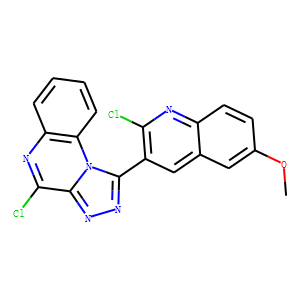
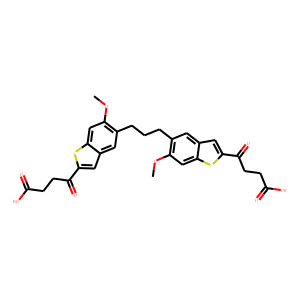
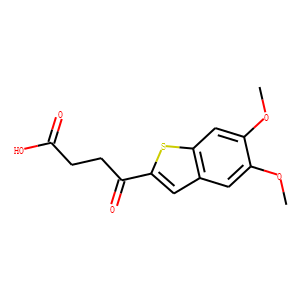
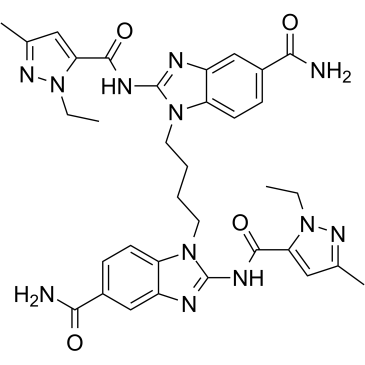
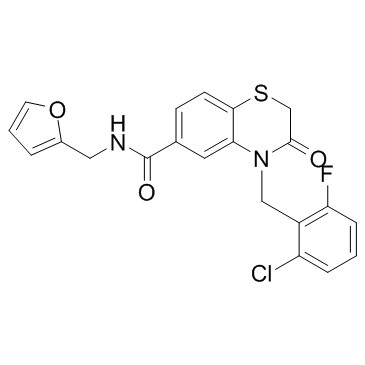
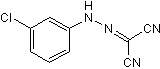
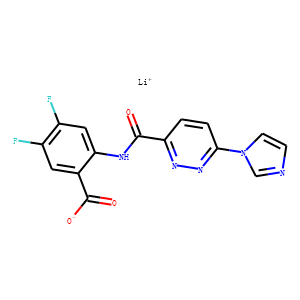
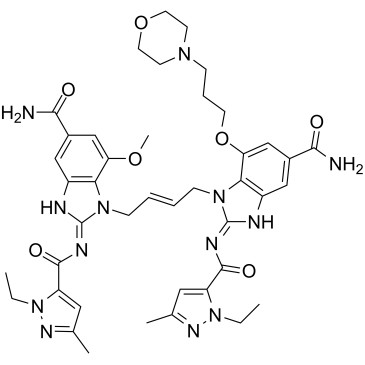
STING
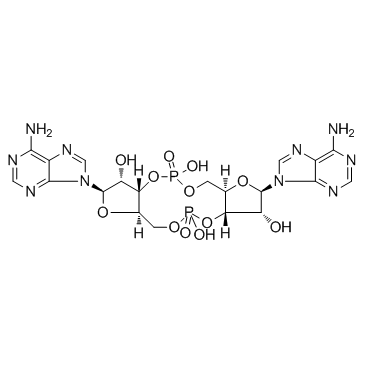
STING (Stimulator of Interferon Genes) is a crucial component of the innate immune response, located in the endoplasmic reticulum. It plays a vital role in detecting cytoplasmic DNA from pathogens or cellular damage, leading to the activation of type I interferon and other inflammatory cytokines. STING is involved in antiviral defenses, cancer immune surveillance, and autoinflammatory diseases. Its pathway can be activated directly by cyclic dinucleotides. Given its central role in immune regulation, STING is a promising therapeutic target for enhancing antitumor immunity and treating viral infections and inflammatory diseases.