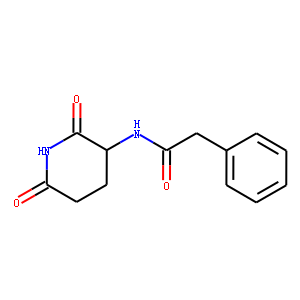
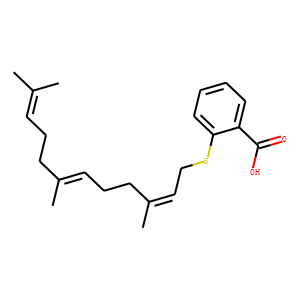
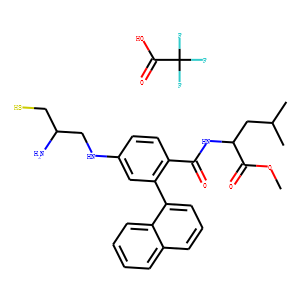
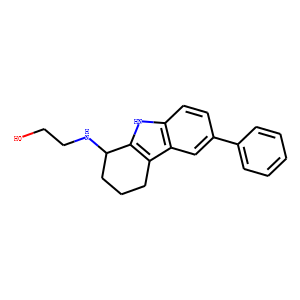
Ras
RAS proteins are a family of GTPases that play pivotal roles in regulating cell growth, survival, and differentiation. Comprising several isoforms, including KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS, these proteins act as binary switches within cellular signaling pathways, toggling between active (GTP-bound) and inactive (GDP-bound) states. Mutations in RAS genes are among the most common in cancer, leading to continuous activation and uncontrolled cell proliferation. Due to their central role in oncogenesis, RAS proteins are significant targets for cancer therapy. However, directly targeting RAS has proven challenging due to their high affinity for GTP and lack of traditional binding pockets, prompting ongoing research into innovative approaches to modulate RAS activity therapeutically.