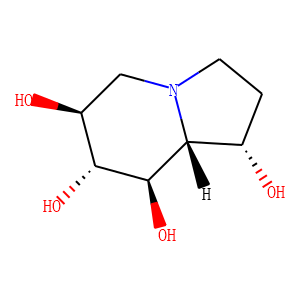
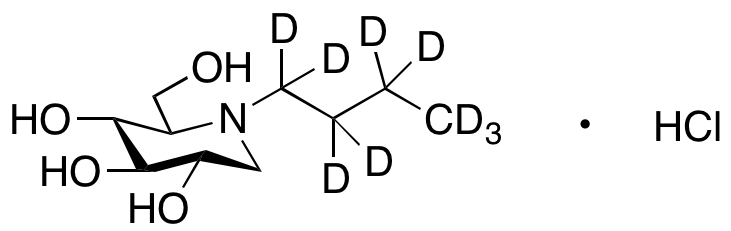
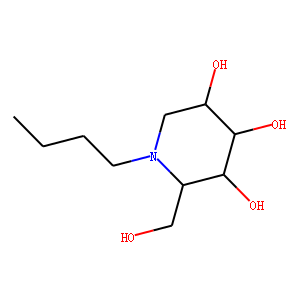
Glycosidase Inhibitors
Glycosidase inhibitors serve as a useful class of tools not only to research the function of oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates, but also as a potential drug for the treatment of diseases associated with abnormal glycoconjugates. Since glycosidases are involved in a wide range of anabolic and catabolic processes, such as biosynthesis, digestion, lysosomal catabolism of glycoconjugates, endoplasmic reticulum quality control, and endoplasmic reticulum-related degradation of glycoproteins, thereby in vivo inhibitors are of great interest for the modification of glycosidase activity. Glycosidase inhibitors have broad prospects for drug development, with a variety of beneficial effects as pesticides and therapeutic agents, such as antifungal drugs, pesticides, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity drugs, antiviral drugs, and some genetic diseases therapeutic drugs.