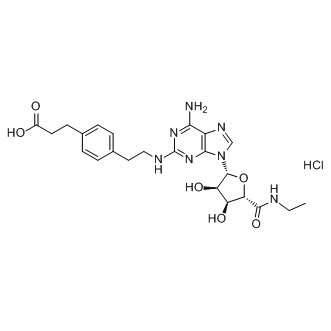
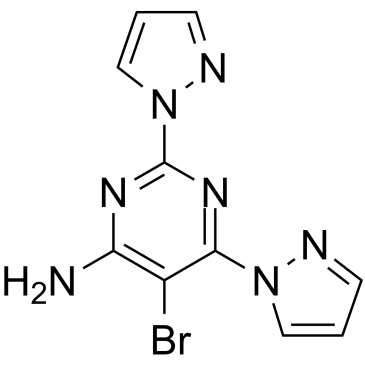
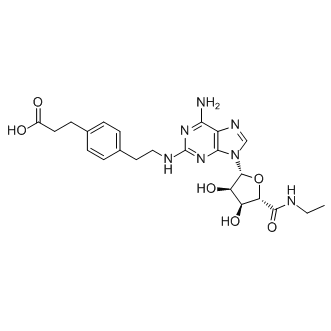
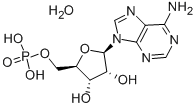
Adenosine Receptor
Adenosine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that respond to the endogenous nucleoside adenosine. They are distributed widely throughout the body, playing key roles in the cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems. There are four main types: A1, A2A, A2B, and A3. Each receptor subtype has a unique pattern of expression and physiological effects. For instance, A1 receptors generally inhibit adenylate cyclase activity, while A2A and A2B receptors typically stimulate it. These receptors are targeted therapeutically to manage various conditions, including cardiac issues, neurological disorders, and inflammation. Drugs targeting adenosine receptors can help regulate heart rate, reduce neuroinflammation, and modulate immune responses, demonstrating their broad therapeutic potential.