Adenosine Deaminase
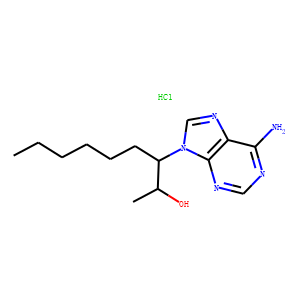
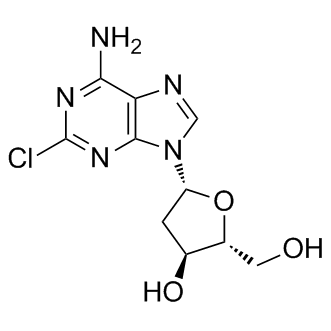
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme crucial for purine metabolism, primarily involved in the breakdown of adenosine and deoxyadenosine, which are components of DNA and RNA. ADA converts adenosine into inosine and deoxyadenosine into deoxyinosine, thereby preventing harmful accumulations of adenosine that can inhibit cellular metabolism and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in ADA is notably linked to severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID), where immune cells fail to develop properly, leading to severe immune dysfunction. ADA is also studied for its role in regulating neurotransmission and inflammation. Therapeutically, ADA activity is targeted in treatments for conditions such as SCID and certain cancers, emphasizing its significance in medical research and clinical applications.