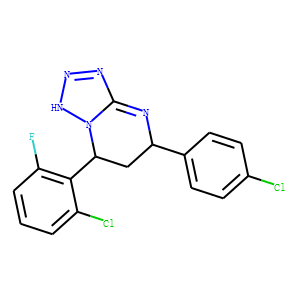
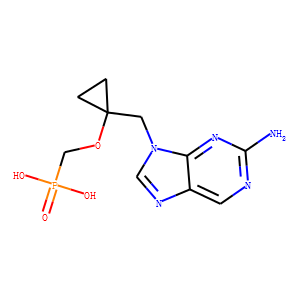
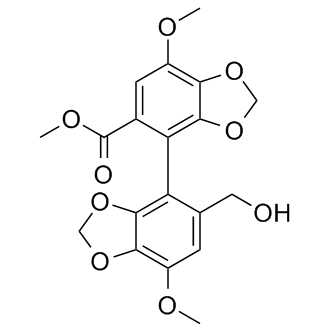
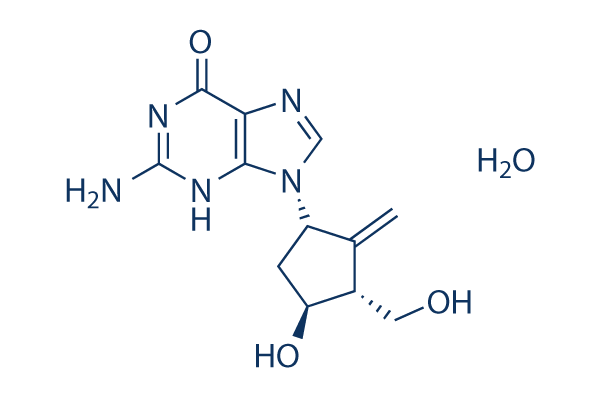
HBV
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a DNA virus that primarily infects the liver, leading to hepatitis B, a major global health concern. HBV transmission occurs through contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions, or from mother to child during childbirth. The infection can manifest in both acute and chronic forms. Acute HBV is often self-limiting, but chronic HBV can lead to serious conditions like cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent HBV infection, offering immunity and reducing the risk of chronic disease and liver cancer.