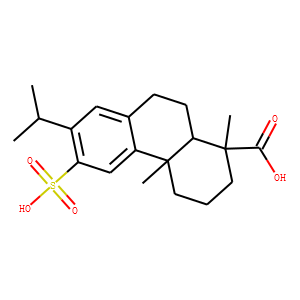
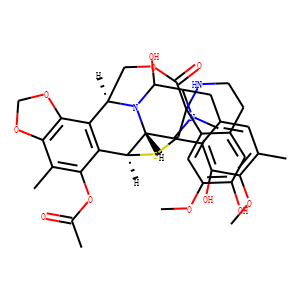
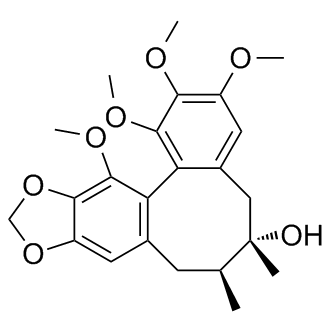
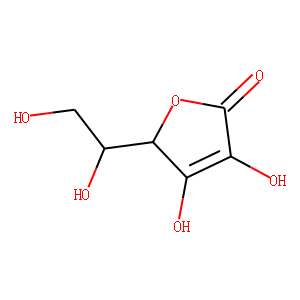
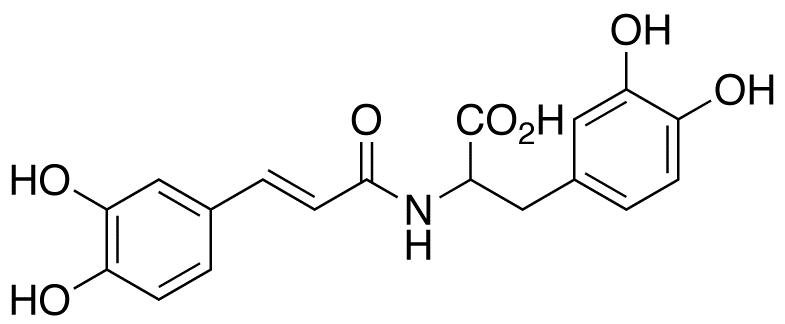
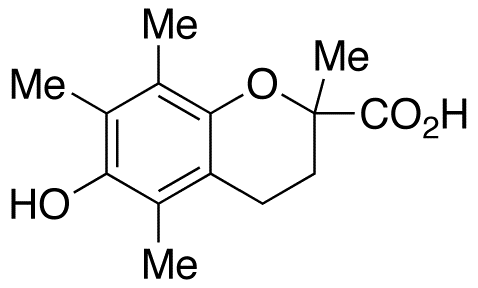
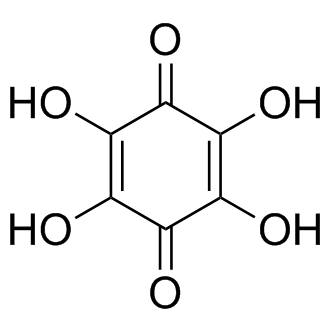
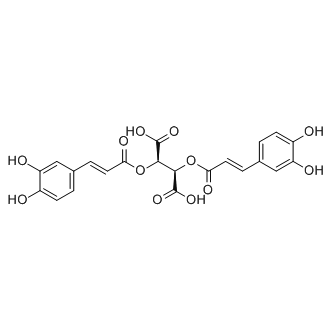
Reactive Oxygen Species
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen, such as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals. While ROS are crucial for normal cellular functions, including signaling and homeostasis, excessive ROS levels can lead to oxidative stress, damaging cells and genetic material. This imbalance contributes to aging and various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Given their dual role as both signaling molecules and damaging agents, ROS are significant targets in medical research. Strategies to modulate ROS levels include antioxidants to mitigate damage, and controlled ROS generation for therapeutic purposes, such as in cancer treatment, where they help induce cancer cell death.