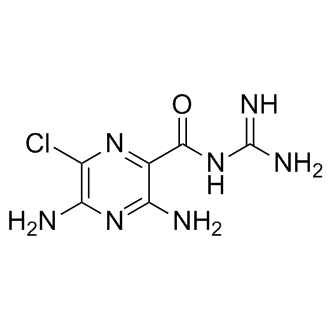
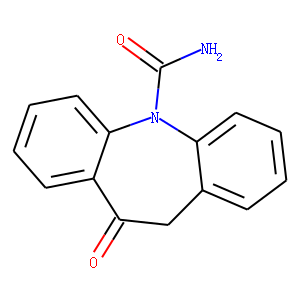
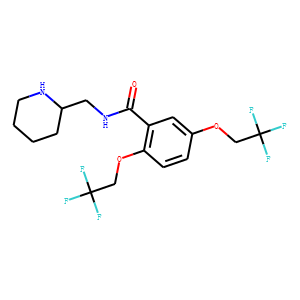
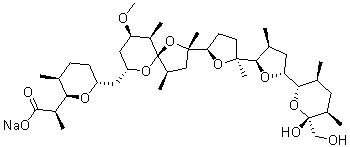
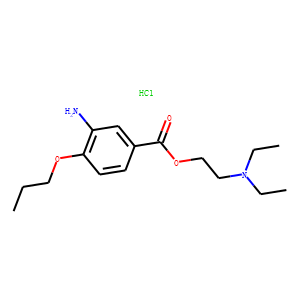
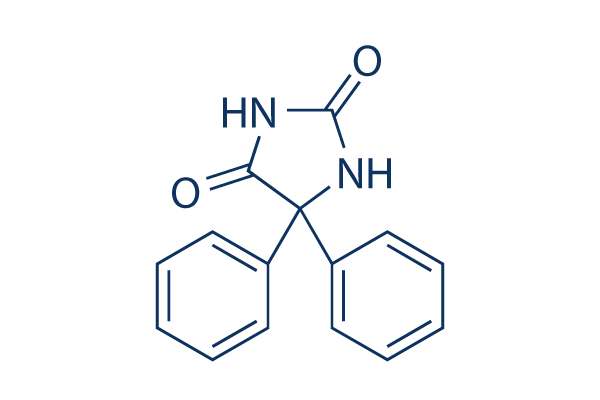
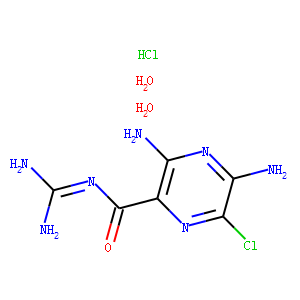
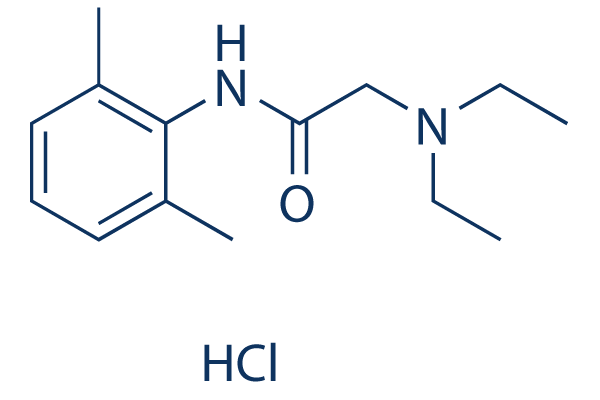
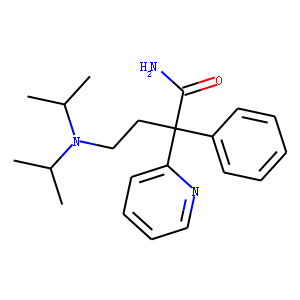
Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are essential ion channels located in the membranes of many types of cells, primarily nerve and muscle cells. They are responsible for the initiation and propagation of electrical signals in these cells, playing a critical role in activities such as muscle contraction, heart function, and neuronal communication. Sodium channels are voltage-gated, opening in response to changes in membrane potential to allow sodium ions (Na⁺) to flow into the cell, thus generating an action potential. Malfunctions in these channels can lead to a variety of disorders, including epilepsy, cardiac arrhythmias, and pain syndromes. As a result, sodium channels are important targets for a range of therapeutic agents aimed at modulating electrical activity in pathological conditions.

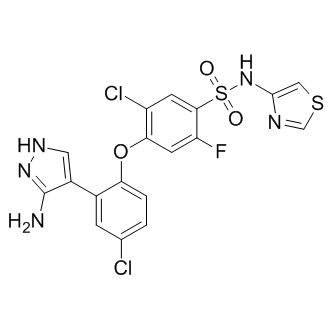
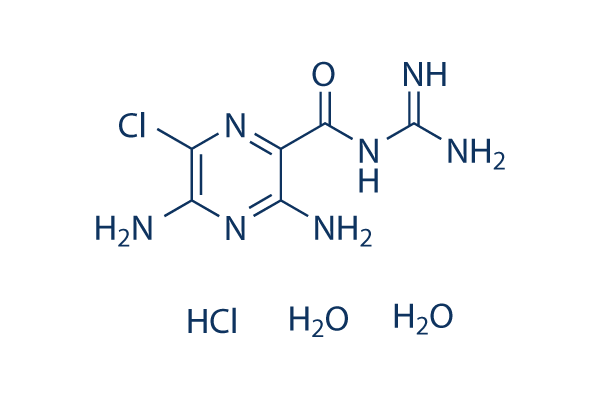
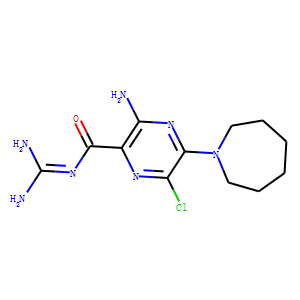
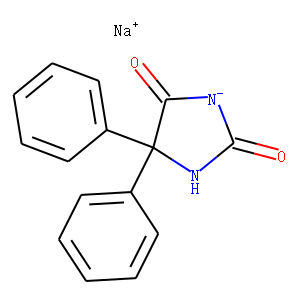
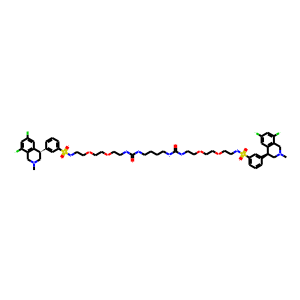
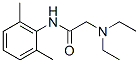
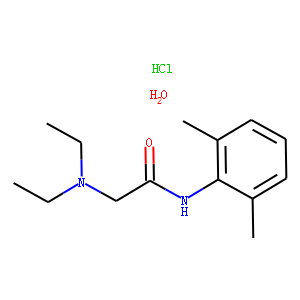
; 6108-05-0 (monohydrate).gif)