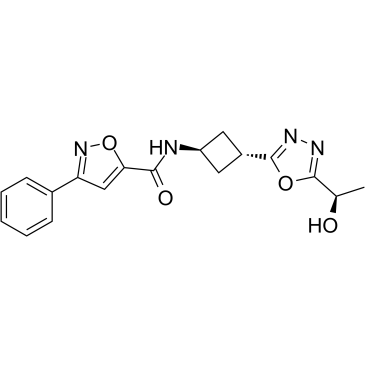
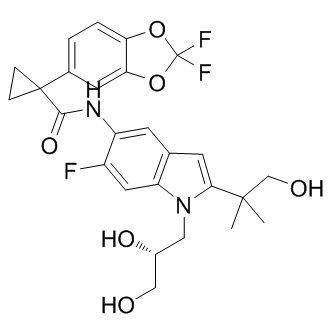
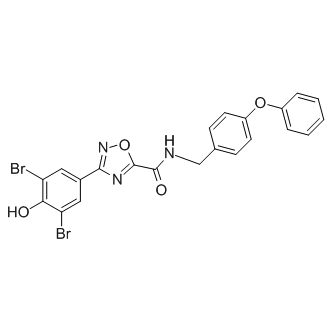
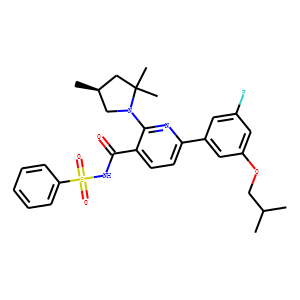
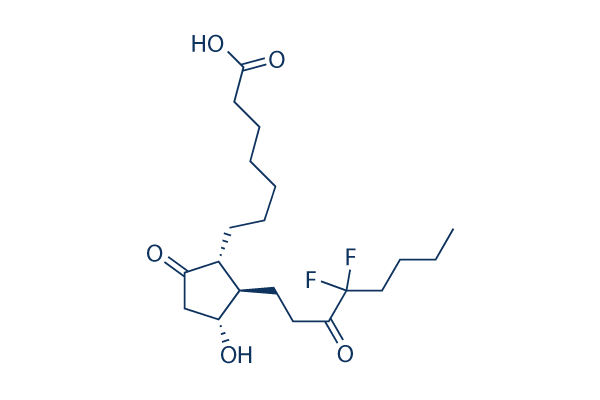
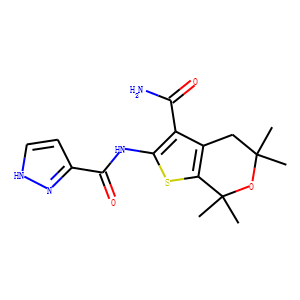
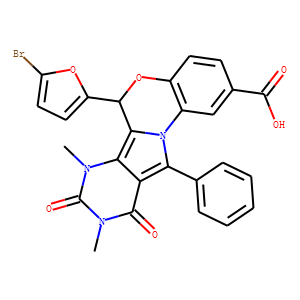
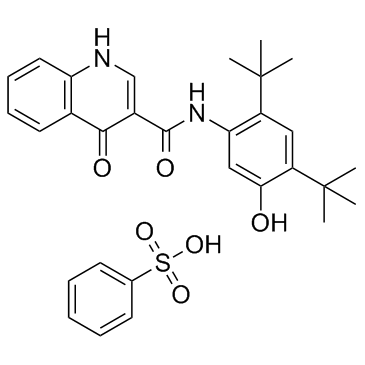
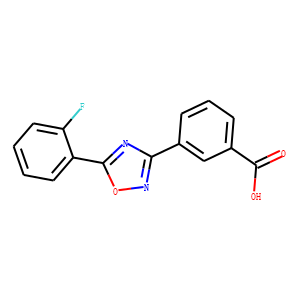
CFTR
The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) is a protein that functions as a channel across the membrane of cells that produce mucus, sweat, saliva, tears, and digestive enzymes. CFTR primarily transports chloride ions into and out of cells, playing a critical role in hydrating and regulating the viscosity of secretions. Mutations in the CFTR gene can lead to cystic fibrosis (CF), a serious genetic disorder that results in thick, sticky mucus that can clog airways and harbor harmful bacteria. The malfunctioning of CFTR affects various organs including the lungs, pancreas, and liver. Therapies targeting CFTR aim to correct its function or compensate for its deficiency.