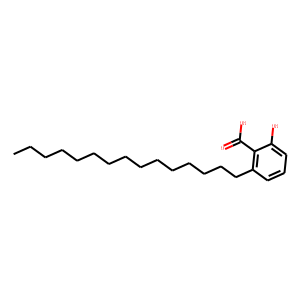
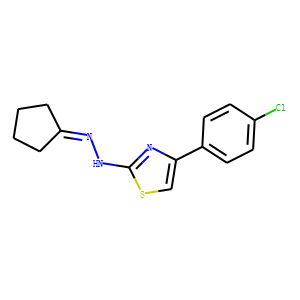
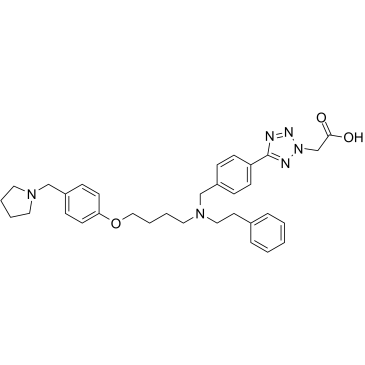
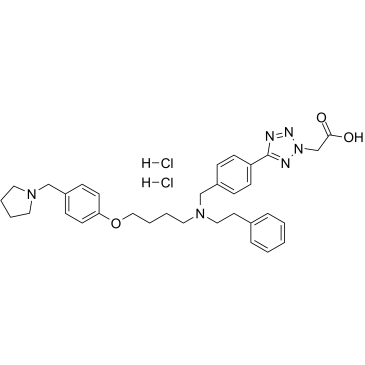
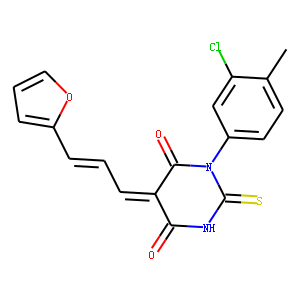
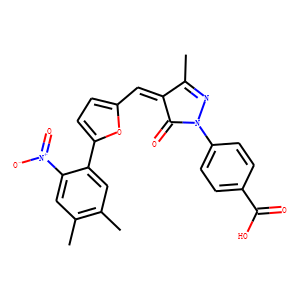
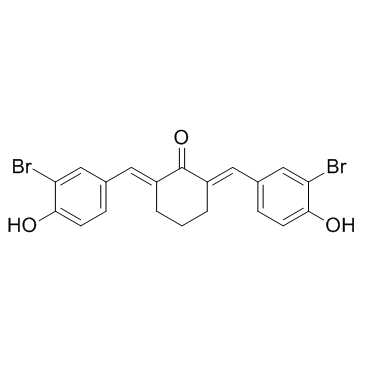
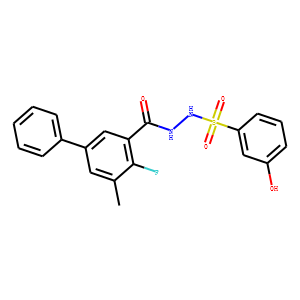
Histone Acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that play a critical role in the regulation of gene expression by adding acetyl groups to lysine residues on histone proteins. This acetylation reduces the positive charge on histones, decreasing their affinity for the negatively charged DNA and thereby enhancing transcriptional accessibility. HATs are key players in chromatin remodeling and function in various cellular processes, including DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis. They are part of larger multiprotein complexes and can also acetylate non-histone proteins, influencing their activity and stability. Dysregulation of HAT activity has been linked to the development of cancers, neurological disorders, and other diseases, highlighting their importance in maintaining cellular health and function.