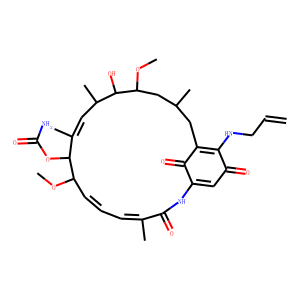
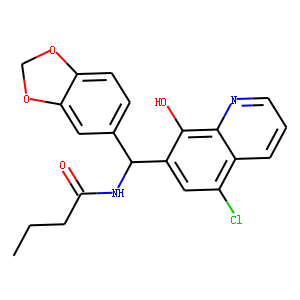
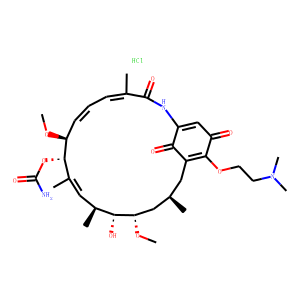
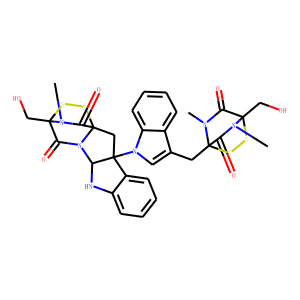
HSP
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are a diverse family of proteins that are highly conserved across species. They function primarily as molecular chaperones, aiding in the proper folding of nascent polypeptides, preventing the aggregation of proteins, and facilitating the refolding or degradation of misfolded proteins. HSPs are typically upregulated in response to stress, such as heat shock, which is the origin of their name. Their role in maintaining cellular protein homeostasis makes them crucial for cell survival under stressful conditions. Importantly, HSPs are involved in various diseases, including cancer, where they help cancer cells survive therapeutic stresses. Consequently, inhibiting HSP function is a promising strategy in cancer therapy to overcome resistance to treatments.