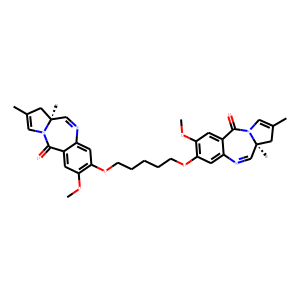
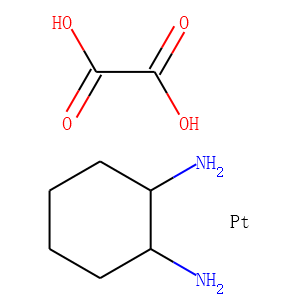
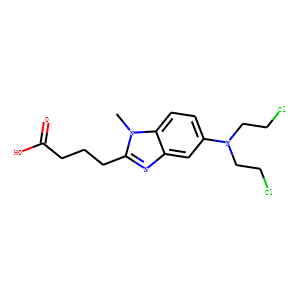
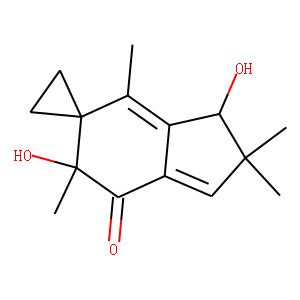
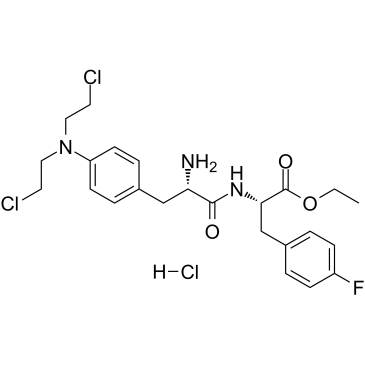
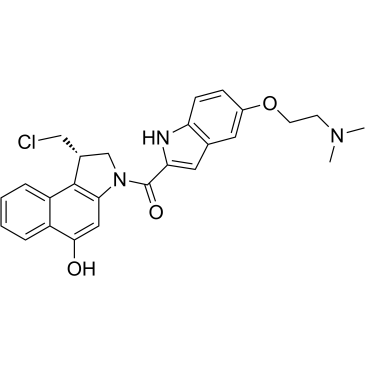
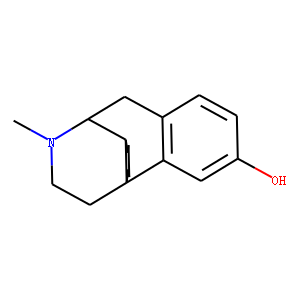
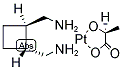DNA Alkylator/Crosslinker
A DNA alkylator/crosslinker is a type of chemical agent used primarily in chemotherapy treatments. These compounds work by adding alkyl groups to the DNA molecules within cells. This process can lead to DNA crosslinking, where two DNA strands or two parts of the same strand become covalently bonded, effectively disrupting DNA replication and transcription. The interruption of these critical cellular processes can lead to cell death, making alkylators effective against rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells. Common examples of DNA alkylators include cyclophosphamide and busulfan. While effective in targeting cancerous cells, these agents can also affect normal cells, leading to various side effects, thus requiring careful management during treatment.