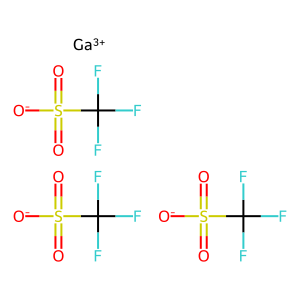
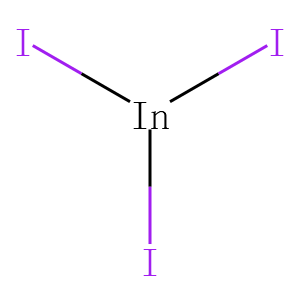
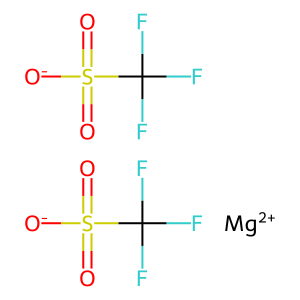
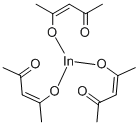
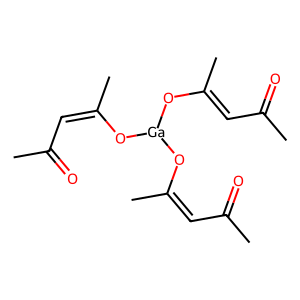
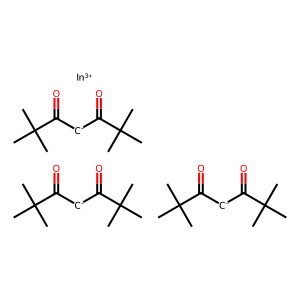
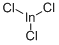IAP
IAPs (Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins) are a family of proteins that play a crucial role in regulating apoptosis, the process of programmed cell death. These proteins function primarily to inhibit cell death by directly binding to and inhibiting caspases, the key enzymes involved in apoptosis. Overexpression of IAPs has been observed in various types of cancers, contributing to tumor growth and resistance to chemotherapy by preventing the apoptotic death of cancer cells. Consequently, IAPs are significant therapeutic targets in cancer treatment. Inhibiting IAPs can reactivate apoptosis in cancer cells, making them more susceptible to anticancer therapies. Research into IAP inhibitors is an active area, with several compounds currently in clinical trials.