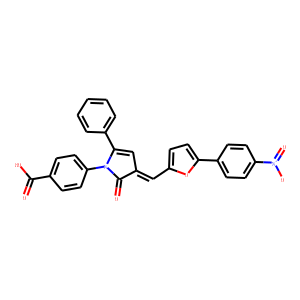
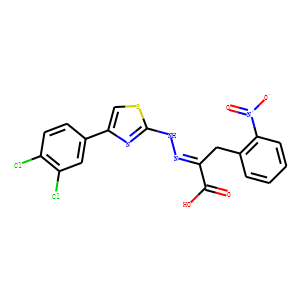
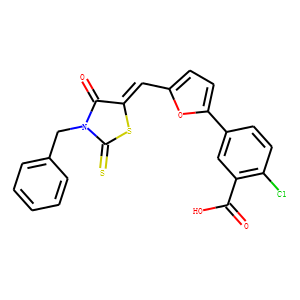
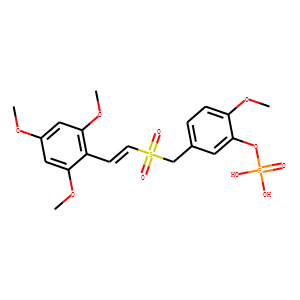
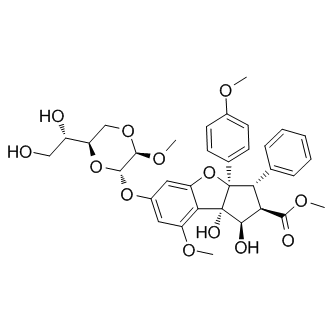
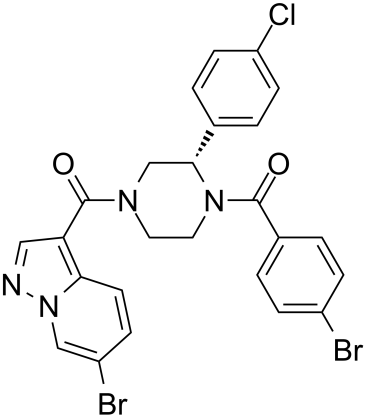
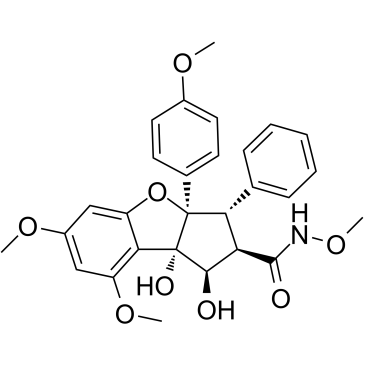
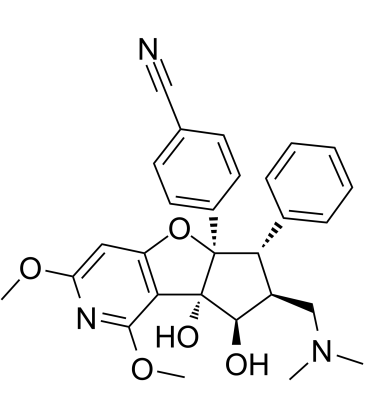
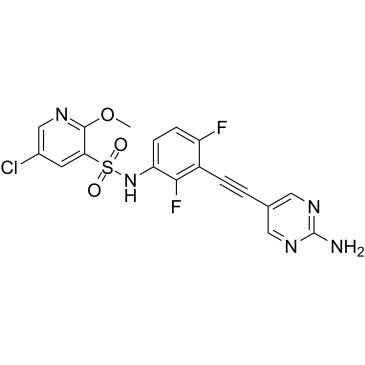
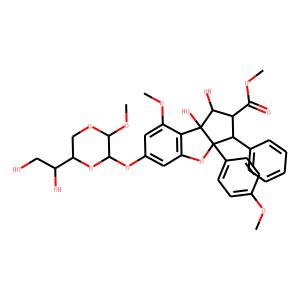
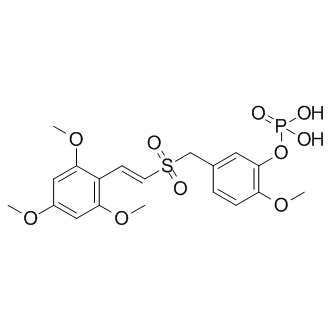
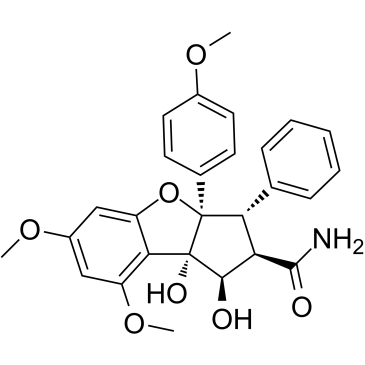
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor (eIF)
Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are essential proteins involved in the initiation phase of mRNA translation, a critical step in protein synthesis within eukaryotic cells. These factors facilitate the assembly of the ribosome, a complex molecular machine, onto the mRNA transcript. They play key roles in various stages: eIF1 and eIF3 promote the formation of a pre-initiation complex, eIF4 is involved in mRNA binding and unwinding, and eIF2 mediates the loading of the initiator tRNA charged with methionine onto the small ribosomal subunit. The activity of eIFs is tightly regulated, influencing cellular growth and homeostasis, and dysregulation of eIF activity is linked to numerous diseases, including cancer.