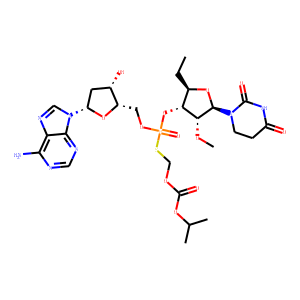
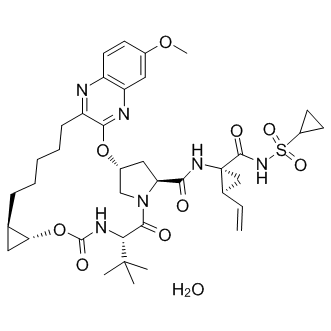
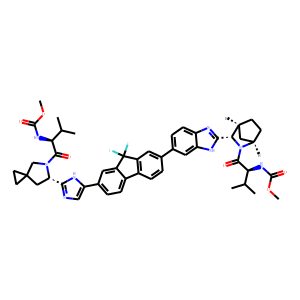
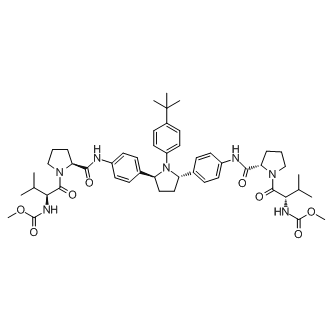
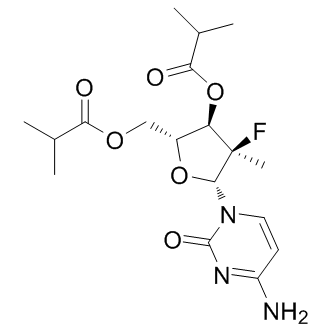
HCV
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a blood-borne virus that primarily infects liver cells, leading to hepatitis C, a disease that can cause both acute and chronic liver inflammation. The infection ranges in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a lifelong illness that attacks the liver. It spreads through contaminated blood, such as through needle sharing, inadequately sterilized medical equipment, and blood transfusions. Chronic HCV can be asymptomatic for decades, but over time it can lead to serious conditions like cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer. Despite its severity, effective antiviral medications can cure most cases of hepatitis C, significantly reducing the risk of death and liver disease.