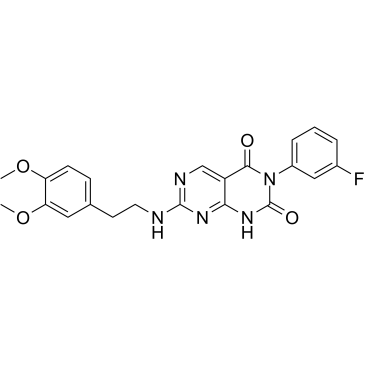
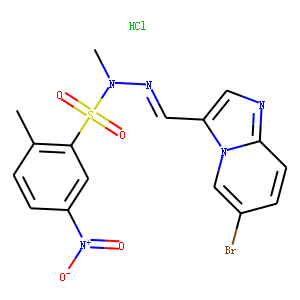
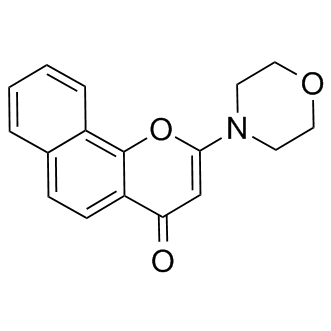
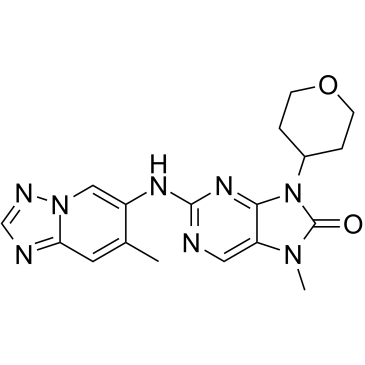
DNA-PK
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a critical enzyme in the cellular response to DNA damage, particularly double-strand breaks. It belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family and plays a pivotal role in the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. DNA-PK consists of a catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and a regulatory component, the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA at breakpoints. Upon binding, DNA-PK orchestrates the repair process by recruiting and phosphorylating other proteins involved in the DNA damage response, thereby facilitating the rejoining of the broken DNA strands. Inhibiting DNA-PK has been explored as a strategy for enhancing the effectiveness of cancer radiotherapy and chemotherapy.