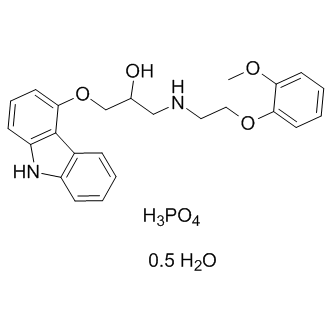
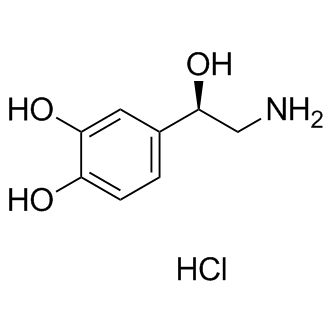
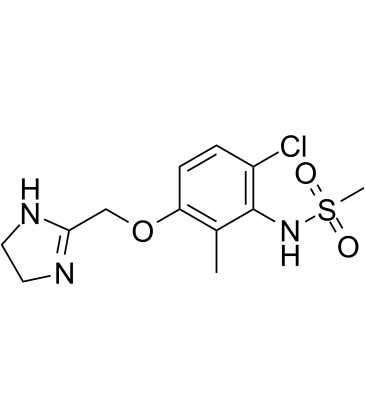
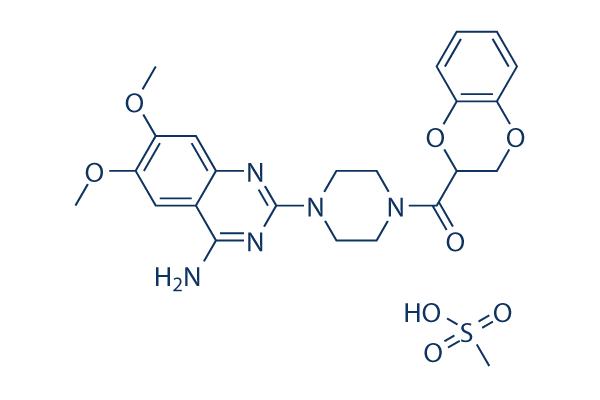
Adrenergic Receptor
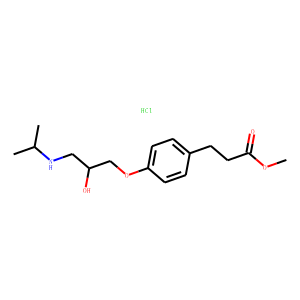
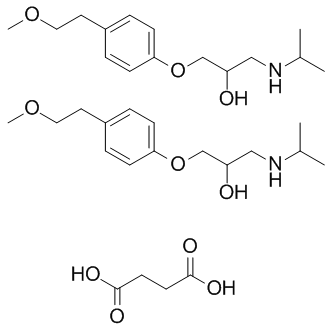
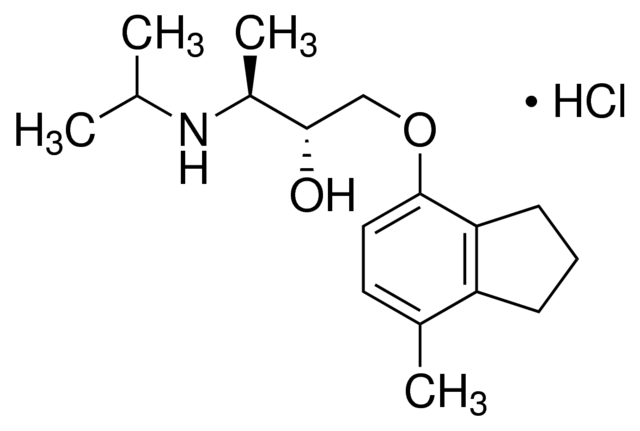
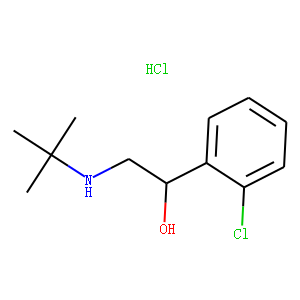
Adrenergic receptors are a critical group of G protein-coupled receptors that mediate the effects of the neurotransmitters adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine). These receptors are key players in the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the body's fight-or-flight responses. They are divided into two main types: alpha (α) and beta (β) receptors, each with several subtypes that have distinct locations and functions. For example, β1-adrenergic receptors are primarily found in the heart, where they increase heart rate and contractility. Adrenergic receptors are significant targets for pharmaceuticals in treating a variety of conditions, including asthma, hypertension, and heart failure, due to their wide-ranging effects on cardiovascular and respiratory functions.