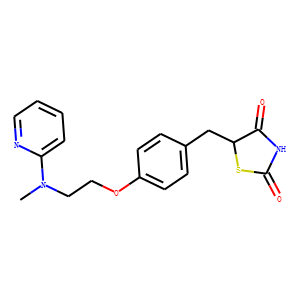
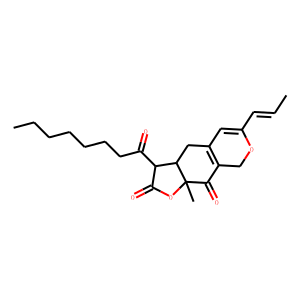
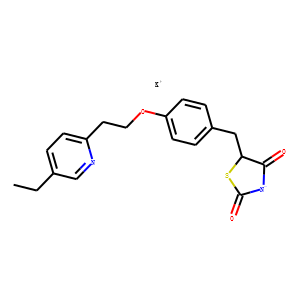
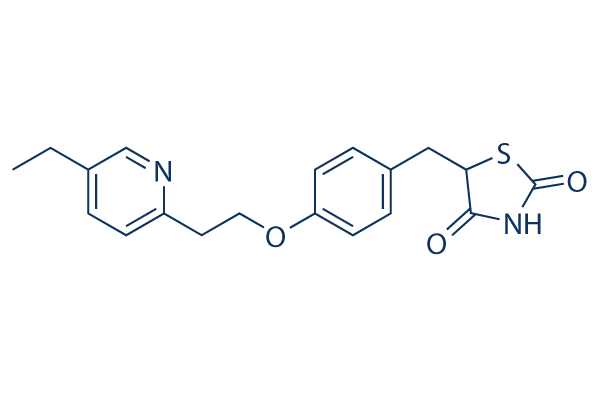
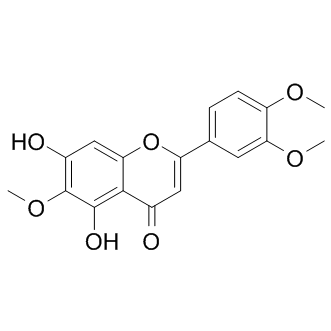
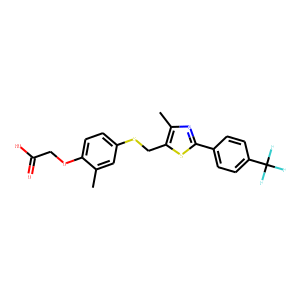
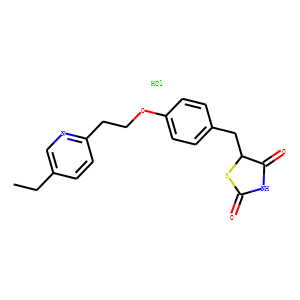
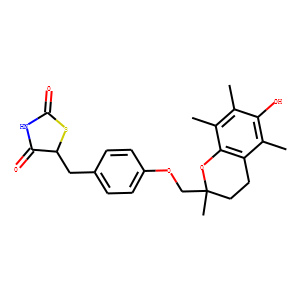
PPAR
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors to regulate the expression of genes. PPARs play essential roles in the body, influencing lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and the immune response. There are three main types: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-gamma, and PPAR-delta (also known as PPAR-beta). PPAR-alpha is involved in the breakdown of fatty acids and lipid metabolism, PPAR-gamma is crucial for adipocyte differentiation and insulin sensitivity, and PPAR-delta influences energy balance and overall metabolism. They are targets for drugs treating hyperlipidemia and type 2 diabetes, as they can modify the body's metabolic pathways.