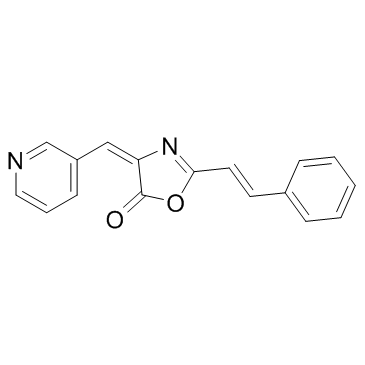
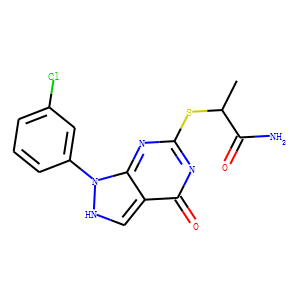
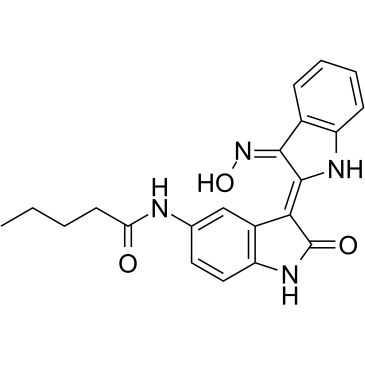
DAPK
Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a significant role in various cellular processes including apoptosis, autophagy, and cytoskeletal reorganization. It functions as a crucial mediator in the programmed cell death pathway, responding to various stress signals to initiate apoptosis, thus serving as a tumor suppressor in many types of cancers. DAPK’s activity is tightly regulated through mechanisms such as phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, highlighting its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing unchecked cell growth. The deregulation of DAPK is associated with the progression of several diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, making it a valuable target for therapeutic interventions aiming to modulate apoptosis and enhance cancer treatment efficacy.