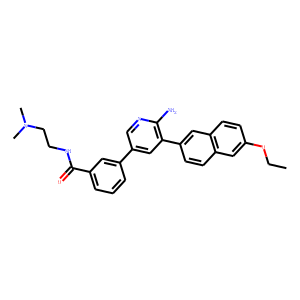
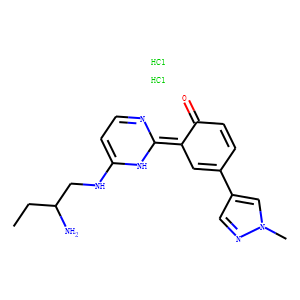
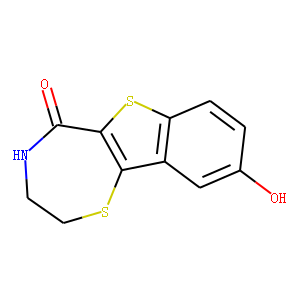
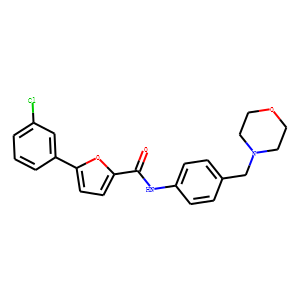
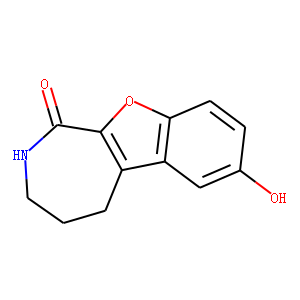
PKD
Protein Kinase D (PKD) refers to a family of serine/threonine kinases that play pivotal roles in many cellular processes, including signal transduction, cell proliferation, and survival. PKDs are implicated in the regulation of diverse functions such as gene expression, membrane trafficking, immune responses, and apoptosis. The PKD family consists of several isoforms, each having unique as well as overlapping functions within cells. Dysregulation of PKD activity is associated with various pathological conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and immune disorders. Due to their central role in multiple signaling pathways, PKDs are viewed as attractive therapeutic targets. Modulating PKD activity with inhibitors can potentially offer new treatments for diseases linked to its dysfunction.