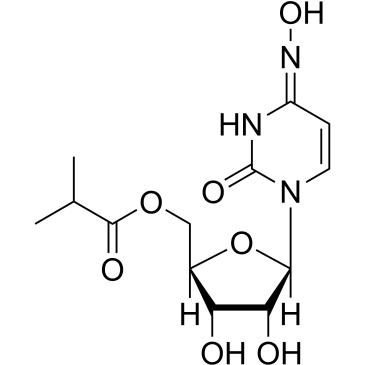
SARS-CoV
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is a viral pathogen that caused a global outbreak in 2002-2003. It belongs to the coronavirus family, known for viruses that can cause illnesses ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases. SARS-CoV originates in bats and can spread to other animals and humans. It primarily transmits through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus causes symptoms that include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing, and can lead to severe respiratory distress and death. The outbreak led to significant public health responses and highlighted the need for global cooperation in managing infectious diseases. While contained, SARS-CoV remains a critical reference point for studying pandemic preparedness.