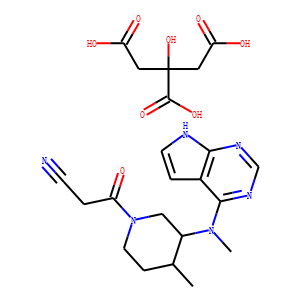
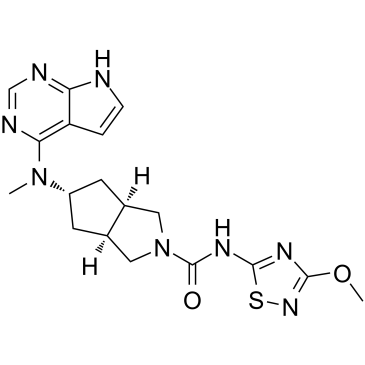
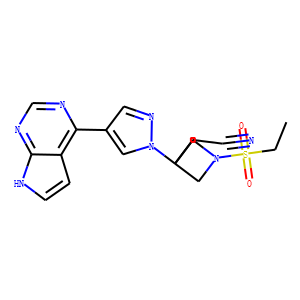
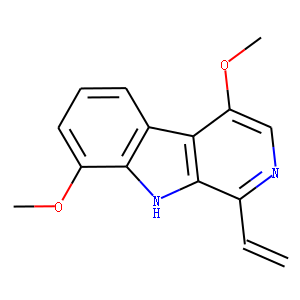
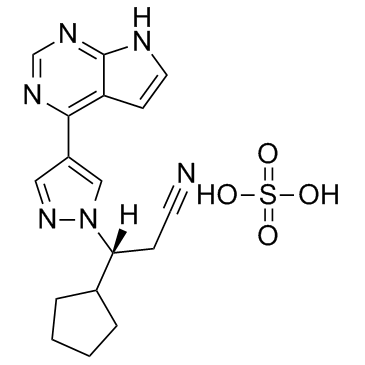
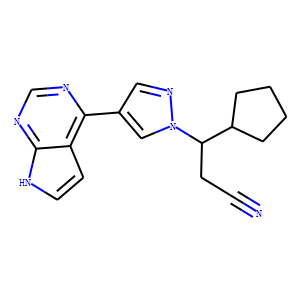
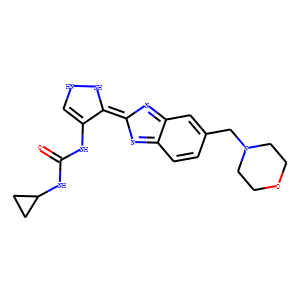
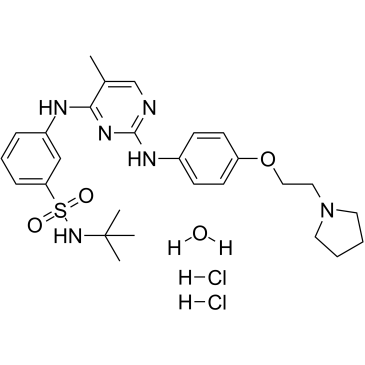
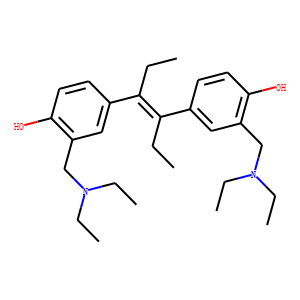
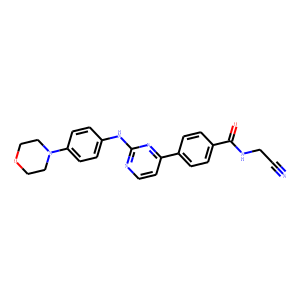
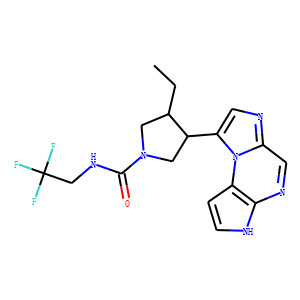
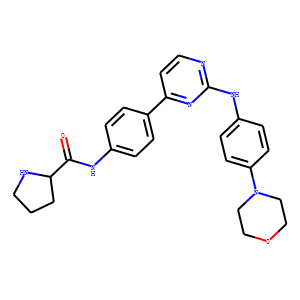
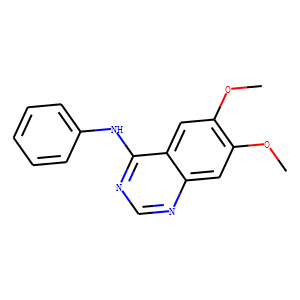
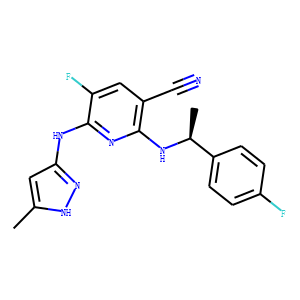
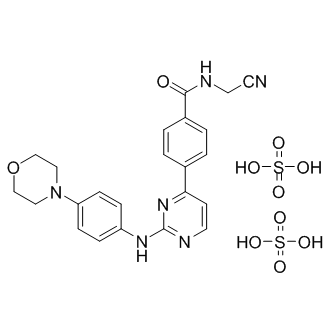
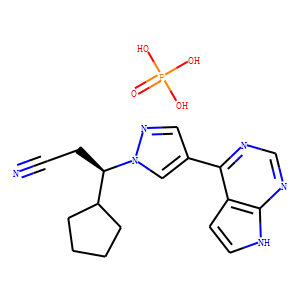
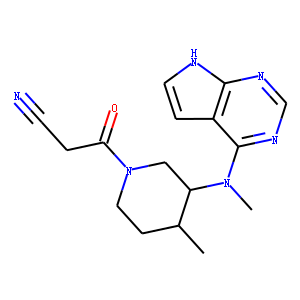
JAK
Janus kinases (JAKs) are a family of intracellular, non-receptor tyrosine kinases that play a pivotal role in the signal transduction of cytokine receptors. This signaling is crucial for the regulation of immune responses, cell growth, and development. The JAK family consists of four members: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2. They are activated upon cytokine binding to receptors, leading to the phosphorylation of JAKs themselves and subsequent activation of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) pathway. Dysregulation or mutation of JAKs is associated with a variety of diseases, including cancers, inflammatory disorders, and immunodeficiencies, making them significant targets in therapeutic development.