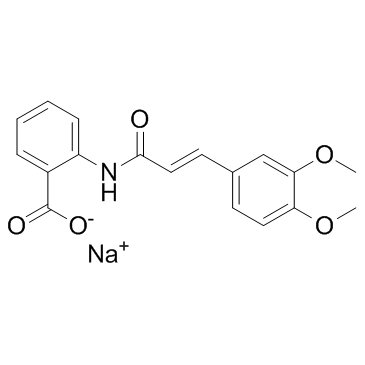
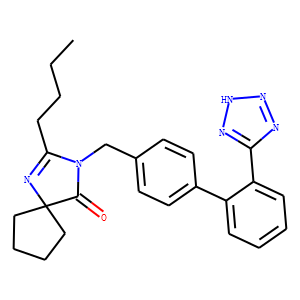
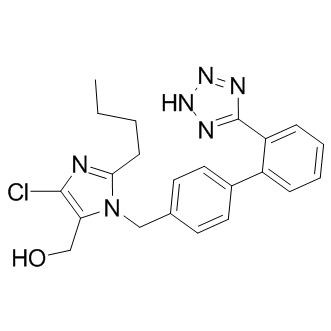
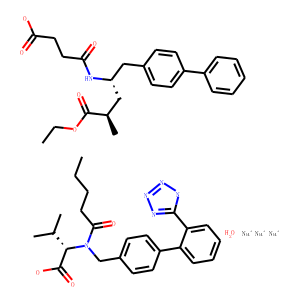
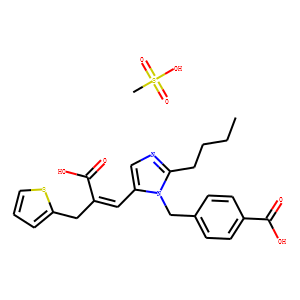
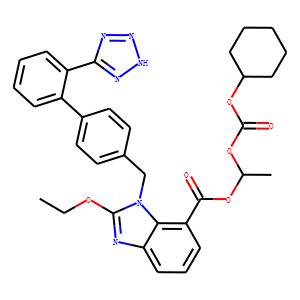
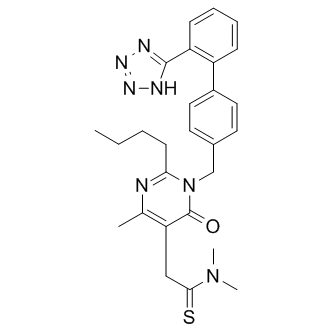
Angiotensin Receptor
Angiotensin receptors are key components of the renin-angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance. These receptors are primarily of two types: AT1 and AT2. The AT1 receptor is the most prevalent and clinically significant, mediating most of the physiological actions of angiotensin II, such as vasoconstriction, aldosterone secretion, and sodium retention, which collectively increase blood pressure. Drugs targeting the AT1 receptor, known as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), are widely used to treat hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy. These therapies help manage these conditions by blocking the harmful effects of angiotensin II, thus providing cardiovascular and renal protection.