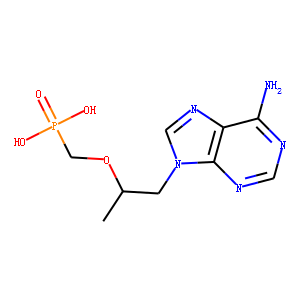
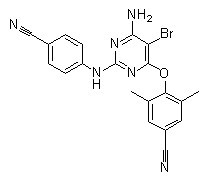
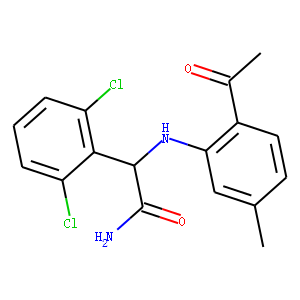
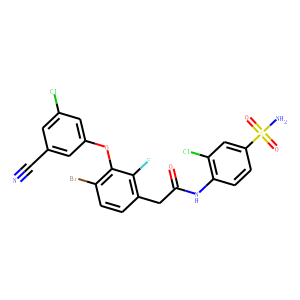
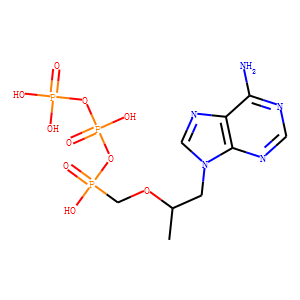
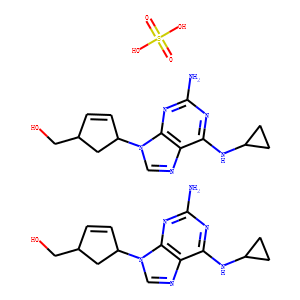
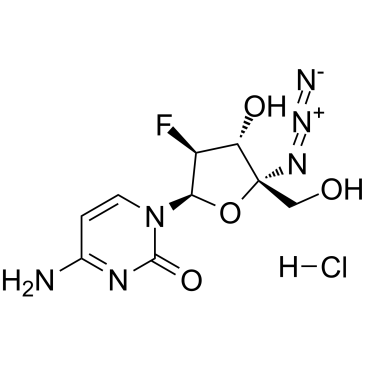
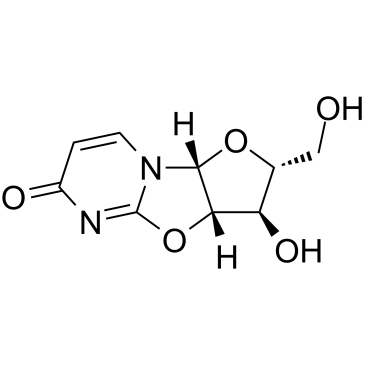
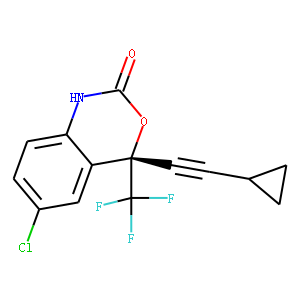
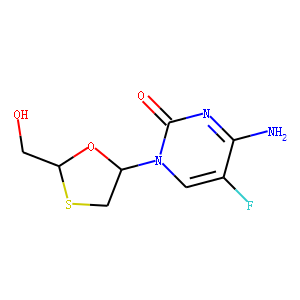
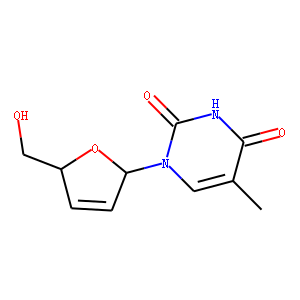
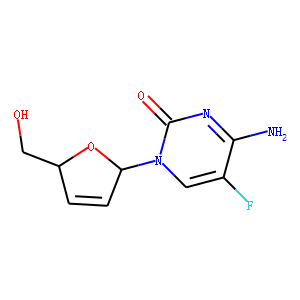
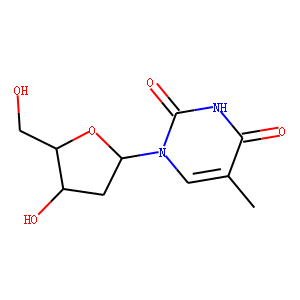
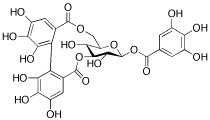
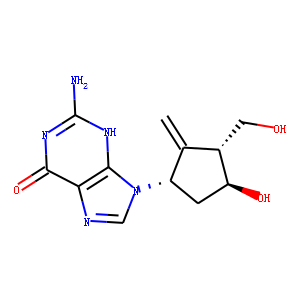
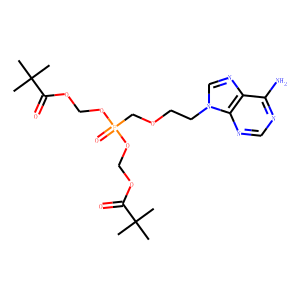
Reverse Transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase is a crucial enzyme used by certain viruses, including retroviruses like HIV, to replicate their genetic material. Unlike most DNA-based life forms, these viruses carry their genetic information in RNA. Once infecting a host cell, reverse transcriptase converts this RNA into DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. This newly synthesized DNA is then integrated into the host's genome, enabling the virus to hijack the cellular machinery to produce more viral particles. The discovery of reverse transcriptase has profound implications in biotechnology and medicine, leading to advancements in viral research, genetic engineering, and the development of antiretroviral drugs that specifically target this enzyme to inhibit viral replication.