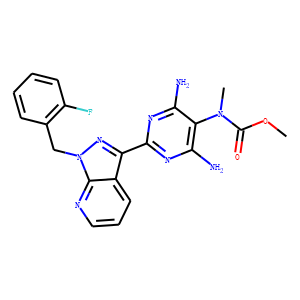
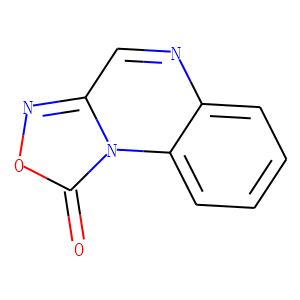
Guanylate Cyclase
Guanylate cyclase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a critical second messenger involved in various physiological processes. There are two main types: soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and membrane-bound guanylate cyclase. UGC is typically activated by nitric oxide (NO), playing a key role in vasodilation and blood pressure regulation. Membrane-bound guanylate cyclase, often triggered by natriuretic peptides, is crucial for volume regulation and electrolyte balance. Targeting guanylate cyclase is beneficial for treating cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and hypertension, by manipulating cGMP levels to improve vascular tone and cardiac function.