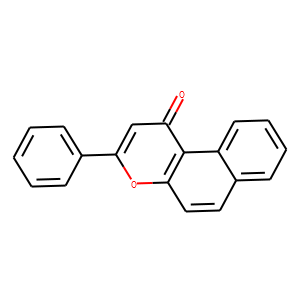
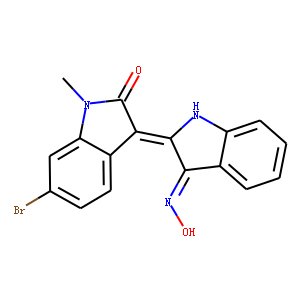
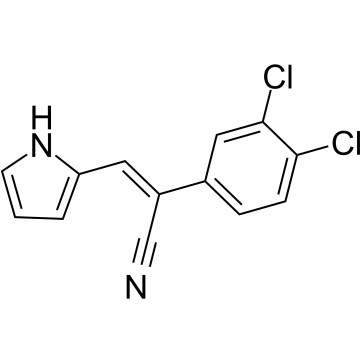
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor involved in the detoxification of harmful compounds. Found in many vertebrates, AhR binds environmental toxins like dioxins and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, triggering changes in gene expression that help metabolize these toxins. Traditionally linked to xenobiotic metabolism, recent research also ties AhR to roles in immune response regulation, cell proliferation, and differentiation. This receptor operates by migrating into the cell nucleus upon activation, where it influences the expression of specific genes involved in biological responses to environmental and dietary chemicals. Its function underscores the critical interface between environmental exposures and biological responses, highlighting its importance in toxicology and therapeutic research.