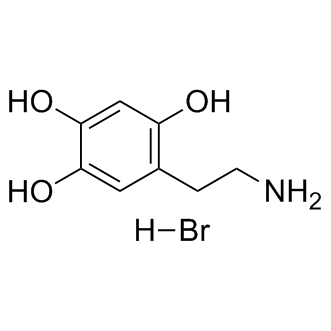
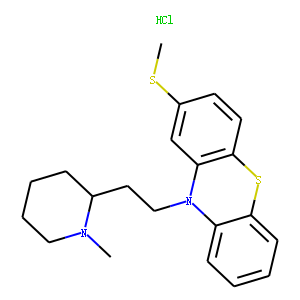
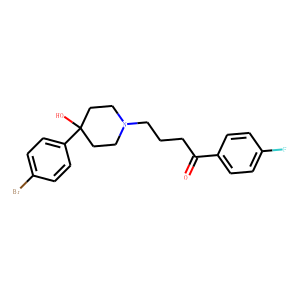
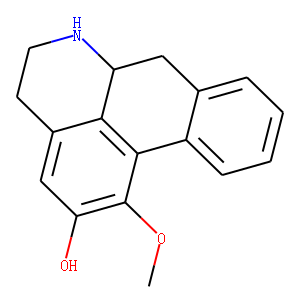
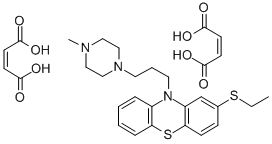
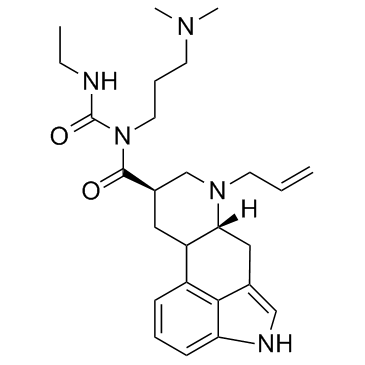
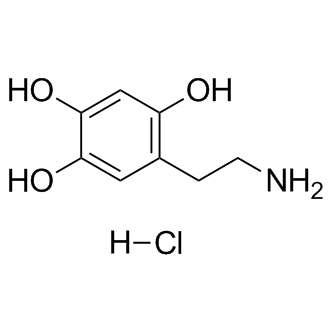
Dopamine Receptor
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter dopamine, a key player in many vital neurological processes including motor control, motivation, reward, and cognition. There are five known subtypes of dopamine receptors, D1 through D5, which are divided into two families based on their pharmacological profiles: D1-like receptors (D1 and D5), which stimulate adenylate cyclase, and D2-like receptors (D2, D3, and D4), which inhibit it. These receptors are distributed throughout the brain and are implicated in various psychiatric and neurological disorders, such as schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, and addiction. As such, dopamine receptors are significant targets for drugs designed to treat these conditions.

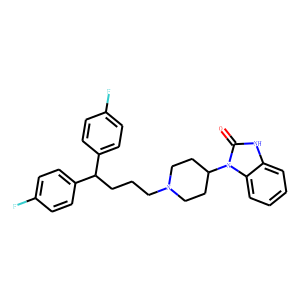
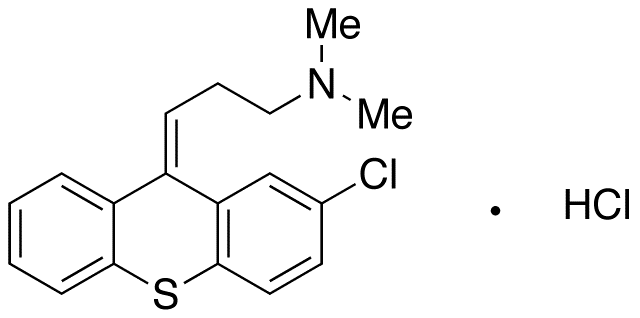
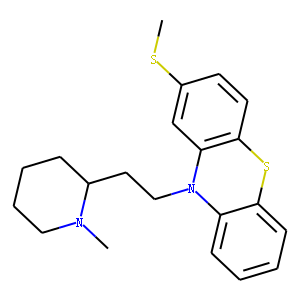
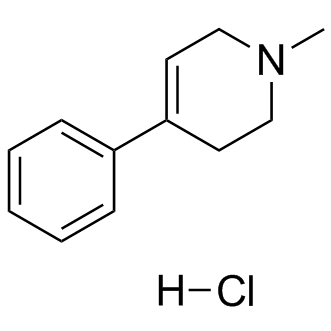
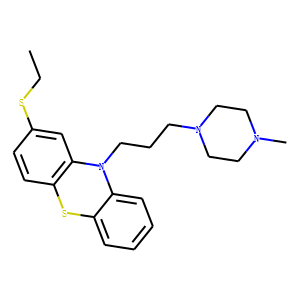
.gif)