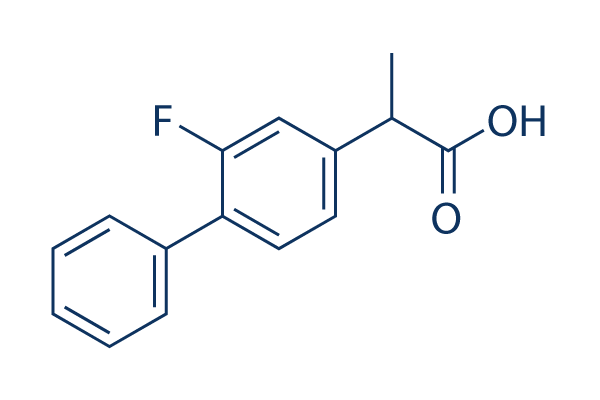
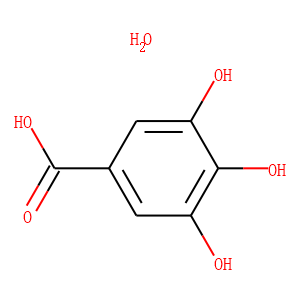
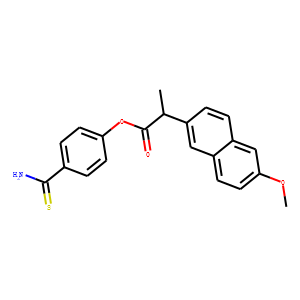
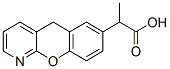
COX
Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are crucial in the biochemical pathway that converts arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, which are key mediators of inflammation, pain, and fever. There are two main isoforms of COX: COX-1, which is expressed in most tissues and involved in regulating normal cellular processes, and COX-2, which is typically induced during inflammatory responses. Due to their roles in mediating inflammation, COX enzymes are common targets for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen. These drugs inhibit the COX enzymes to reduce the production of prostaglandins, thereby alleviating pain, inflammation, and fever. Understanding and targeting COX pathways are essential for developing effective anti-inflammatory therapies.