Thrombin
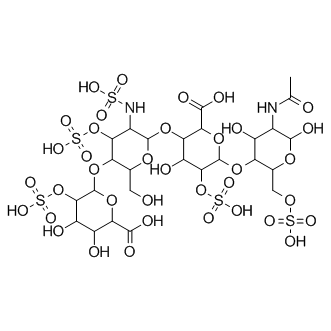
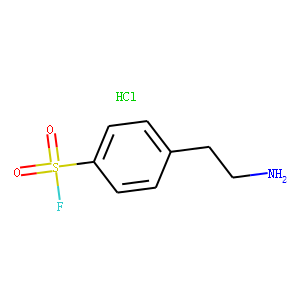
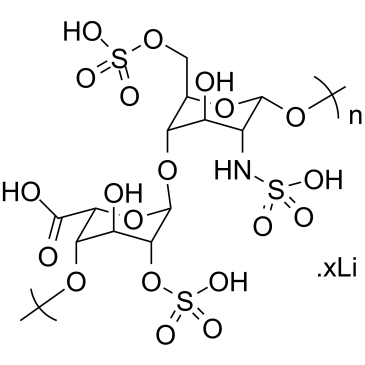
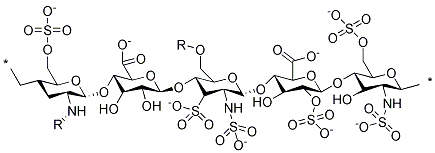
Thrombin is a serine protease enzyme that plays a central role in the coagulation cascade, converting fibrinogen to fibrin and thereby facilitating blood clot formation. Its activity is essential for hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding at injury sites. Beyond clotting, thrombin also influences various other biological processes, including inflammation and wound healing. Due to its pivotal role in thrombosis and hemostasis, thrombin is a key target for anticoagulant drugs, which are used to prevent and treat blood clots. Drugs such as dabigatran directly inhibit thrombin, reducing the risk of clots in conditions like atrial fibrillation and deep vein thrombosis, making thrombin inhibition a critical strategy in cardiovascular disease management.