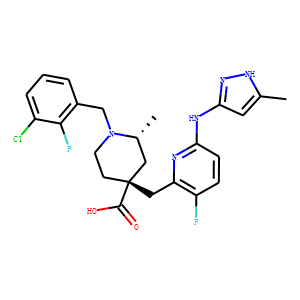
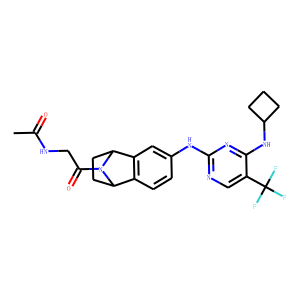
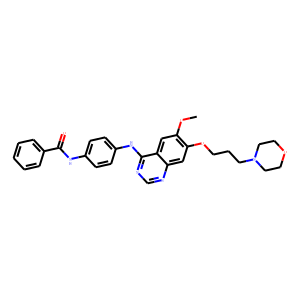
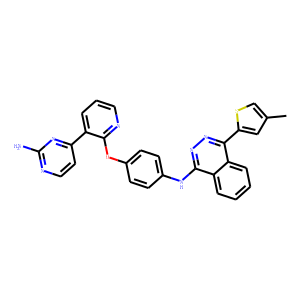
Aurora Kinase
Aurora kinases are a family of serine/threonine kinases that play critical roles in cell division, specifically during mitosis. They are key regulators of chromosome alignment, segregation, and cytokinesis, ensuring accurate distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells. The family consists mainly of three members: Aurora A, Aurora B, and Aurora C, each with distinct functions within the cell cycle. Due to their pivotal roles in cell division, dysregulation of Aurora kinases is often associated with cancer progression, as it can lead to aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Consequently, Aurora kinases have emerged as significant targets for cancer therapy, with inhibitors being developed to disrupt their activity and halt the proliferation of cancer cells.