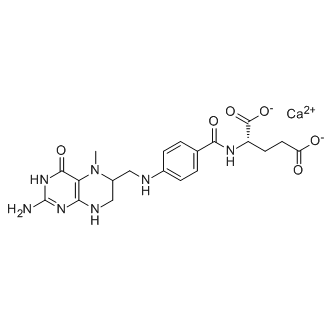
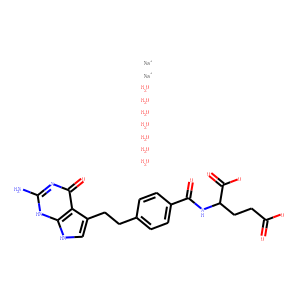
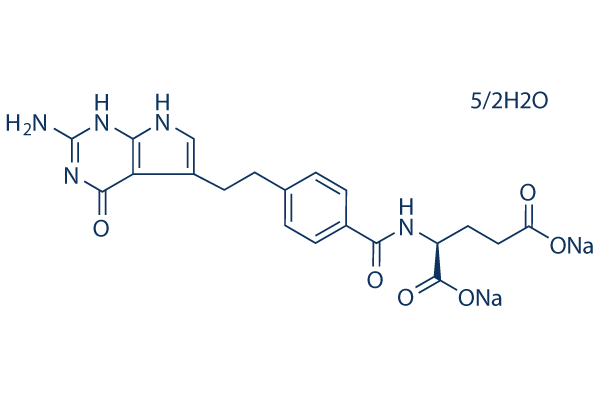
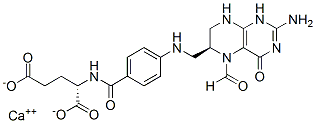
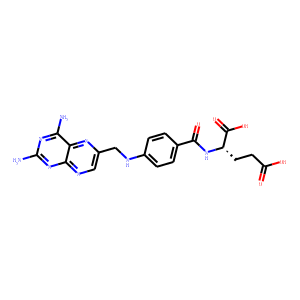
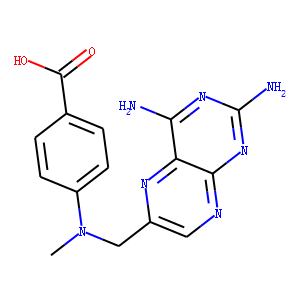
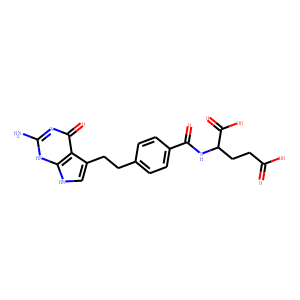
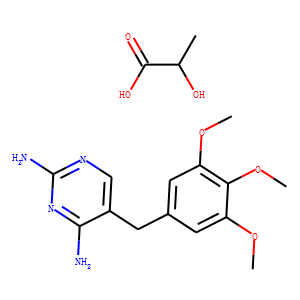
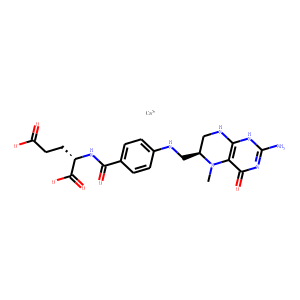
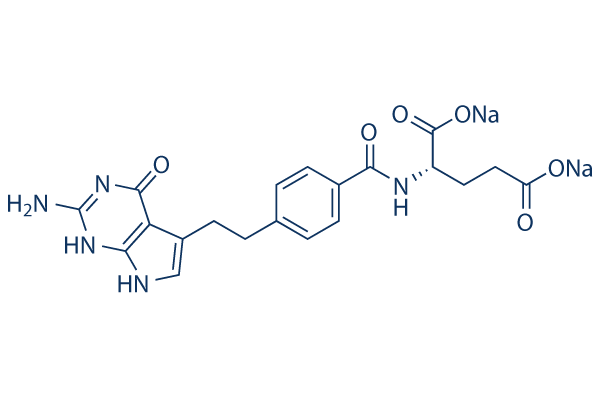
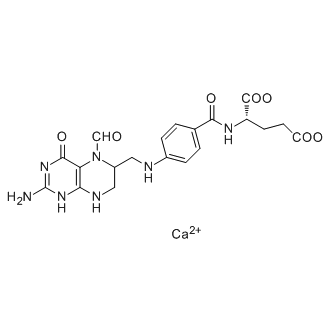
Antifolate
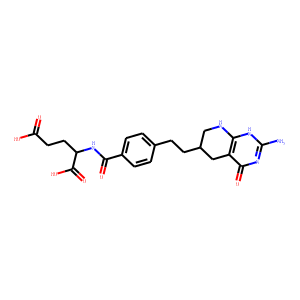
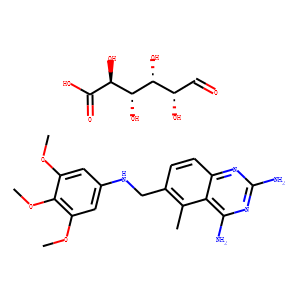
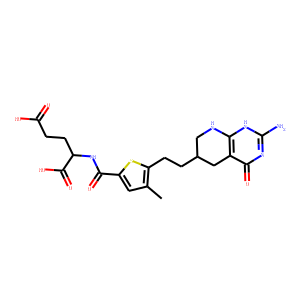
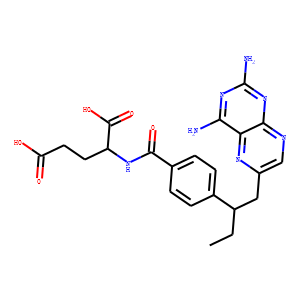
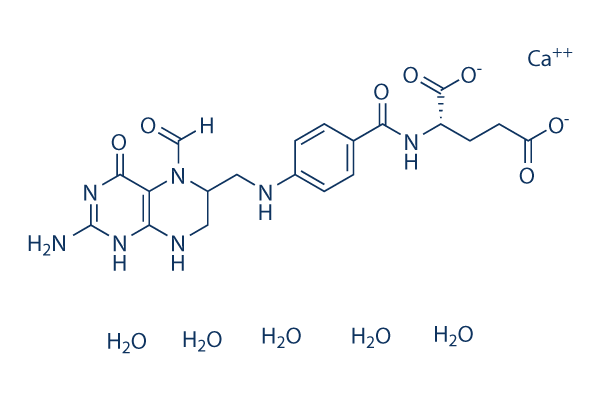
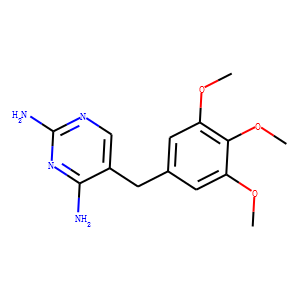
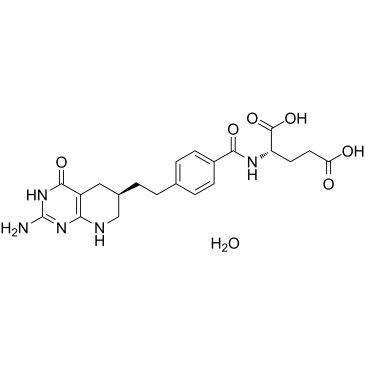
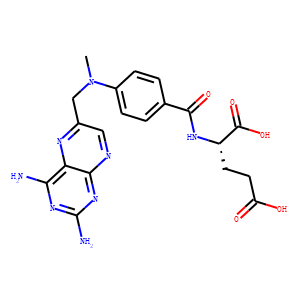
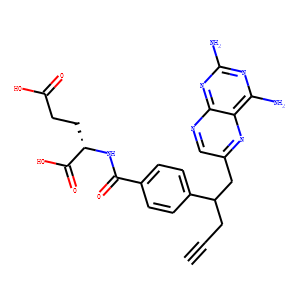
Antifolates are a class of drugs that inhibit the enzymes involved in the synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin essential for DNA and RNA synthesis. By blocking these pathways, antifolates prevent the replication and repair of DNA, particularly in rapidly dividing cells such as cancer cells. Methotrexate is one of the most well-known antifolates, widely used in the treatment of various cancers, including leukemia, and autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. Pemetrexed is another example, used primarily for lung cancer. Antifolates are also effective in treating some infectious diseases by targeting microbial folate synthesis pathways. Their ability to disrupt cell proliferation makes antifolates valuable in chemotherapy regimens and disease management.