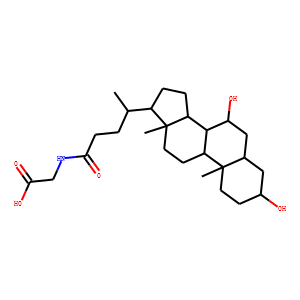
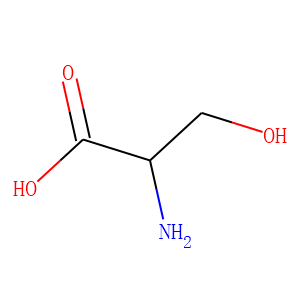
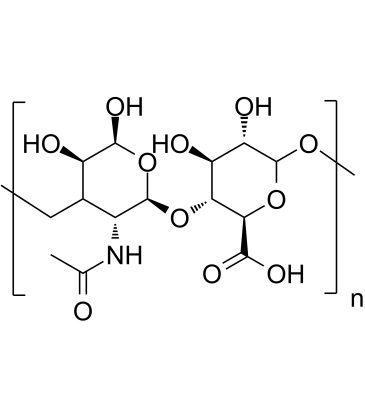
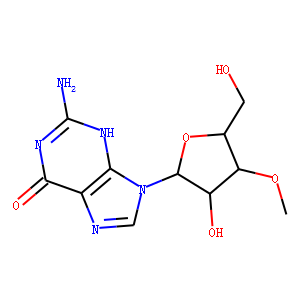
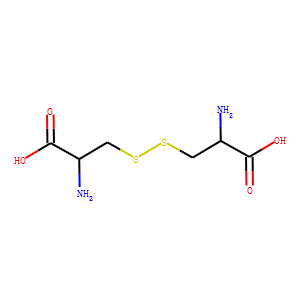
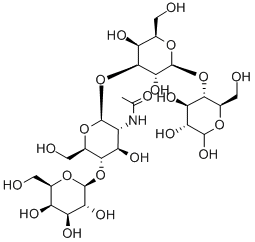
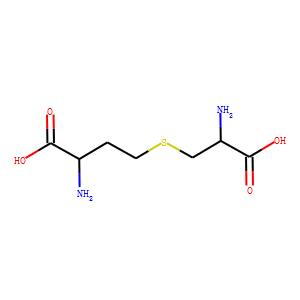
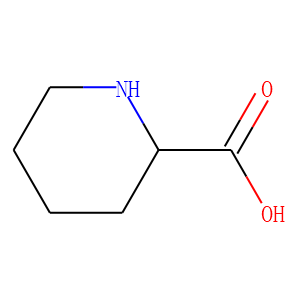
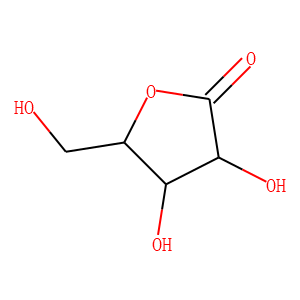
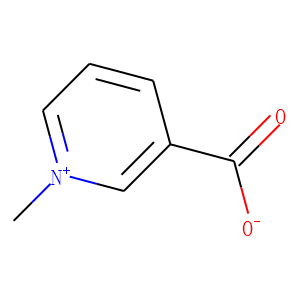
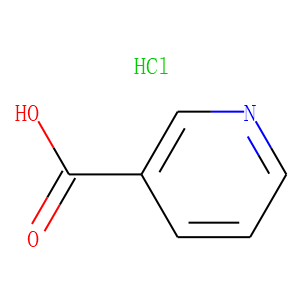
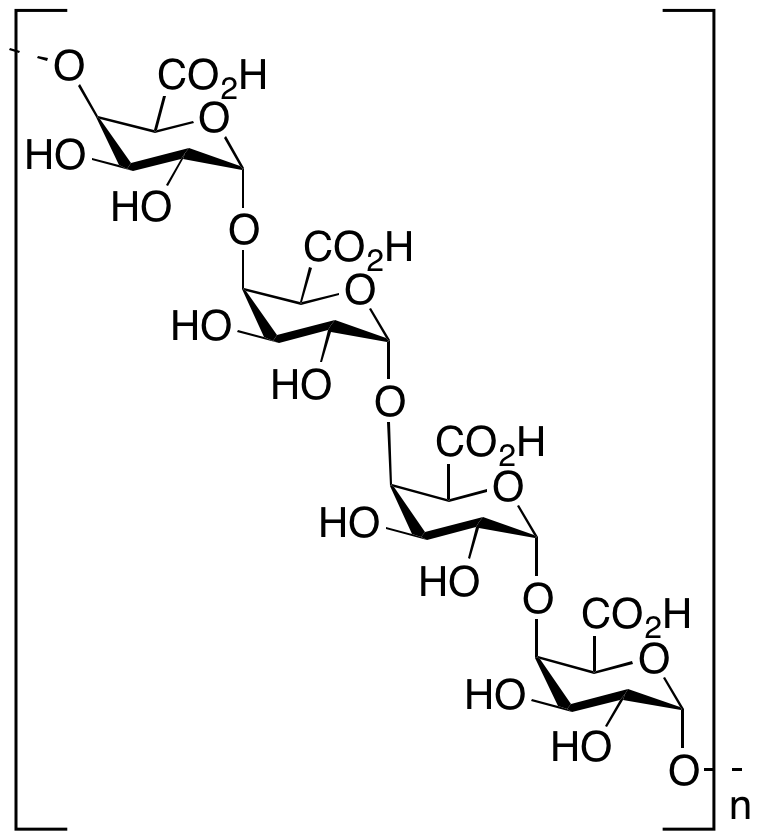
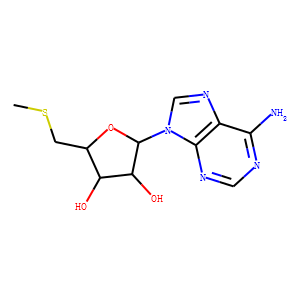
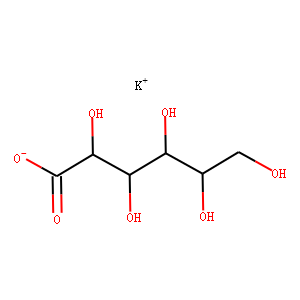
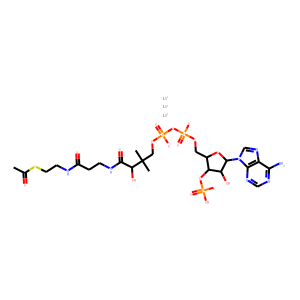
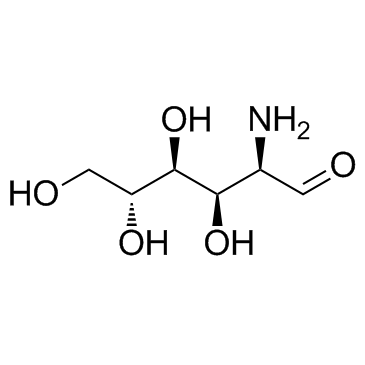
Endogenous Metabolite
Endogenous metabolites are molecules produced internally as byproducts or intermediates in metabolic processes within organisms. These compounds are essential for various biological functions, including energy production, cellular signaling, and the synthesis of complex molecules like proteins and nucleic acids. Metabolites can be broadly categorized into primary metabolites, such as amino acids, nucleotides, and sugars, which are directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction; and secondary metabolites, which often play roles in organismal defense mechanisms, such as alkaloids and phenolics. The study of these metabolites, through metabolomics, provides insights into cellular health, disease states, and overall biological functions, making them crucial to both basic biology and medical research.