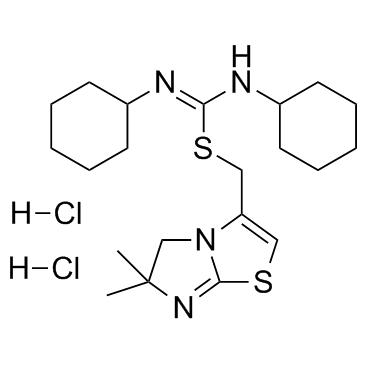
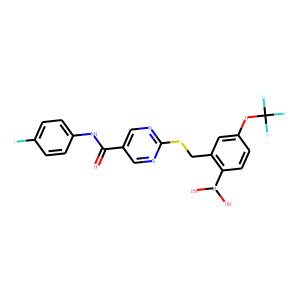
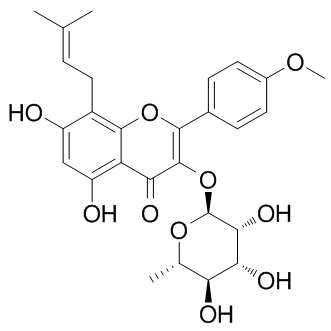
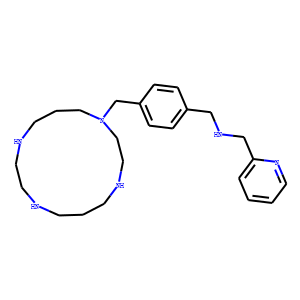
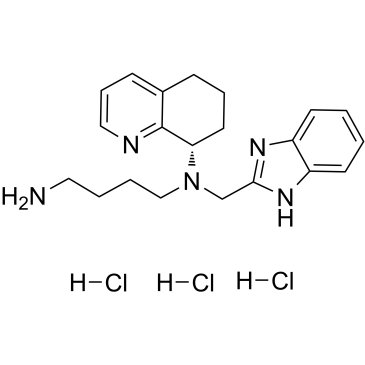
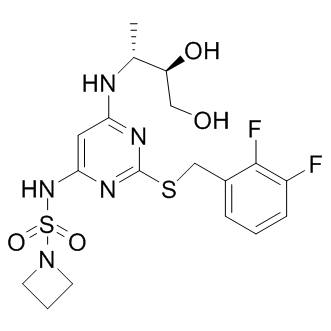
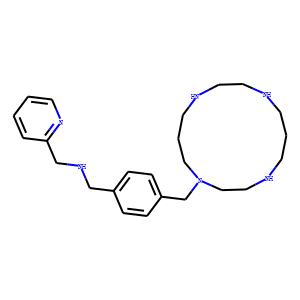
CXCR
CXCR, or C-X-C chemokine receptor, represents a subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that specifically bind to chemokines with a C-X-C motif. These receptors are vital for the function of the immune system, orchestrating the movement and activity of immune cells across body tissues, particularly in response to infections and inflammation. Prominent members include CXCR4 and CXCR5, which are essential in directing the migration of lymphocytes to specific tissue sites, impacting lymph node development and function. CXCRs are significant therapeutic targets in managing cancer, HIV infection (where CXCR4 serves as a co-receptor for viral entry), and autoimmune diseases by modulating immune cell trafficking and activity.