Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel
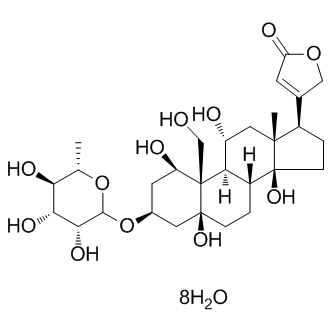
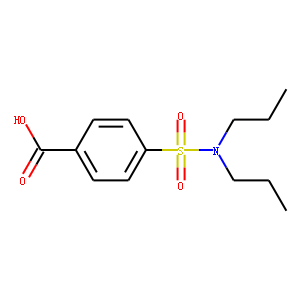
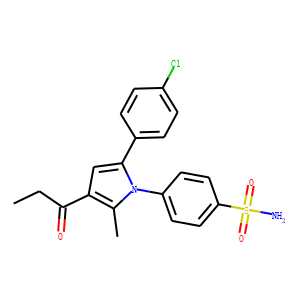
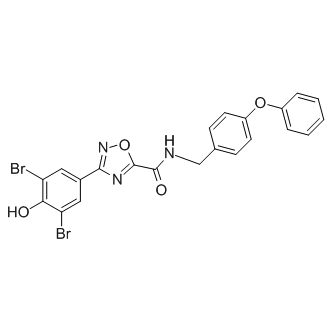
Most molecules enter and leave cells mainly through membrane transporters, which play an important role in cell metabolism, ion homeostasis, signal transduction, immune system recognition, energy transduction, etc. At present, there are three major transporters, namely ATP-driven pump (a family of carrier proteins that use the energy released from ATP hydrolysis as a source of active transport), channel protein, and transporter. Ion channels and transporters play an important role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis. Mutations of these transporter genes have been found in the pathogenesis of many genetic diseases. In the central nervous system, ion channels participate in but are not limited to many diseases, such as ataxia, paralysis, epilepsy, and deafness, which shows that ion channels play an important role in initiating and coordinating movement, sensory perception, and information coding and processing. In addition, drug transporters can be used as drug targets or as a mechanism to promote drug delivery to cells and tissues. Therefore, ion channels are one of the main targets of drug development.